Avro and Parquet are popular data serialization formats widely used in big data processing for efficient storage and fast retrieval. Avro excels with its compact binary format and schema evolution capabilities, making it ideal for streaming data, while Parquet offers optimized columnar storage that significantly improves query performance in analytics workloads. Explore the rest of the article to understand how these formats can enhance Your data processing strategy.
Table of Comparison
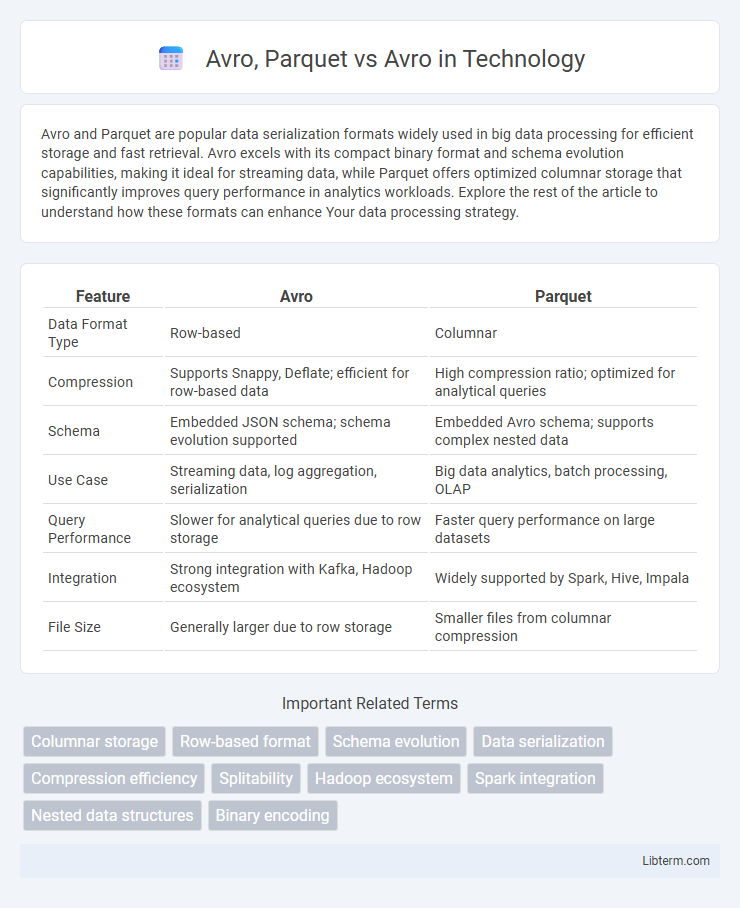
| Feature | Avro | Parquet |
|---|---|---|
| Data Format Type | Row-based | Columnar |
| Compression | Supports Snappy, Deflate; efficient for row-based data | High compression ratio; optimized for analytical queries |
| Schema | Embedded JSON schema; schema evolution supported | Embedded Avro schema; supports complex nested data |
| Use Case | Streaming data, log aggregation, serialization | Big data analytics, batch processing, OLAP |
| Query Performance | Slower for analytical queries due to row storage | Faster query performance on large datasets |
| Integration | Strong integration with Kafka, Hadoop ecosystem | Widely supported by Spark, Hive, Impala |
| File Size | Generally larger due to row storage | Smaller files from columnar compression |
Introduction to Avro and Parquet
Avro and Parquet are popular data serialization formats widely used in big data processing. Avro is a row-based storage format designed for efficient schema evolution and compact binary serialization, making it ideal for streaming and batch processing with Apache Hadoop. In contrast, Parquet is a columnar storage format optimized for analytic queries, offering efficient compression and encoding schemes that enhance performance in read-heavy workloads such as data warehousing and business intelligence applications.
What is Avro?
Avro is a compact, fast, binary data serialization format developed within the Apache Hadoop project, designed for efficient data exchange between systems. It uses JSON for defining schemas and serializes data in a compact binary format, enabling robust data serialization and deserialization with schema evolution support. Unlike Parquet, which is a columnar storage format optimized for analytical querying, Avro is row-based, making it ideal for streaming and batch processing scenarios where schema flexibility and data interchange are critical.
Avro’s Key Features
Avro excels in data serialization with its compact, fast binary encoding and rich schema evolution capabilities, making it ideal for streaming and log data applications. It uses JSON-defined schemas to enforce data structure while supporting dynamic typing and schema resolution, enhancing flexibility in data processing pipelines. Compared to Parquet, Avro prioritizes row-based storage and serialization efficiency, which benefits use cases requiring frequent reads and writes of small records.
Parquet Overview
Parquet is a columnar storage file format optimized for big data processing, offering efficient compression and encoding schemes that significantly reduce storage space and enhance query performance. Unlike Avro, which is row-oriented and excels in write-heavy transactional workloads, Parquet's columnar design enables faster analytical queries by reading only the necessary columns. This makes Parquet highly suitable for data warehousing, OLAP, and large-scale data analytics use cases.
Parquet’s Main Advantages
Parquet offers superior compression and efficient columnar storage, significantly reducing storage costs and improving query performance in big data environments. Unlike Avro's row-based format, Parquet optimizes analytical workloads by enabling faster data retrieval through column pruning and predicate pushdown. This makes Parquet the preferred choice for schema evolution, complex nested data, and high-speed queries in platforms like Apache Spark and Hadoop.
Data Serialization: How Avro Works
Avro employs a compact, fast, binary data serialization format that integrates schema evolution directly within the serialized data, ensuring seamless compatibility across different application versions. It stores data along with its schema in JSON format, enabling efficient compression and reducing storage requirements while supporting dynamic typing. Unlike Parquet, which is columnar and optimized for read-heavy analytical queries, Avro is row-oriented, making it ideal for write-intensive and real-time streaming data serialization tasks.
Comparative Analysis: Avro vs Parquet
Avro and Parquet are both efficient data serialization formats widely used in big data ecosystems, with Avro optimized for row-based storage and schema evolution, making it ideal for streaming and write-heavy workloads. Parquet, on the other hand, is a columnar storage file format designed for efficient read-heavy analytical queries and compression, which significantly reduces I/O for large-scale data processing. Choosing between Avro and Parquet depends on the specific use case, as Avro excels in write-intensive operations and schema compatibility, while Parquet offers superior performance in query speed and storage efficiency for columnar data access.
Use Cases: When to Use Avro vs Parquet
Avro is ideal for row-based data serialization, making it suitable for streaming data pipelines and scenarios requiring fast write and read operations, such as log aggregation and message serialization. Parquet excels in columnar storage, optimized for complex analytical queries and large-scale batch processing in data warehouses or data lakes, providing superior compression and read efficiency for selective queries. Choose Avro for real-time processing and Parquet for batch analytics and long-term data storage.
Performance Benchmarks: Avro vs Parquet
Parquet consistently outperforms Avro in read-heavy workloads due to its columnar storage format, which optimizes query efficiency and reduces I/O operations. Avro, using row-based storage, excels in write-intensive tasks and streaming data scenarios by offering faster serialization and lower latency. Benchmark tests reveal Parquet's superior compression ratios and scan speeds for analytical processing, while Avro demonstrates lower overhead for data serialization and real-time data pipelines.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Data Format
Avro offers efficient serialization with schema evolution ideal for row-based data processing, while Parquet excels in analytical queries through its columnar storage, reducing I/O and improving compression. Selecting the right format depends on workload needs; Avro is better for write-heavy, streaming applications, whereas Parquet suits read-heavy, batch analytics on large datasets. Evaluating data access patterns, query requirements, and storage optimization guides optimal data format choice.
Avro, Parquet Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com