Access control safeguards your digital and physical assets by regulating who can enter or use resources based on predefined security policies. Implementing robust access control systems minimizes potential breaches and enhances overall security efficiency. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to effectively protect your environment with the right access control strategies.
Table of Comparison
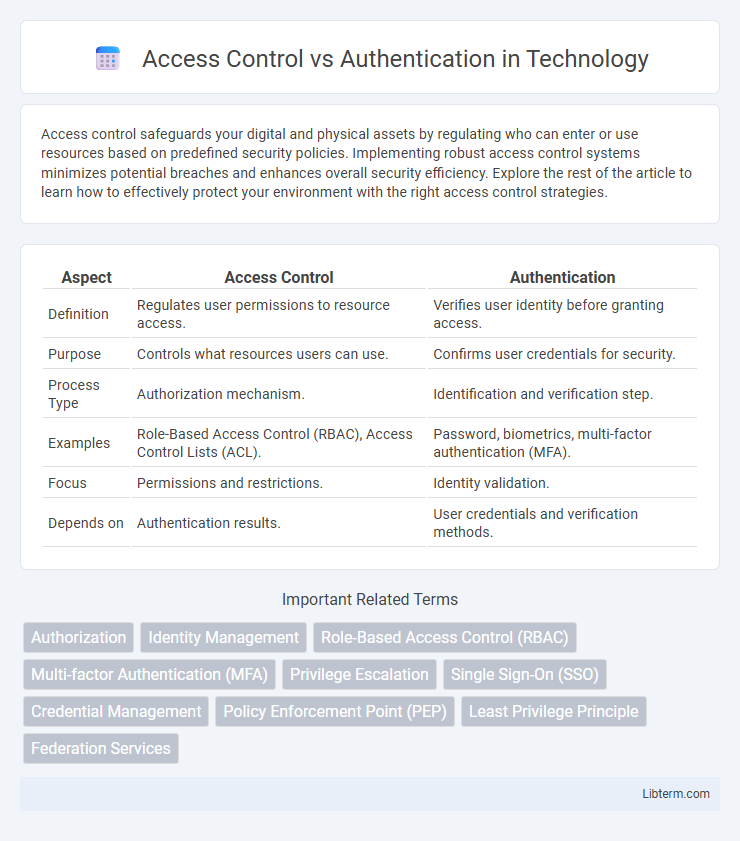
| Aspect | Access Control | Authentication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Regulates user permissions to resource access. | Verifies user identity before granting access. |
| Purpose | Controls what resources users can use. | Confirms user credentials for security. |
| Process Type | Authorization mechanism. | Identification and verification step. |
| Examples | Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), Access Control Lists (ACL). | Password, biometrics, multi-factor authentication (MFA). |
| Focus | Permissions and restrictions. | Identity validation. |
| Depends on | Authentication results. | User credentials and verification methods. |
Introduction to Access Control and Authentication
Access control defines the policies and mechanisms that regulate user permissions and resource accessibility within a system, ensuring only authorized entities can perform specific actions. Authentication verifies the identity of users or devices through credentials like passwords, biometrics, or tokens before granting access. Together, authentication establishes identity, while access control enforces the level of access granted based on that verified identity.
Defining Access Control
Access control is a security mechanism that regulates user permissions to resources based on predefined policies and roles, ensuring only authorized individuals can access specific data or systems. Unlike authentication, which verifies user identity, access control determines the level of access granted after identity confirmation. Key models of access control include discretionary access control (DAC), mandatory access control (MAC), and role-based access control (RBAC), each defining how permissions are assigned and enforced.
Understanding Authentication
Authentication verifies the identity of a user or system by requiring credentials such as passwords, biometrics, or multi-factor authentication. It ensures that the entity requesting access is who they claim to be before granting permissions. Strong authentication mechanisms reduce the risk of unauthorized access and protect sensitive data from cyber threats.
Key Differences Between Access Control and Authentication
Access control manages user permissions to determine who can access specific resources, while authentication verifies the identity of users before granting access. Authentication processes include methods such as passwords, biometrics, or two-factor authentication, ensuring a user is legitimate. Access control leverages authenticated identities to enforce policies based on roles, attributes, or rules, defining the scope and extent of resource access.
Types of Access Control Mechanisms
Access control mechanisms primarily include discretionary access control (DAC), mandatory access control (MAC), and role-based access control (RBAC), each offering distinct methods for regulating user permissions. DAC allows owners to set access rights, MAC enforces policies defined by a central authority, and RBAC assigns permissions based on user roles within an organization. These mechanisms are critical for securing sensitive data by ensuring that only authorized users can access specific resources according to predefined rules.
Common Authentication Methods
Common authentication methods include password-based systems, biometric verification such as fingerprint or facial recognition, and multi-factor authentication (MFA) combining two or more credentials for enhanced security. Access control relies on these authentication methods to verify user identities before granting permissions to resources or data. Strong authentication processes mitigate unauthorized access risks and are foundational to effective access control frameworks in cybersecurity.
How Access Control and Authentication Work Together
Access control and authentication work together to secure systems by first verifying the user's identity through authentication methods such as passwords, biometrics, or multi-factor authentication. Once identity is confirmed, access control mechanisms enforce permissions and policies to determine what resources or actions the authenticated user is allowed to access. This dynamic collaboration ensures that only authorized users gain appropriate access, minimizing security risks and safeguarding sensitive data.
Importance in Cybersecurity
Access control and authentication are critical components in cybersecurity that work together to protect sensitive information and systems. Authentication verifies the identity of users through methods such as passwords, biometrics, or multi-factor authentication, ensuring that only authorized individuals gain entry. Access control then enforces policies that determine the level of resources and data each authenticated user can access, minimizing the risk of unauthorized actions and potential security breaches.
Challenges and Risks
Access control faces challenges such as managing complex permission hierarchies and ensuring dynamic policy enforcement, which increases the risk of unauthorized access if misconfigured. Authentication struggles with risks like credential theft, phishing attacks, and weak password practices that can compromise identity verification processes. Both mechanisms require robust security measures and continuous monitoring to mitigate vulnerabilities and prevent data breaches.
Best Practices for Implementation
Access control and authentication serve distinct roles in securing digital environments, where authentication verifies user identity and access control determines permissions based on that identity. Best practices for implementation include enforcing multi-factor authentication (MFA) to strengthen identity verification and applying the principle of least privilege in access control to minimize unnecessary permissions. Regular audits and role-based access control (RBAC) ensure ongoing compliance and adapt to evolving security requirements.
Access Control Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com