Service discovery enables automatic detection of devices and services on a network, streamlining communication and improving efficiency for your applications. It plays a crucial role in dynamic environments such as cloud computing and microservices architectures by facilitating seamless integration. Explore the rest of the article to understand how service discovery can optimize your network operations.
Table of Comparison
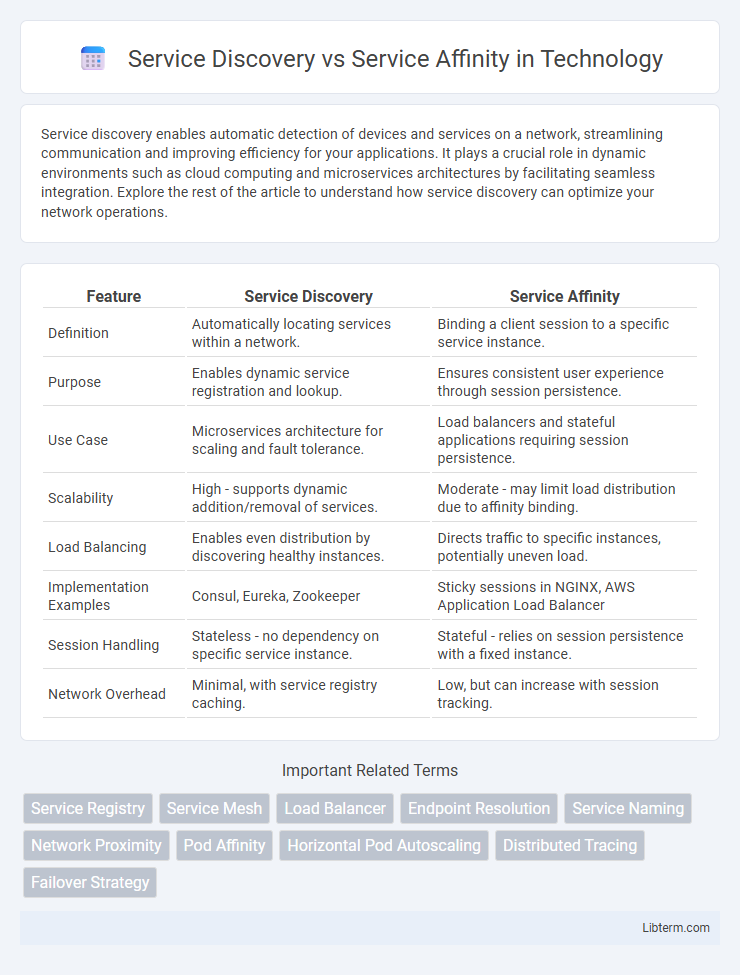
| Feature | Service Discovery | Service Affinity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automatically locating services within a network. | Binding a client session to a specific service instance. |
| Purpose | Enables dynamic service registration and lookup. | Ensures consistent user experience through session persistence. |
| Use Case | Microservices architecture for scaling and fault tolerance. | Load balancers and stateful applications requiring session persistence. |
| Scalability | High - supports dynamic addition/removal of services. | Moderate - may limit load distribution due to affinity binding. |
| Load Balancing | Enables even distribution by discovering healthy instances. | Directs traffic to specific instances, potentially uneven load. |
| Implementation Examples | Consul, Eureka, Zookeeper | Sticky sessions in NGINX, AWS Application Load Balancer |
| Session Handling | Stateless - no dependency on specific service instance. | Stateful - relies on session persistence with a fixed instance. |
| Network Overhead | Minimal, with service registry caching. | Low, but can increase with session tracking. |
Introduction to Service Discovery and Service Affinity
Service Discovery enables dynamic detection of network services by automatically locating service instances via a registry, improving scalability and fault tolerance in microservices architectures. Service Affinity, also known as session affinity or sticky sessions, ensures that requests from a particular client consistently reach the same service instance, enhancing stateful interactions and reducing latency. Understanding these concepts is crucial for designing efficient load balancing and service communication strategies in distributed systems.
Defining Service Discovery
Service Discovery is a mechanism that enables automatic detection and location of services within a network, facilitating dynamic communication between distributed components. It maintains an updated registry of service instances, allowing clients to discover available services without hardcoding endpoints. Unlike Service Affinity, which binds clients to specific service instances, Service Discovery emphasizes flexibility and scalability by dynamically routing requests to optimal service instances.
Understanding Service Affinity
Service Affinity refers to the practice of routing client requests to the same service instance or node to maintain session state or improve performance, ensuring consistent user experience. Unlike Service Discovery, which dynamically locates available service instances within a network for load balancing and fault tolerance, Service Affinity emphasizes stable connections by leveraging identifiers like cookies or IP addresses. Understanding Service Affinity is crucial for designing applications that require sticky sessions or stateful interactions, particularly in microservices and distributed architectures.
Key Differences Between Service Discovery and Service Affinity
Service Discovery dynamically identifies and locates available services within a network, enabling scalable and flexible communication between microservices. Service Affinity maintains session consistency by routing client requests to the same service instance, improving stateful interactions and user experience. Key differences lie in their purposes: Service Discovery optimizes service availability and load balancing, while Service Affinity ensures persistence and session stickiness.
The Role of Service Discovery in Microservices Architecture
Service discovery plays a crucial role in microservices architecture by enabling dynamic location and communication between distributed services without hardcoding IP addresses or endpoints. It ensures that microservices can find and interact with each other efficiently, supporting scalability and fault tolerance through automated registration and health checks. Service affinity, by contrast, emphasizes routing requests to specific instances to maintain session state or optimize performance, often relying on service discovery mechanisms for initial endpoint resolution.
The Importance of Service Affinity for Performance
Service affinity ensures consistent routing of requests to the same service instance, significantly enhancing cache utilization and reducing latency in distributed systems. Unlike service discovery, which dynamically locates service instances, service affinity maintains session persistence, leading to improved application performance and user experience. High-performance environments such as microservices architectures and load-balanced web applications benefit from service affinity by minimizing overhead and optimizing resource usage.
Choosing Between Service Discovery and Service Affinity
Choosing between service discovery and service affinity depends on the complexity and dynamic nature of the microservices environment. Service discovery offers automatic detection and routing of service instances, enhancing scalability and fault tolerance, while service affinity ensures that user sessions consistently interact with the same service instance, improving performance and user experience in stateful applications. Balancing these approaches requires assessing factors such as load distribution, session persistence needs, and infrastructure agility.
Common Use Cases and Scenarios
Service Discovery is commonly used in dynamic microservices architectures where services need to locate each other automatically and handle scaling or failure scenarios without manual configuration. Service Affinity is often applied in stateful applications or session-based workloads where directing requests consistently to the same instance improves performance and user experience. Scenarios involving load balancing for stateless services favor Service Discovery, while scenarios requiring session persistence or caching best leverage Service Affinity.
Challenges and Best Practices
Service Discovery faces challenges like dynamic IP addressing and scaling in microservices environments, requiring automated registry updates and health checks for optimal routing. Service Affinity struggles with load balancing and stateful session management, best addressed by leveraging sticky sessions or consistent hashing to ensure user request continuity. Implementing robust monitoring and fallback mechanisms enhances reliability and performance in both approaches.
Conclusion: Finding the Right Balance
Striking the optimal balance between Service Discovery and Service Affinity is crucial for achieving scalable and resilient microservices architecture. Service Discovery enhances dynamic load balancing and fault tolerance by enabling services to locate each other without hard-coded endpoints, while Service Affinity ensures session persistence by directing requests to specific instances. Organizations must evaluate their application requirements and traffic patterns to implement a hybrid approach that combines the flexibility of Service Discovery with the stability of Service Affinity.
Service Discovery Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com