Network virtualization transforms physical network resources into flexible, software-based environments that enhance scalability and efficiency. It enables seamless management of multiple virtual networks on a single physical infrastructure, reducing costs and simplifying operations. Explore the rest of the article to discover how your organization can leverage network virtualization for improved performance and agility.
Table of Comparison
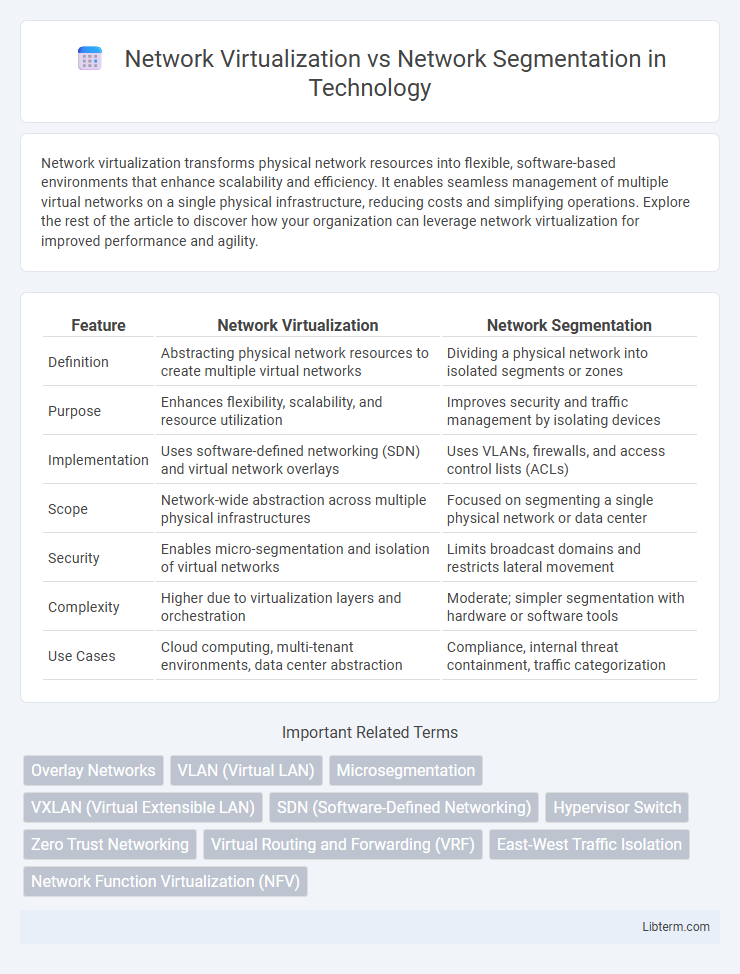
| Feature | Network Virtualization | Network Segmentation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Abstracting physical network resources to create multiple virtual networks | Dividing a physical network into isolated segments or zones |
| Purpose | Enhances flexibility, scalability, and resource utilization | Improves security and traffic management by isolating devices |
| Implementation | Uses software-defined networking (SDN) and virtual network overlays | Uses VLANs, firewalls, and access control lists (ACLs) |
| Scope | Network-wide abstraction across multiple physical infrastructures | Focused on segmenting a single physical network or data center |
| Security | Enables micro-segmentation and isolation of virtual networks | Limits broadcast domains and restricts lateral movement |
| Complexity | Higher due to virtualization layers and orchestration | Moderate; simpler segmentation with hardware or software tools |
| Use Cases | Cloud computing, multi-tenant environments, data center abstraction | Compliance, internal threat containment, traffic categorization |
Understanding Network Virtualization
Network virtualization creates multiple virtual networks on a single physical infrastructure, allowing for improved resource utilization, flexibility, and isolation without additional hardware. This technology enables dynamic network management by abstracting physical devices into software-defined entities, supporting scalable and efficient cloud environments. Unlike network segmentation, which divides a physical network into isolated segments typically for security, virtualization maximizes operational efficiency through comprehensive network abstraction and automation.
What is Network Segmentation?
Network segmentation involves dividing a computer network into smaller, isolated segments to improve security and performance by limiting broadcast traffic and containing potential cyber threats within specific zones. It uses VLANs, firewalls, and access controls to restrict data flow between segments, thereby minimizing attack surfaces and enabling better policy enforcement. This approach contrasts with network virtualization, which abstracts network resources to create flexible, software-defined environments without necessarily isolating traffic physically.
Key Differences Between Network Virtualization and Segmentation
Network virtualization creates multiple virtual networks on a single physical infrastructure, enabling flexible resource allocation and isolation through software-defined networking (SDN). Network segmentation divides a physical network into distinct segments to enhance security and performance by limiting broadcast domains and controlling data flow. The primary difference lies in virtualization abstracting and pooling resources for agility, whereas segmentation partitions networks for containment and improved traffic management.
Core Benefits of Network Virtualization
Network virtualization enables the creation of multiple virtual networks on a single physical infrastructure, enhancing resource utilization and simplifying network management through centralized control. It improves scalability and agility by allowing dynamic provisioning and isolation of network resources without hardware changes. Core benefits include reduced capital and operational expenses, increased flexibility in deploying network services, and improved security via isolated virtual environments.
Advantages of Implementing Network Segmentation
Network segmentation enhances security by isolating sensitive data and limiting lateral movement for attackers within a network, reducing the attack surface. It improves performance by containing broadcast traffic and minimizing congestion in large, complex network environments. Implementing network segmentation also simplifies compliance with regulatory standards by enabling granular control over data flows and access management.
Use Cases: When to Choose Virtualization or Segmentation
Network virtualization is ideal for creating multiple isolated virtual networks over a single physical infrastructure, allowing for flexible resource allocation in cloud environments and multi-tenant data centers. Network segmentation is best suited for enhancing security by dividing a network into smaller segments, limiting lateral movement of threats in enterprise environments and regulatory compliance scenarios. Choose virtualization for agility and scalability, and segmentation for security and traffic management.
Security Implications: Virtualization vs Segmentation
Network virtualization creates multiple virtual networks on a single physical infrastructure, improving isolation and flexibility but increasing attack surface risks due to shared resources and hypervisor vulnerabilities. Network segmentation divides the physical network into smaller, isolated segments, limiting lateral movement of attackers and reducing the blast radius of breaches through strict access controls. While virtualization enhances scalability and efficiency, segmentation provides stronger containment of threats by enforcing strict boundaries at the hardware or software-defined perimeter level.
Performance Considerations for Both Approaches
Network virtualization improves performance by abstracting physical hardware, enabling flexible resource allocation and load balancing across multiple virtual networks. Network segmentation enhances security and limits broadcast domain size, reducing network congestion and improving latency through targeted traffic isolation. Both approaches optimize network efficiency, but virtualization offers dynamic scalability, while segmentation provides consistent performance stability in multi-tenant environments.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Solution
Network virtualization faces challenges such as increased complexity in managing virtual networks and potential performance overhead due to resource sharing, along with security risks from multi-tenant environments. Network segmentation encounters limitations in scalability, as rigid segmentation can hinder network flexibility and increase administrative burden through complex policy management. Both solutions require robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access and ensure efficient traffic isolation, but balancing flexibility and control remains a significant operational challenge.
Future Trends in Network Virtualization and Segmentation
Future trends in network virtualization emphasize advanced automation, AI-driven orchestration, and deeper integration with cloud-native environments to enable scalable, agile, and secure network infrastructures. Network segmentation is evolving with zero-trust architectures and micro-segmentation techniques that enhance granular security controls in hybrid and multi-cloud deployments. The convergence of these technologies will drive dynamic, programmable networks that optimize performance and mitigate sophisticated cyber threats in increasingly complex digital ecosystems.
Network Virtualization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com