Bandit testing is a powerful method for optimizing your website or app by dynamically allocating traffic to multiple versions, ensuring the best-performing variant gets the most exposure. This approach efficiently balances exploration and exploitation, minimizing losses while gathering valuable data. Discover how bandit testing can enhance your conversion rates and user experience by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
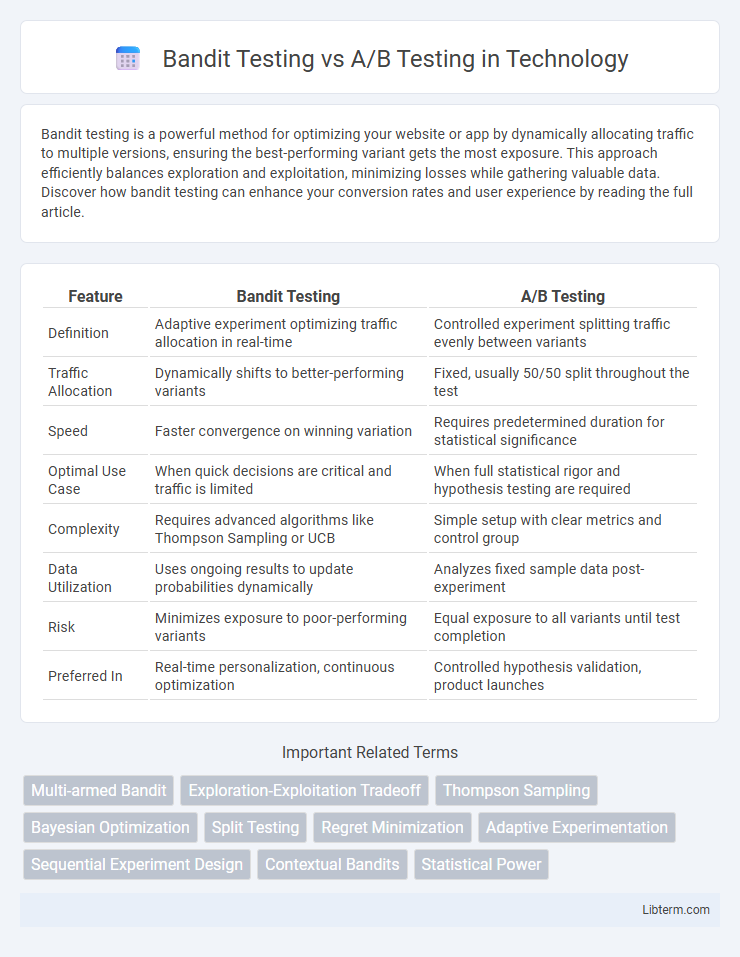
| Feature | Bandit Testing | A/B Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adaptive experiment optimizing traffic allocation in real-time | Controlled experiment splitting traffic evenly between variants |
| Traffic Allocation | Dynamically shifts to better-performing variants | Fixed, usually 50/50 split throughout the test |
| Speed | Faster convergence on winning variation | Requires predetermined duration for statistical significance |
| Optimal Use Case | When quick decisions are critical and traffic is limited | When full statistical rigor and hypothesis testing are required |
| Complexity | Requires advanced algorithms like Thompson Sampling or UCB | Simple setup with clear metrics and control group |
| Data Utilization | Uses ongoing results to update probabilities dynamically | Analyzes fixed sample data post-experiment |
| Risk | Minimizes exposure to poor-performing variants | Equal exposure to all variants until test completion |
| Preferred In | Real-time personalization, continuous optimization | Controlled hypothesis validation, product launches |
Introduction to Bandit Testing and A/B Testing
Bandit testing is an adaptive experimentation method that dynamically allocates traffic to variations based on real-time performance, optimizing for faster identification of the best option. A/B testing, known as split testing, evenly divides traffic between two or more variants to compare their performance using statistical analysis after a fixed period. Both methods aim to improve decision-making in product development and marketing, but bandit testing excels in efficiency by continuously learning and adapting, while A/B testing relies on predetermined experiment durations.
Core Concepts: What Are Bandit and A/B Testing?
Bandit testing uses adaptive algorithms to dynamically allocate traffic to different variants based on real-time performance, optimizing for maximum reward by balancing exploration and exploitation. A/B testing divides traffic evenly between two or more fixed variants to statistically compare their effectiveness over a pre-determined period. Bandit testing continuously updates probabilities to favor higher-performing options, while A/B testing relies on fixed sample sizes to determine a winner.
How Bandit Testing Works
Bandit testing dynamically allocates traffic to different variants based on real-time performance data, leveraging algorithms like the multi-armed bandit to maximize overall conversion rates. Unlike A/B testing, which splits traffic evenly and waits for fixed periods, bandit testing continuously updates the allocation ratio to favor better-performing options. This adaptive approach reduces opportunity costs by minimizing exposure to underperforming variants while accelerating decision-making.
How A/B Testing Works
A/B testing works by randomly dividing a sample audience into two groups to compare different versions of a webpage or app, measuring specific metrics such as conversion rates or click-through rates. Each group is exposed to one variant, and statistical analysis determines which version performs better based on user interactions. This method provides clear insights through controlled experimentation, ensuring data-driven decisions for optimization.
Key Differences Between Bandit and A/B Testing
Bandit testing dynamically allocates traffic to winning variants based on real-time performance, whereas A/B testing splits traffic evenly between variants for a fixed duration. Bandit testing aims to maximize overall conversions during the experiment, reducing opportunity cost, while A/B testing emphasizes statistical significance to identify the best variant with confidence. The design of bandit algorithms adapts continuously to new data, in contrast to static A/B testing frameworks that require pre-specified sample sizes and durations.
Advantages of Bandit Testing
Bandit testing offers dynamic allocation of traffic to higher-performing variants, leading to faster optimization and reduced loss from suboptimal choices compared to traditional A/B testing. This method continuously learns and adapts, maximizing conversion rates in real-time and minimizing regret during experimentation. Bandit testing is particularly advantageous in environments requiring rapid decision-making and frequent updates.
Benefits of A/B Testing
A/B testing offers precise control by splitting traffic evenly between variations, enabling clear comparison and statistically significant results that improve decision-making. It simplifies analysis with straightforward metrics, making it easier to identify the winning variant and optimize user experience. Businesses benefit from reduced risks as A/B testing isolates changes, minimizing potential negative impact on conversion rates or customer satisfaction.
When to Use Bandit Testing vs A/B Testing
Bandit testing is ideal when real-time optimization and quick adaptation to user behavior are necessary, especially in dynamic environments with fluctuating user preferences. A/B testing is more suitable for controlled experiments where statistical significance is required to compare two distinct variants over a fixed period. Choose bandit testing for maximizing conversions during the test, and A/B testing when the goal is to gather conclusive evidence on the impact of each variant.
Common Use Cases and Examples
Bandit testing is commonly used in dynamic environments like online advertising, where real-time adjustments optimize click-through rates by allocating more traffic to higher-performing variants. A/B testing is ideal for controlled experiments with clear, static hypotheses, such as evaluating the impact of website layout changes on user engagement over a fixed period. E-commerce platforms often employ bandit testing for personalized product recommendations, while A/B testing is favored for validating marketing email designs and conversion funnel improvements.
Choosing the Right Testing Method for Your Business
Bandit Testing dynamically allocates traffic to the best-performing variations, maximizing conversion rates and minimizing losses during the experiment, making it ideal for businesses needing rapid adaptation. A/B Testing provides statistically significant comparisons between fixed variants, suitable for businesses seeking clear, controlled insights over longer periods. Selecting the right method depends on your business goals: prioritize Bandit Testing for fast optimization in volatile markets and A/B Testing for rigorous analysis when testing a limited number of stable variables.
Bandit Testing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com