Canarytokens are small, deployable pieces of code designed to detect unauthorized access by triggering alerts when activated. These digital tripwires help protect your networks and data by providing early warnings of potential breaches without requiring extensive security infrastructure. Explore the rest of this article to understand how Canarytokens enhance cybersecurity and how you can implement them effectively.
Table of Comparison
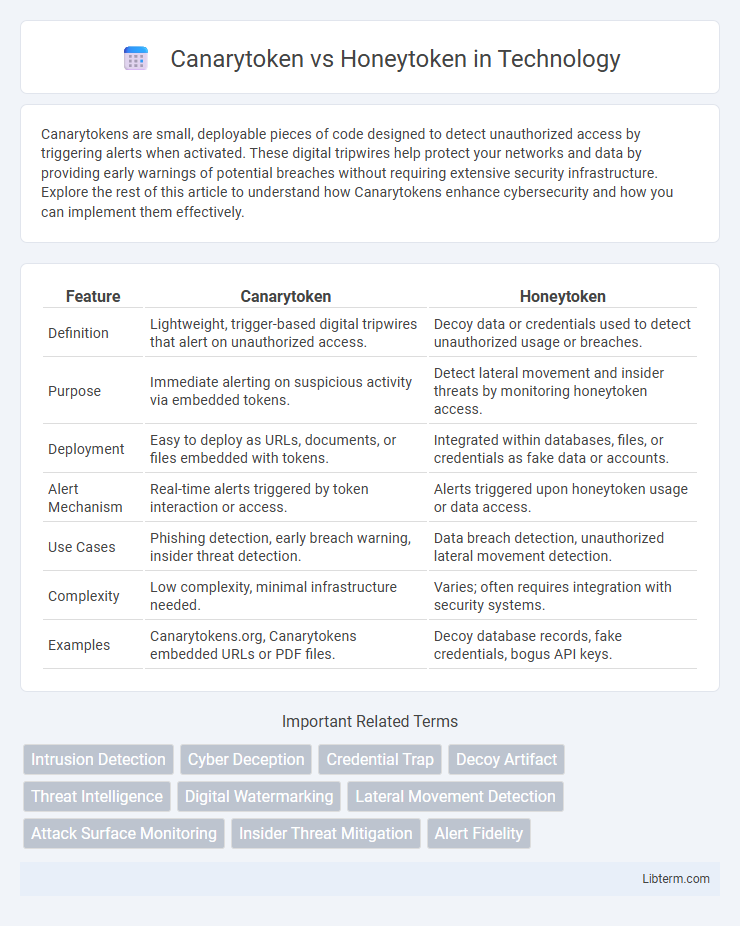
| Feature | Canarytoken | Honeytoken |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lightweight, trigger-based digital tripwires that alert on unauthorized access. | Decoy data or credentials used to detect unauthorized usage or breaches. |
| Purpose | Immediate alerting on suspicious activity via embedded tokens. | Detect lateral movement and insider threats by monitoring honeytoken access. |
| Deployment | Easy to deploy as URLs, documents, or files embedded with tokens. | Integrated within databases, files, or credentials as fake data or accounts. |
| Alert Mechanism | Real-time alerts triggered by token interaction or access. | Alerts triggered upon honeytoken usage or data access. |
| Use Cases | Phishing detection, early breach warning, insider threat detection. | Data breach detection, unauthorized lateral movement detection. |
| Complexity | Low complexity, minimal infrastructure needed. | Varies; often requires integration with security systems. |
| Examples | Canarytokens.org, Canarytokens embedded URLs or PDF files. | Decoy database records, fake credentials, bogus API keys. |
Introduction to Canarytokens and Honeytokens
Canarytokens are small, stealthy, and customizable digital tripwires designed to detect unauthorized access by triggering alerts when activated. Honeytokens serve as deceptive data elements, such as fake credentials or files, planted strategically to lure attackers and reveal intrusion attempts. Both tools enhance cybersecurity by providing early warnings about potential breaches through monitoring interactions with these planted tokens.
What Are Canarytokens?
Canarytokens are small, customizable digital tripwires designed to detect unauthorized access or data breaches by triggering alerts when interacted with. These tokens can be embedded in documents, URLs, or code to monitor and track malicious activities in real time. Unlike traditional honeytokens, Canarytokens emphasize rapid notification and ease of deployment to enhance security monitoring and incident response.
What Are Honeytokens?
Honeytokens are deceptive digital artifacts intentionally planted within a network or system to detect unauthorized access or malicious activity by triggering alerts when interacted with. These can include fake files, credentials, or database entries designed to appear valuable to attackers but serve solely as early warning systems. Canarytokens, a specific type of honeytoken, offer customizable and easily deployable traps that notify administrators instantly upon compromise, enhancing real-time threat detection.
Key Differences Between Canarytokens and Honeytokens
Canarytokens are specialized digital tripwires designed to alert organizations immediately upon unauthorized access by embedding unique, trackable markers such as fake files or URLs. Honeytokens, broader in scope, serve as deceptive data elements like bogus credentials or fake database entries intended to detect, mislead, and analyze malicious insider or external activity. The key difference lies in Canarytokens' primary role of rapid breach notification through active triggers, whereas honeytokens function as passive deception tools integrated into security strategies to identify threat vectors over time.
Use Cases for Canarytokens
Canarytokens serve as deceptive security tools designed to detect unauthorized access by embedding covert markers like fake credentials, documents, or URLs in sensitive environments. These tokens alert administrators instantly when triggered, enabling early breach detection, insider threat identification, and rapid incident response across cloud infrastructure, network segments, and endpoints. Unlike honeytokens, which often attract attackers to bait data, canarytokens primarily act as tripwires for monitoring specific access points and sensitive asset interactions.
Use Cases for Honeytokens
Honeytokens are decoy data elements designed to detect unauthorized access and insider threats by alerting security teams when accessed. They are commonly deployed as fake login credentials, bogus database entries, or dummy files to identify malicious actors within networks or cloud environments. Use cases for honeytokens include monitoring sensitive data leaks, tracking lateral movement in breached systems, and triggering incident response when attackers interact with these planted assets.
Deployment and Implementation
Canarytokens are lightweight, easily deployable digital tripwires that activate alerts when triggered, often embedded in files, URLs, or DNS entries for swift detection of unauthorized access. Honeytokens function as decoy data such as fake credentials or databases designed to lure attackers and monitor their actions within a network environment, requiring more extensive integration into existing systems. Deployment of Canarytokens is typically faster and more flexible for immediate intrusion detection, while Honeytokens demand careful planning and configuration to simulate realistic assets and gather actionable intelligence.
Benefits and Limitations
Canarytokens provide proactive threat detection by generating unique, trackable tokens that alert organizations when triggered, enhancing early breach identification and response capabilities. Honeytokens, as deceptive digital assets, help detect unauthorized access by mimicking real data, aiding in insider threat detection and forensic analysis. While canarytokens offer high specificity and reduce false positives, they may require ongoing management and integration; honeytokens broaden detection scope but can be less precise and risk exposure if improperly configured.
Choosing Between Canarytokens and Honeytokens
Choosing between Canarytokens and Honeytokens depends on your security goals and deployment environment. Canarytokens provide simple, low-interaction traps that alert teams when accessed, ideal for early breach detection without complex setup. Honeytokens offer more customizable, high-interaction decoys capable of deeper attacker engagement, suitable for organizations seeking detailed intrusion data and behavioral analysis.
Future Trends in Token-Based Threat Detection
Future trends in token-based threat detection emphasize the integration of Canarytokens and Honeytokens with AI-driven analytics to enhance real-time anomaly detection and reduce false positives. Advancements in cloud-native deployments and automation promise scalable, context-aware token generation that adapts dynamically to evolving attacker behaviors. Increasingly, organizations prioritize seamless integration of these tokens within broader Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) and Extended Detection and Response (XDR) platforms to optimize incident response and threat intelligence.
Canarytoken Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com