SOAP, an acronym for Simple Object Access Protocol, is a protocol used for exchanging structured information in web services and computer networks. It relies on XML for its message format and usually operates over HTTP or SMTP to ensure interoperability between applications running on different platforms. Explore the rest of this article to understand how SOAP enhances your web service communications and integrations.
Table of Comparison
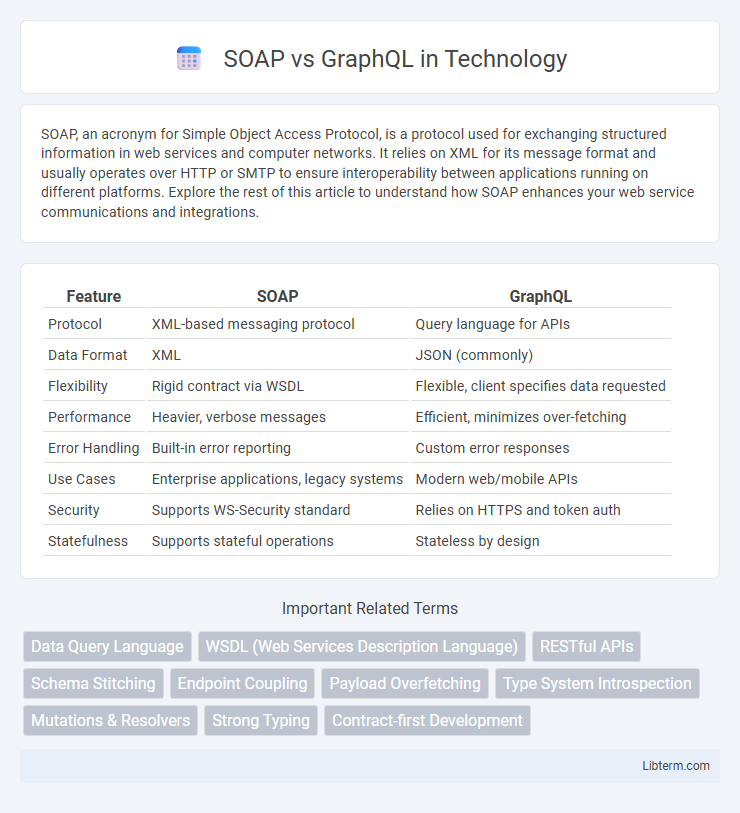
| Feature | SOAP | GraphQL |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol | XML-based messaging protocol | Query language for APIs |
| Data Format | XML | JSON (commonly) |
| Flexibility | Rigid contract via WSDL | Flexible, client specifies data requested |
| Performance | Heavier, verbose messages | Efficient, minimizes over-fetching |
| Error Handling | Built-in error reporting | Custom error responses |
| Use Cases | Enterprise applications, legacy systems | Modern web/mobile APIs |
| Security | Supports WS-Security standard | Relies on HTTPS and token auth |
| Statefulness | Supports stateful operations | Stateless by design |
Introduction to SOAP and GraphQL
SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) is a protocol for exchanging structured information in web services, relying on XML-based messaging and strict standards for security and transaction compliance. GraphQL is a query language for APIs that enables clients to request exactly the data they need, offering flexibility and efficiency through a single endpoint and strong typing. Both technologies serve API communication but differ fundamentally in design, data format, and interaction style.
Core Principles and Architecture
SOAP relies on a strict contract defined by WSDL for message structure, emphasizing standardized protocols like HTTP, SMTP, and XML-based messaging to ensure strong typing and formal operations. GraphQL operates on a flexible schema with a single endpoint, allowing clients to specify queries precisely, reducing data over-fetching and under-fetching through its declarative query language and runtime execution. While SOAP uses a message-based protocol architecture emphasizing security and ACID compliance, GraphQL embraces a client-driven approach with a graph-based data model optimizing performance and developer experience.
Data Retrieval Methods
SOAP uses XML-based messaging protocols with predefined operations for data retrieval, typically relying on WSDL to define services and enforce strict contract-based communication. GraphQL employs a flexible query language allowing clients to specify exactly which fields to retrieve in a single request, minimizing over-fetching and under-fetching of data. While SOAP retrieves data through fixed endpoints and operations, GraphQL enables dynamic data querying by allowing clients to request nested and related resources in a customizable structure.
Flexibility and Scalability
SOAP APIs enforce strict contracts and rigid message formats, which limit flexibility but ensure standardized communication for enterprise-level scalability. GraphQL offers high flexibility by allowing clients to request exactly the data they need, optimizing performance and adapting easily to evolving requirements. Scalability in GraphQL is enhanced through efficient data fetching, reducing payload sizes, while SOAP's robust protocols support complex transaction integrity and security across large-scale systems.
Performance and Efficiency
GraphQL improves performance by allowing clients to request precisely the data they need, reducing payload size and minimizing over-fetching compared to SOAP's rigid XML-based messaging. SOAP relies on complex XML envelopes and extensive processing, which can increase latency and resource consumption, impacting overall efficiency. GraphQL's ability to aggregate multiple resources in a single query enhances efficiency in data retrieval, while SOAP's strict protocols can result in additional overhead and slower communication.
Security Features and Concerns
SOAP provides robust security features through WS-Security, including message integrity, confidentiality, and authentication via XML signatures and encryption. GraphQL lacks built-in security standards, making it vulnerable to injection attacks and data overexposure without proper validation, authorization, and query complexity analysis. Enterprises often implement custom security layers in GraphQL, while SOAP's standardized protocols offer more consistent and mature protection for sensitive data transactions.
Tooling and Ecosystem Support
GraphQL boasts a rapidly growing ecosystem with powerful tools like Apollo Client, GraphiQL, and Relay that facilitate efficient query building, real-time data fetching, and schema introspection. SOAP benefits from mature tooling in enterprise environments, including robust support in platforms like IBM WebSphere, Microsoft WCF, and extensive XML-based message validation frameworks. While GraphQL emphasizes flexibility and developer-friendly interfaces, SOAP's tooling excels in transactional reliability and security features critical for legacy enterprise systems.
Use Cases and Application Scenarios
SOAP is ideal for enterprise-level applications requiring strict security, transactional reliability, and formal contracts, such as banking and telecommunications systems. GraphQL excels in scenarios needing flexible, efficient data retrieval, like mobile apps and dynamic web interfaces, allowing clients to request exactly the data they need. Use cases involving multiple data sources or rapidly evolving APIs benefit significantly from GraphQL's schema and query adaptability compared to SOAP's rigid structure.
Migration Challenges and Considerations
Migrating from SOAP to GraphQL involves addressing challenges such as data structure differences, since SOAP relies on rigid XML schemas while GraphQL supports flexible queries and JSON responses. Considerations include restructuring backend services to accommodate GraphQL's schema definition language and resolver functions, ensuring API clients can handle dynamic query capabilities. Performance implications and security models must be reassessed to optimize GraphQL endpoints while maintaining the robust SOAP-level guarantees.
Choosing Between SOAP and GraphQL
Choosing between SOAP and GraphQL depends on specific application needs and integration goals. SOAP excels in enterprise environments requiring strict standards, comprehensive security protocols like WS-Security, and formal contracts via WSDL. GraphQL offers flexibility with dynamic queries, optimized data retrieval, and simplified client-server interactions, making it ideal for modern web and mobile applications demanding efficient data fetching.
SOAP Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com