Key-value stores offer a simple, efficient way to manage data by associating unique keys with their corresponding values, enabling rapid data retrieval and scalability. They are widely used in applications requiring high-speed access and flexible schema design, such as caching, session management, and real-time analytics. Explore the full article to understand how a key-value store can optimize your data management strategy.
Table of Comparison
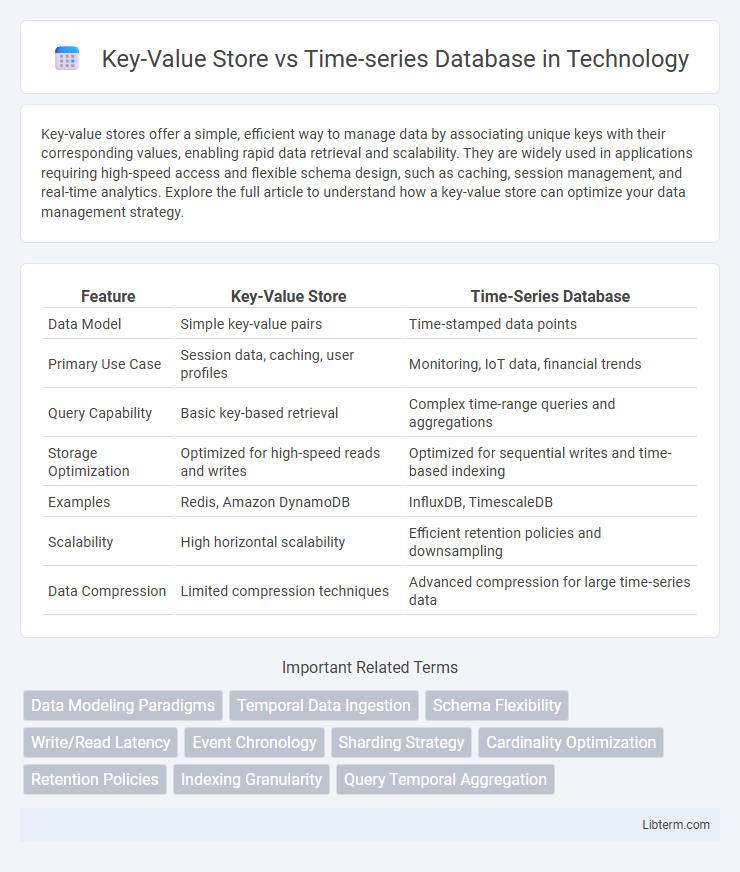
| Feature | Key-Value Store | Time-Series Database |
|---|---|---|
| Data Model | Simple key-value pairs | Time-stamped data points |
| Primary Use Case | Session data, caching, user profiles | Monitoring, IoT data, financial trends |
| Query Capability | Basic key-based retrieval | Complex time-range queries and aggregations |
| Storage Optimization | Optimized for high-speed reads and writes | Optimized for sequential writes and time-based indexing |
| Examples | Redis, Amazon DynamoDB | InfluxDB, TimescaleDB |
| Scalability | High horizontal scalability | Efficient retention policies and downsampling |
| Data Compression | Limited compression techniques | Advanced compression for large time-series data |
Introduction to Data Storage Solutions
Key-value stores provide a highly efficient method for storing and retrieving data by using unique keys associated with specific values, making them ideal for caching and session management in large-scale applications. Time-series databases specialize in handling time-stamped data, offering optimized storage and querying capabilities for metrics, events, and continuous sensor data in domains like IoT, finance, and monitoring systems. Choosing between these data storage solutions depends on the nature of the data and the required query patterns, with key-value stores excelling in simplicity and speed, while time-series databases deliver advanced temporal analysis and data compression.
What is a Key-Value Store?
A Key-Value Store is a type of NoSQL database that organizes data as a collection of key-value pairs, where each key is unique and directly maps to a specific value, such as a string, number, or complex object. It excels in scenarios requiring fast read and write operations, simple data models, and horizontal scalability, making it ideal for caching, session management, and real-time applications. Unlike Time-series Databases, Key-Value Stores do not inherently handle time-indexed data, lacking built-in features for time-based queries, aggregations, and retention policies.
Understanding Time-series Databases
Time-series databases are optimized for storing and querying sequential data points indexed by timestamps, enabling efficient analysis of trends and patterns over time. Unlike key-value stores that handle arbitrary key-value pairs with no inherent temporal ordering, time-series databases support complex time-based queries, data compression, and downsampling to manage high-volume time-stamped data. Their specialized architecture makes them ideal for use cases in monitoring, IoT, financial market analysis, and real-time analytics where continuous time-dependent data ingestion and retrieval are critical.
Core Data Models: Key-Value vs Time-series
Key-value stores organize data as simple pairs of keys and values, enabling rapid retrieval through unique keys without inherent temporal context. Time-series databases structure data as sequences of timestamped entries optimized for storing, querying, and analyzing time-dependent information such as sensor readings or financial metrics. The core difference lies in key-value stores emphasizing flexible, schema-less storage for diverse data types, while time-series databases specialize in handling ordered, time-stamped data with built-in functions for time-based aggregation and analysis.
Performance and Scalability Comparison
Key-value stores excel in high-throughput performance by enabling fast read and write operations through simple key-based retrieval, making them ideal for caching and session management. Time-series databases optimize performance for time-indexed data by using compression techniques and specialized storage engines that support efficient querying over time ranges. Scalability in key-value stores is achieved via horizontal partitioning with minimal coordination, while time-series databases often incorporate time-based sharding and downsampling to handle large volumes of sequential data without compromising query speed.
Data Retrieval and Query Capabilities
Key-Value Stores excel in simple, fast data retrieval using unique keys but lack advanced querying capabilities and time-based data analysis. Time-series Databases are optimized for storing and querying chronological data, providing robust time-range, aggregation, and downsampling queries, essential for monitoring and IoT applications. Efficient time-indexed data retrieval and complex query support differentiate Time-series Databases from the straightforward key-based access in Key-Value Stores.
Use Cases: When to Use Each Solution
Key-value stores excel in scenarios requiring simple, fast retrieval of data by unique keys, making them ideal for caching, session management, and real-time analytics where low latency is critical. Time-series databases are specifically designed for handling large volumes of chronological data, perfect for use cases such as monitoring IoT devices, financial market analysis, and infrastructure performance tracking. Choosing between them depends on data structure and query patterns; key-value stores suit unstructured or semi-structured data with straightforward lookups, while time-series databases optimize storage and queries for sequential, timestamped data.
Data Consistency and Integrity
Key-value stores prioritize high availability and partition tolerance, often employing eventual consistency models that may sacrifice immediate data integrity for performance in distributed systems. In contrast, time-series databases emphasize strong data consistency and integrity to accurately capture and maintain chronological data points, utilizing ACID-compliant transactions and precise timestamp ordering. This focus ensures reliable, sequential data storage crucial for time-based analytics and monitoring applications.
Scalability and High-Availability Features
Key-value stores excel in horizontal scalability by distributing data across multiple nodes using consistent hashing, ensuring rapid read and write operations for large-scale applications. Time-series databases are optimized for high availability with built-in replication and partitioning schemes tailored for continuous data ingestion and real-time analytics of timestamped data. Both architectures implement robust failover mechanisms and clustering to minimize downtime, but time-series databases often provide specialized compression and indexing to efficiently handle voluminous time-stamped entries while maintaining scalability.
Choosing the Right Database for Your Application
Choosing the right database depends on your application's data structure and query needs. Key-value stores excel at simple, fast retrieval of data using unique keys, making them ideal for caching, session management, and real-time applications. Time-series databases are optimized for handling high-volume, timestamped data with efficient storage and advanced time-based querying, suitable for monitoring, IoT, and financial analytics.
Key-Value Store Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com