Star topology connects all devices to a central hub, facilitating efficient data transmission and easy network management. This structure minimizes the impact of a single device failure but depends heavily on the central hub's reliability. Discover how star topology can enhance Your network's performance and resilience in the full article.
Table of Comparison
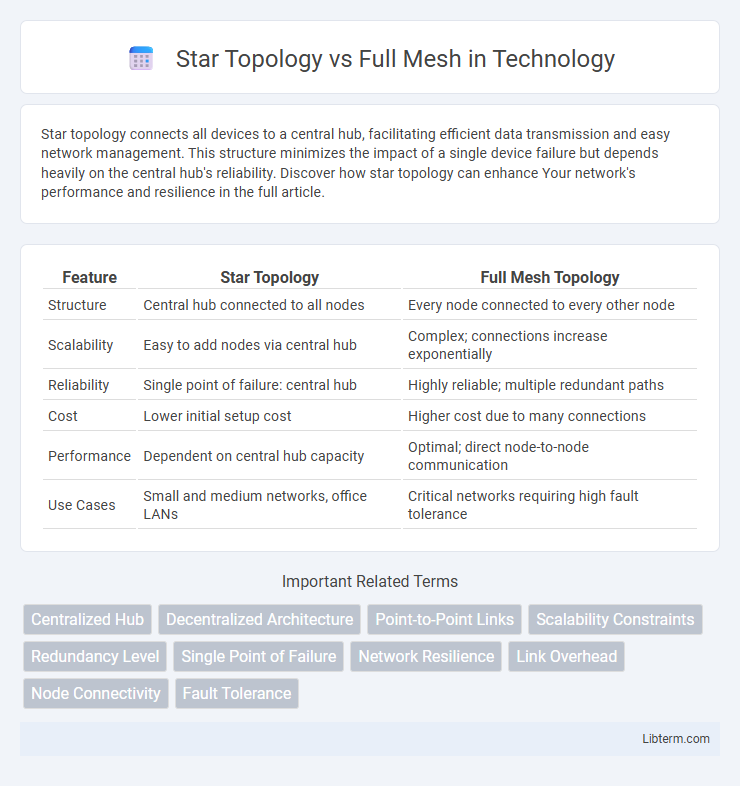
| Feature | Star Topology | Full Mesh Topology |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Central hub connected to all nodes | Every node connected to every other node |
| Scalability | Easy to add nodes via central hub | Complex; connections increase exponentially |
| Reliability | Single point of failure: central hub | Highly reliable; multiple redundant paths |
| Cost | Lower initial setup cost | Higher cost due to many connections |
| Performance | Dependent on central hub capacity | Optimal; direct node-to-node communication |
| Use Cases | Small and medium networks, office LANs | Critical networks requiring high fault tolerance |
Introduction to Network Topologies
Star topology features a central hub that connects all nodes individually, optimizing ease of management and fault isolation in wired and wireless networks. Full mesh topology, with every node linked to every other node, maximizes redundancy and ensures high availability but requires more cabling and configuration. Network topologies are fundamental frameworks that define how devices in a network communicate, impacting performance, scalability, and reliability.
Overview of Star Topology
Star topology features a central hub or switch to which all network devices connect individually, simplifying management and fault isolation. This structure reduces data collisions and makes troubleshooting more efficient compared to other topologies. It is ideal for small to medium-sized networks requiring scalability and easy maintenance.
Overview of Full Mesh Topology
Full Mesh Topology is a network structure where every node is directly connected to every other node, ensuring maximum redundancy and fault tolerance. This topology provides high reliability and reduces the chance of network failure since multiple paths exist for data transmission between devices. The complexity and cost increase significantly with the number of nodes due to the exponential growth of required connections.
Key Differences Between Star and Full Mesh
Star topology features a central hub connecting all nodes, simplifying management and fault isolation, whereas full mesh topology interconnects every node with multiple direct links, ensuring high redundancy and fault tolerance. Star networks are easier to scale and troubleshoot but can suffer from a single point of failure at the hub, while full mesh networks provide maximum reliability with complex installation and higher costs. Latency is typically lower in star topology due to fewer hops, whereas full mesh can optimize path selection but may introduce more overhead.
Performance and Scalability Comparison
Star topology centralizes network traffic through a single hub, limiting performance scalability as network size increases due to potential bottlenecks and hub failures. Full mesh topology offers superior performance and scalability by providing direct communication links between all nodes, reducing latency and enhancing fault tolerance at the cost of increased complexity and wiring. Enterprises demanding high availability often prefer full mesh for its resilience, while star topology suits smaller networks prioritizing simpler setup and maintenance.
Reliability and Fault Tolerance
Star topology centralizes network connections through a single hub, which simplifies fault isolation but creates a single point of failure, potentially reducing overall reliability. Full mesh topology enhances fault tolerance by providing multiple redundant paths between devices, ensuring network resilience even if several connections break. Although full mesh offers superior reliability through complex link redundancy, it demands higher infrastructure costs and maintenance compared to star topology.
Cost and Resource Requirements
Star topology requires fewer cables and network interfaces compared to full mesh topology, resulting in lower initial installation costs and simpler maintenance. Full mesh topology demands extensive cabling and more network interface cards to connect every device directly, significantly increasing both material and labor expenses. Resource-wise, star topology utilizes less bandwidth and computing power, while full mesh provides higher redundancy and fault tolerance at the expense of greater resource consumption.
Use Cases and Applications
Star topology is ideal for small to medium-sized networks where centralized management and ease of troubleshooting are critical, commonly used in office LAN setups and home networks. Full mesh topology suits large-scale, high-reliability environments such as data centers, financial institutions, and military communications, where maximum fault tolerance and low latency path redundancy are essential. Both topologies support unique applications: star for simplicity and cost-effectiveness, full mesh for mission-critical connectivity and high availability.
Pros and Cons of Each Topology
Star topology offers straightforward management and easy fault isolation with a central hub, but it creates a single point of failure that can disrupt the entire network. Full mesh topology provides robust redundancy and high fault tolerance by interconnecting every node, yet it demands significant cabling and complex configuration, increasing costs and maintenance challenges. Choosing between star and full mesh depends on prioritizing simplicity and cost-effectiveness or reliability and network resilience.
Choosing the Right Topology for Your Network
Selecting the right network topology depends on factors like network size, scalability, and fault tolerance needs. Star topology offers simpler management and easy device addition, ideal for small to medium networks with centralized control. Full mesh topology provides robust redundancy and high availability, suited for larger, mission-critical networks requiring continuous connectivity and minimal downtime.
Star Topology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com