Database as a Service (DBaaS) offers seamless access to cloud-based database solutions, eliminating the need for physical hardware management and reducing IT costs. This model provides scalability, automated backups, and high availability, ensuring your data is secure and accessible whenever needed. Explore the rest of this article to discover how DBaaS can transform your data management strategy.
Table of Comparison
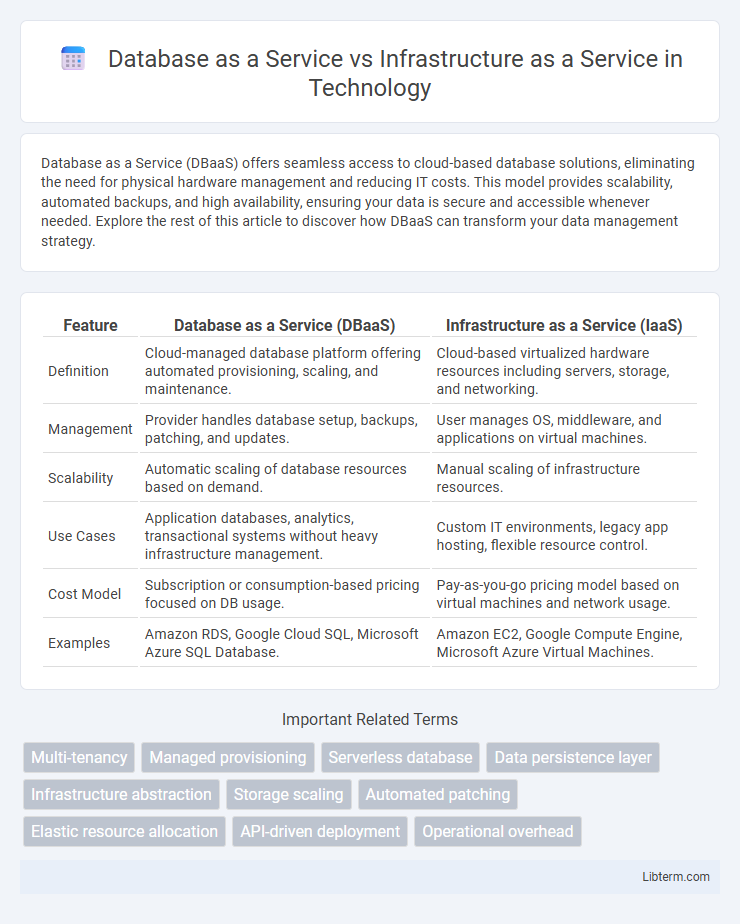
| Feature | Database as a Service (DBaaS) | Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cloud-managed database platform offering automated provisioning, scaling, and maintenance. | Cloud-based virtualized hardware resources including servers, storage, and networking. |
| Management | Provider handles database setup, backups, patching, and updates. | User manages OS, middleware, and applications on virtual machines. |
| Scalability | Automatic scaling of database resources based on demand. | Manual scaling of infrastructure resources. |
| Use Cases | Application databases, analytics, transactional systems without heavy infrastructure management. | Custom IT environments, legacy app hosting, flexible resource control. |
| Cost Model | Subscription or consumption-based pricing focused on DB usage. | Pay-as-you-go pricing model based on virtual machines and network usage. |
| Examples | Amazon RDS, Google Cloud SQL, Microsoft Azure SQL Database. | Amazon EC2, Google Compute Engine, Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines. |
Introduction to DBaaS and IaaS
Database as a Service (DBaaS) provides a fully managed database platform, enabling users to deploy, operate, and scale databases without handling infrastructure maintenance or administrative tasks. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) delivers virtualized computing resources over the internet, offering flexible hardware, storage, and networking capabilities for users to deploy and manage their own operating systems and applications. DBaaS simplifies database management with features like automated backups, scaling, and updates, while IaaS grants greater control over the infrastructure stack, requiring users to manage database installation, configuration, and maintenance.
Key Differences Between DBaaS and IaaS
Database as a Service (DBaaS) provides a fully managed database platform with automated backups, scaling, and patching, focusing on database-specific operations. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) offers virtualized computing resources such as servers, storage, and networking, requiring users to manage and configure the database software themselves. Key differences include management responsibility, with DBaaS handling database maintenance and IaaS providing raw infrastructure for greater customization and control.
Core Features of Database as a Service
Database as a Service (DBaaS) offers fully managed database solutions with automated backups, high availability, scalability, and built-in security, eliminating the need for manual database administration. Core features include serverless architecture, automated patching, continuous monitoring, and seamless integration with analytics tools, optimizing performance and reducing operational overhead. Unlike Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), which provides raw computing resources and requires users to install and manage database software, DBaaS delivers a ready-to-use database environment designed for rapid deployment and simplified management.
Core Features of Infrastructure as a Service
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, including scalable servers, storage, and networking components, enabling businesses to manage operating systems, applications, and middleware with complete control. Core features of IaaS include automated scaling, pay-as-you-go pricing models, flexible virtual machine configurations, and robust security frameworks such as firewalls and identity management. Unlike Database as a Service (DBaaS), which focuses on managed database solutions, IaaS offers a broad infrastructure foundation that supports diverse workloads and custom software deployments.
Benefits of Choosing DBaaS
Database as a Service (DBaaS) offers simplified database management by automating maintenance, backups, and scaling, reducing operational overhead for businesses. DBaaS ensures high availability and disaster recovery through built-in replication and failover mechanisms, enhancing data reliability and uptime. By leveraging DBaaS, organizations can achieve faster deployment and focus on application development rather than infrastructure management, resulting in increased agility and cost efficiency compared to traditional Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS).
Benefits of Choosing IaaS
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) offers scalable computing resources, including virtual machines, storage, and networking, providing greater flexibility and control compared to Database as a Service (DBaaS). Choosing IaaS allows organizations to customize their infrastructure environments to meet specific performance and security requirements, supporting diverse workloads beyond just databases. Cost efficiency is achieved through pay-as-you-go pricing models and the ability to optimize resource allocation dynamically.
Use Cases for DBaaS and IaaS
Database as a Service (DBaaS) is ideal for developers needing rapid deployment of scalable databases without managing hardware, commonly used in web and mobile app development, analytics, and real-time data processing. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) suits organizations requiring customizable virtual machines, storage, and network resources for diverse workloads such as large-scale enterprise applications, disaster recovery, and high-performance computing. DBaaS is streamlined for database management and optimization, while IaaS provides broader control over the underlying infrastructure for complex IT environments.
Security Considerations in DBaaS vs IaaS
Database as a Service (DBaaS) offers built-in security features such as automated patching, encryption, and access control tailored specifically for databases, reducing administrative overhead and risk exposure. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) requires users to manage security configurations at multiple layers including the operating system, network, and database, which can increase vulnerability if not properly maintained. Compliance requirements and data residency are critical factors in choosing DBaaS or IaaS, as DBaaS vendors often provide certifications and managed safeguards while IaaS grants more control but demands rigorous security management.
Cost Comparison: DBaaS vs IaaS
Database as a Service (DBaaS) typically offers a lower upfront cost compared to Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) by eliminating the need for dedicated hardware and database administration resources. While IaaS charges are primarily based on virtual machine usage and storage, DBaaS pricing includes managed database features, automated backups, and scalability, often resulting in higher operational efficiency and potentially lower total cost of ownership. Companies should evaluate workload requirements, expected data growth, and management overhead when comparing DBaaS and IaaS costs to determine the most economically viable option.
How to Choose the Right Service for Your Business
Selecting between Database as a Service (DBaaS) and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) depends on your business's technical requirements and resource capabilities. DBaaS offers managed database solutions with automated backups, scaling, and maintenance, ideal for businesses seeking streamlined data management without extensive in-house expertise. IaaS provides more granular control over virtualized hardware and software environments, suitable for organizations needing customizable infrastructure for diverse workloads and applications.
Database as a Service Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com