Avro and ORC are powerful data serialization formats widely used in big data processing to optimize storage and improve query performance. Avro excels in schema evolution and compact binary encoding, making it ideal for streaming data, while ORC offers advanced compression and efficient columnar storage, which thrives in analytical workloads. Discover how understanding these formats can enhance your data infrastructure by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
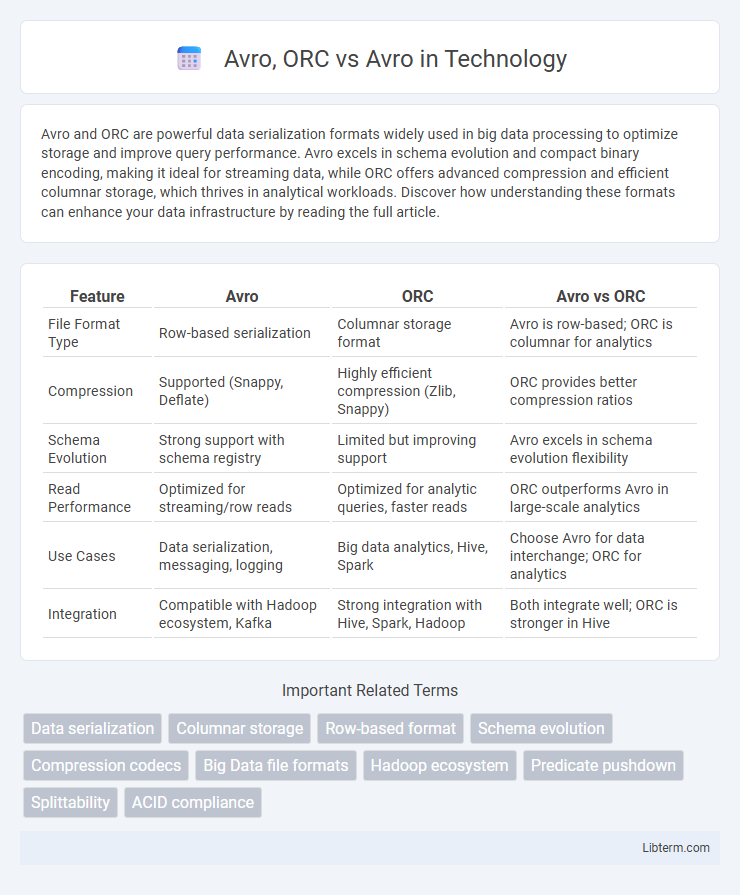
| Feature | Avro | ORC | Avro vs ORC |
|---|---|---|---|
| File Format Type | Row-based serialization | Columnar storage format | Avro is row-based; ORC is columnar for analytics |
| Compression | Supported (Snappy, Deflate) | Highly efficient compression (Zlib, Snappy) | ORC provides better compression ratios |
| Schema Evolution | Strong support with schema registry | Limited but improving support | Avro excels in schema evolution flexibility |
| Read Performance | Optimized for streaming/row reads | Optimized for analytic queries, faster reads | ORC outperforms Avro in large-scale analytics |
| Use Cases | Data serialization, messaging, logging | Big data analytics, Hive, Spark | Choose Avro for data interchange; ORC for analytics |
| Integration | Compatible with Hadoop ecosystem, Kafka | Strong integration with Hive, Spark, Hadoop | Both integrate well; ORC is stronger in Hive |
Introduction to Avro and ORC
Avro is a row-based storage format designed for efficient serialization and schema evolution, widely used in Apache Hadoop environments for data interchange. ORC (Optimized Row Columnar) is a columnar storage format that provides high compression and fast read performance, particularly suited for complex analytic queries in big data processing. Both formats support schema definitions, but Avro excels in write-heavy, streaming scenarios while ORC optimizes read-heavy, batch analytics workloads.
What is Avro?
Avro is a row-oriented remote procedure call and data serialization framework developed within the Apache Hadoop project, designed for efficient data exchange and storage. Unlike ORC (Optimized Row Columnar), which is a columnar storage format optimized for read-heavy analytic workloads, Avro is best suited for streaming data and schema evolution due to its compact binary serialization and rich data structures. Avro stores schema along with the data, enabling seamless data serialization and deserialization in distributed systems and big data environments.
Key Features of Avro
Avro offers compact, fast, binary serialization with rich data structures and schema evolution support, making it ideal for data exchange and storage. Its key features include a JSON-defined schema that enables seamless compatibility across different programming languages and an efficient serialization format that minimizes data size. Unlike ORC, which is optimized for columnar storage and analytics, Avro excels in row-based serialization for stream processing and message-oriented systems.
What is ORC?
ORC (Optimized Row Columnar) is a highly efficient, columnar storage file format designed to improve performance and reduce storage costs in big data processing, particularly within the Hadoop ecosystem. Compared to Avro, which is a row-based serialization format optimized for streaming and schema evolution, ORC provides superior compression and faster read times for analytical workloads by storing data in a columnar structure. This makes ORC ideal for complex queries on large datasets, whereas Avro excels in scenarios requiring schema flexibility and data interchange.
Key Features of ORC
ORC (Optimized Row Columnar) offers superior compression and faster read performance compared to Avro, making it ideal for large-scale data analytics in Hadoop environments. Key features of ORC include lightweight compression algorithms like Zlib and Snappy, support for complex nested data types, and built-in indexes that accelerate query processing. Unlike Avro's row-based storage format, ORC's columnar storage enables efficient data skipping and predicate pushdown, reducing I/O operations during queries.
Avro Use Cases and Applications
Avro is widely used in big data ecosystems for its compact, fast, and schema-based serialization, making it ideal for data exchange between systems and long-term storage in Hadoop environments. Its support for schema evolution and seamless integration with Apache Kafka, Apache Hadoop, and Apache Spark ensures efficient streaming data pipelines and analytics workflows. Unlike ORC, which excels in optimized columnar storage for query performance in data warehousing, Avro's row-based format is preferred for real-time data ingestion and metadata-rich message processing applications.
ORC Use Cases and Applications
ORC (Optimized Row Columnar) format excels in high-performance analytics and large-scale data warehousing by providing efficient compression and faster read speeds compared to Avro, which is optimized for data serialization and schema evolution. ORC is widely used in Hadoop ecosystems for processing complex queries on massive datasets, making it ideal for business intelligence, log analytics, and ETL workflows. Key applications include Apache Hive for SQL querying, Apache Spark for distributed data processing, and cloud platforms leveraging ORC for cost-effective storage and query optimization.
Performance Comparison: ORC vs Avro
ORC files demonstrate superior performance compared to Avro for large-scale data processing due to their high compression rates and optimized columnar storage, which significantly reduces I/O and speeds up query execution in Hadoop ecosystems. Avro, with its row-based storage format, offers faster write performance and better support for schema evolution, making it suitable for streaming and real-time applications. While ORC excels in batch processing scenarios with complex queries, Avro remains preferred for scenarios demanding flexible, fast writes and efficient serialization.
Schema Evolution and Data Compatibility
Avro excels in schema evolution by supporting backward and forward compatibility through its embedded JSON schema, allowing seamless data serialization and deserialization even when schemas change. ORC handles schema evolution with restrictions, often requiring careful column management to avoid compatibility issues, as it embeds schema metadata directly within its file footer in a binary format. Data compatibility in Avro is more flexible due to its explicit schema usage at both write and read times, whereas ORC's schema evolution requires stricter adherence to existing column structures to ensure accurate data interpretation.
Choosing Between ORC and Avro
Choosing between ORC and Avro depends on the specific use case and data processing requirements. ORC excels in complex analytical queries with efficient columnar storage and compression, making it ideal for Hive and big data frameworks focused on read performance. Avro provides robust row-based serialization, schema evolution, and efficient write performance, preferred for data exchange and streaming pipelines where schema flexibility is crucial.
Avro, ORC Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com