Pub/Sub is a messaging pattern that enables asynchronous communication between publishers and subscribers, decoupling message producers from consumers for scalable and reliable event-driven systems. It supports real-time data streaming and distribution across distributed applications, making it ideal for cloud services, IoT, and microservices architectures. Discover how Pub/Sub can enhance your system's responsiveness and scalability by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
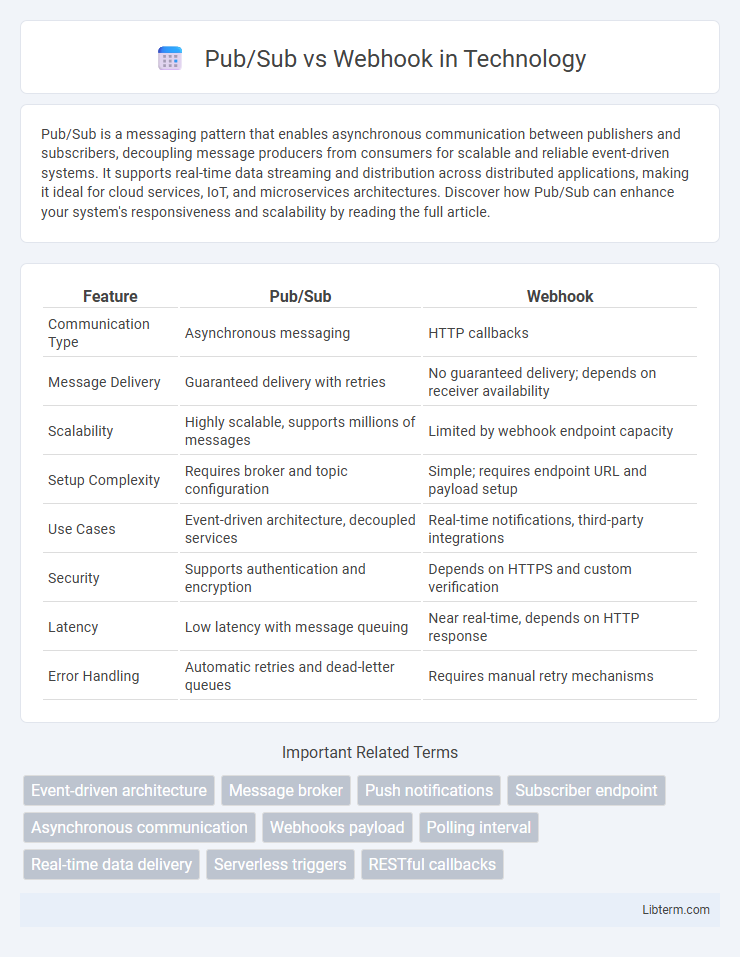
| Feature | Pub/Sub | Webhook |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Type | Asynchronous messaging | HTTP callbacks |
| Message Delivery | Guaranteed delivery with retries | No guaranteed delivery; depends on receiver availability |
| Scalability | Highly scalable, supports millions of messages | Limited by webhook endpoint capacity |
| Setup Complexity | Requires broker and topic configuration | Simple; requires endpoint URL and payload setup |
| Use Cases | Event-driven architecture, decoupled services | Real-time notifications, third-party integrations |
| Security | Supports authentication and encryption | Depends on HTTPS and custom verification |
| Latency | Low latency with message queuing | Near real-time, depends on HTTP response |
| Error Handling | Automatic retries and dead-letter queues | Requires manual retry mechanisms |
Introduction to Pub/Sub and Webhooks
Pub/Sub is a messaging pattern where publishers send messages to topics and subscribers receive messages asynchronously, enabling scalable and decoupled communication between services. Webhooks operate through HTTP callbacks, allowing one system to send real-time data or event notifications to another by triggering predefined URLs. Pub/Sub is ideal for scalable, distributed systems, while webhooks suit straightforward, synchronous event delivery.
How Pub/Sub Works
Pub/Sub operates by decoupling message producers and consumers through a message broker that manages topics and subscriptions. Publishers send messages to specific topics, which are then asynchronously delivered to all subscribers registered to those topics in real-time or near real-time. This model ensures scalable, reliable, and efficient event-driven communication without requiring direct knowledge of subscribers by the publishers.
How Webhooks Operate
Webhooks operate by sending real-time HTTP POST requests to a predefined URL whenever a specific event occurs, enabling instant data transmission without continuous polling. This event-driven approach allows seamless integration between applications, reducing latency and server overhead. Unlike Pub/Sub systems that use message brokers to decouple publishers and subscribers, webhooks provide a direct and immediate notification mechanism.
Key Differences Between Pub/Sub and Webhook
Pub/Sub operates on a message broker model where publishers send messages to topics and subscribers asynchronously receive these messages, enabling decoupled and scalable communication. Webhooks rely on real-time HTTP callbacks where a server sends data directly to a client URL upon triggering events, requiring the receiver to be online and reachable. Key differences include Pub/Sub's support for asynchronous, many-to-many messaging with message queuing, contrasted with Webhook's synchronous, point-to-point communication dependent on immediate availability and direct HTTP requests.
Use Cases for Pub/Sub
Pub/Sub systems excel in use cases requiring real-time, scalable, and decoupled communication, such as distributing live updates in large-scale applications, processing event streams in IoT or telemetry data, and enabling asynchronous workflows in microservices architectures. They support multiple subscribers simultaneously, making them ideal for broadcasting messages across diverse consumers without tight coupling. This scalability and flexibility outperform webhooks in scenarios demanding high throughput and robust message delivery guarantees.
Use Cases for Webhooks
Webhooks excel in real-time event notifications where immediate data delivery is critical, such as payment processing alerts, CRM system updates, and automated workflow triggers. They are ideal for one-way communication scenarios that require low latency and direct endpoint invocation, enabling seamless integration with third-party applications and microservices. Webhooks simplify event-driven architectures by pushing updates as they occur, eliminating the need for continuous polling and reducing system resource consumption.
Advantages of Pub/Sub
Pub/Sub offers robust scalability by efficiently handling millions of messages per second across distributed systems, ensuring real-time data streaming without performance bottlenecks. Its decoupled architecture supports asynchronous communication, reducing dependencies between services and improving overall system resilience. Built-in message durability and retry mechanisms guarantee message delivery even in case of consumer or network failures, enhancing reliability beyond traditional webhook implementations.
Benefits of Webhooks
Webhooks provide real-time data delivery by pushing updates instantly to the subscribed URL, reducing latency compared to the polling mechanism of Pub/Sub systems. They simplify integration by eliminating the need for continuous message polling, which conserves server resources and lowers operational costs. Webhooks enable event-driven architectures that enhance responsiveness and streamline workflows across APIs and third-party services.
Choosing Between Pub/Sub and Webhook
Choosing between Pub/Sub and Webhook depends on the scale and real-time requirements of your application. Pub/Sub offers asynchronous messaging with guaranteed delivery, ideal for decoupled, high-throughput systems, while Webhook provides simple HTTP callbacks suitable for lightweight, real-time event notifications. Evaluate the need for message durability, retry mechanisms, and system complexity to determine the best fit for your event-driven architecture.
Conclusion: Which Integration is Right for You?
Pub/Sub excels in scalable, event-driven architectures requiring asynchronous communication and high throughput, ideal for distributed systems needing loose coupling and reliability. Webhooks provide real-time, request-driven notifications best suited for straightforward, low-latency integrations with specific external services or APIs. Choose Pub/Sub for complex workflows with multiple consumers and Webhooks for simpler, immediate event delivery scenarios.
Pub/Sub Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com