Split URL testing helps you analyze how different versions of a webpage perform by directing traffic to multiple URLs simultaneously. This method provides clear insights into user behavior and conversion rates across distinct site designs or content variations. Explore the rest of the article to learn how split URL testing can optimize Your website's performance effectively.
Table of Comparison
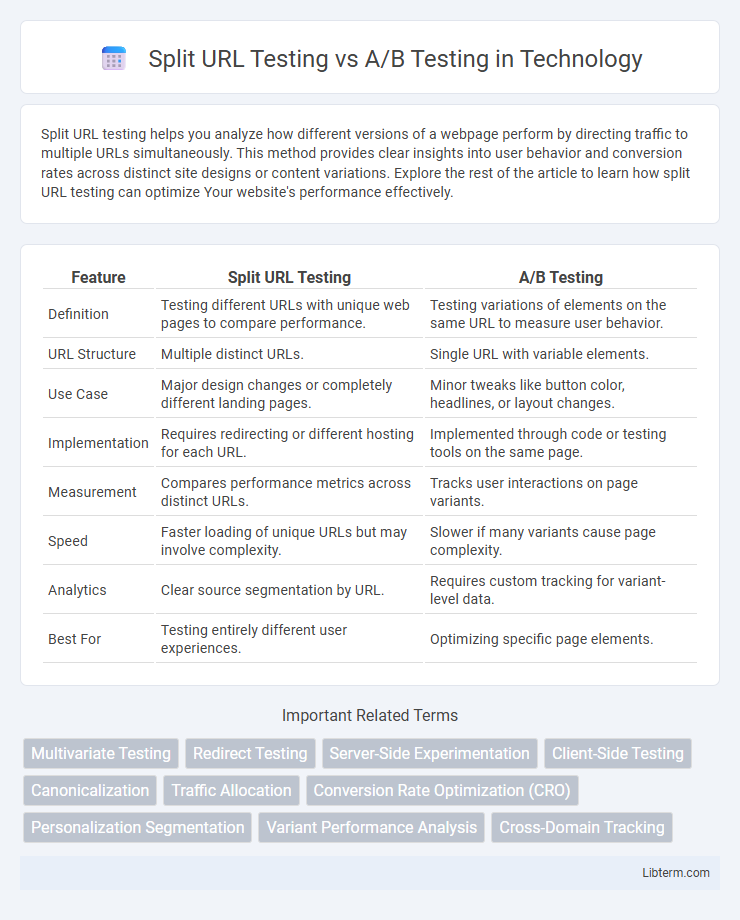
| Feature | Split URL Testing | A/B Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Testing different URLs with unique web pages to compare performance. | Testing variations of elements on the same URL to measure user behavior. |
| URL Structure | Multiple distinct URLs. | Single URL with variable elements. |
| Use Case | Major design changes or completely different landing pages. | Minor tweaks like button color, headlines, or layout changes. |
| Implementation | Requires redirecting or different hosting for each URL. | Implemented through code or testing tools on the same page. |
| Measurement | Compares performance metrics across distinct URLs. | Tracks user interactions on page variants. |
| Speed | Faster loading of unique URLs but may involve complexity. | Slower if many variants cause page complexity. |
| Analytics | Clear source segmentation by URL. | Requires custom tracking for variant-level data. |
| Best For | Testing entirely different user experiences. | Optimizing specific page elements. |
Introduction to Split URL Testing and A/B Testing
Split URL Testing involves comparing two different web pages hosted on separate URLs to evaluate performance by directing traffic between them, ideal for significant design or content changes. A/B Testing tests variations within the same URL by altering elements such as headlines, images, or buttons to identify which version yields better user engagement. Both methods are essential for conversion rate optimization but differ in implementation scope and testing capabilities.
How Split URL Testing Works
Split URL Testing divides traffic between multiple, distinct URLs to compare performance metrics such as conversion rates or user engagement on different web page versions. Each URL hosts a separate variant, allowing precise measurement of user behavior without overlapping elements interfering, making it ideal for testing major design changes or entirely different layouts. Traffic is automatically directed based on predefined percentage allocations, and analytics track outcomes to identify the best-performing URL.
Understanding A/B Testing Methodology
A/B testing methodology involves comparing two versions of a webpage or app against each other to determine which one performs better based on a specific metric such as click-through rate or conversions. Split URL testing directs different traffic to entirely separate URLs to measure variations in user behavior, whereas traditional A/B testing varies elements within the same URL to isolate changes. Understanding these methodologies helps businesses optimize user experience and increase conversion rates by systematically evaluating changes and measuring their impact on key performance indicators.
Key Differences Between Split URL Testing and A/B Testing
Split URL Testing directs traffic to entirely different web pages, allowing comprehensive comparison of distinct designs or layouts, whereas A/B Testing varies elements within the same URL to measure incremental changes. Split URL Testing suits experiments requiring significant structural changes, while A/B Testing is ideal for testing content, headlines, or button colors on a single page. Metrics such as conversion rate, bounce rate, and user engagement are commonly analyzed in both, but Split URL Testing often involves longer test durations due to traffic segmentation.
Best Use Cases for Split URL Testing
Split URL testing is ideal for evaluating entirely different website designs or landing pages where URL structure changes are necessary, such as in major redesigns or new product launches. It effectively isolates user experience variations by directing traffic to distinct web addresses, providing clear performance data on layout, navigation, and content impact. This method excels in assessing large-scale changes that cannot be implemented via simple A/B test variations on a single page.
Ideal Scenarios for A/B Testing
A/B testing is ideal for comparing two variations of a single web element such as headlines, call-to-action buttons, or images to identify which version drives higher user engagement or conversion rates. It works best when testing incremental changes on a webpage with consistent traffic, allowing clear insights into the performance impact of specific design or content tweaks. This method is most effective in scenarios where the goal is to optimize a single variable with controlled conditions to improve key metrics like click-through rates or sales.
Pros and Cons of Split URL Testing
Split URL Testing offers precise control by directing traffic to entirely different web pages, making it ideal for testing significant design or structural changes, but it requires more development effort and can complicate SEO due to multiple URLs. This method allows tracking user behavior on distinct URLs, providing clearer performance insights, though it may lead to longer load times and inconsistent user experiences if not managed properly. Compared to A/B Testing, Split URL Testing is less suited for minor tweaks and can increase costs due to maintaining separate web environments.
Pros and Cons of A/B Testing
A/B Testing allows marketers to compare two variations of a webpage or app to determine which performs better by splitting traffic evenly, providing clear insights on user preferences. Its pros include simplicity, statistical relevance, and straightforward implementation, making it ideal for testing minor changes. However, A/B Testing can be limited by small sample sizes, longer duration to reach significance, and challenges in testing multiple variables simultaneously.
Choosing the Right Testing Method for Your Website
Split URL testing is ideal for testing major changes that require separate web pages, offering clear performance insights by comparing distinct URLs, while A/B testing excels in evaluating smaller elements like headlines or button colors within the same page. Selecting the right testing method depends on the scale and nature of changes; use split URL testing for redesigns or different page structures, and A/B testing for incremental optimizations that do not require URL changes. Consider traffic volume, test duration, and the complexity of user behavior to ensure accurate data-driven decisions for website optimization.
Final Thoughts: Enhancing Conversion Optimization
Split URL Testing offers precise insights by directing traffic to entirely different web pages, making it ideal for major design or structural changes. A/B Testing excels in refining specific elements like headlines or call-to-action buttons within the same URL, optimizing incremental improvements. Combining both methods enhances conversion optimization by balancing broad user experience modifications with targeted content adjustments.
Split URL Testing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com