Hybrid cloud integrates private and public cloud environments to offer businesses enhanced flexibility, security, and scalability. This model allows organizations to optimize resource allocation and maintain control over sensitive data while leveraging the cost-efficiency of public clouds. Discover how hybrid cloud can transform your IT infrastructure by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
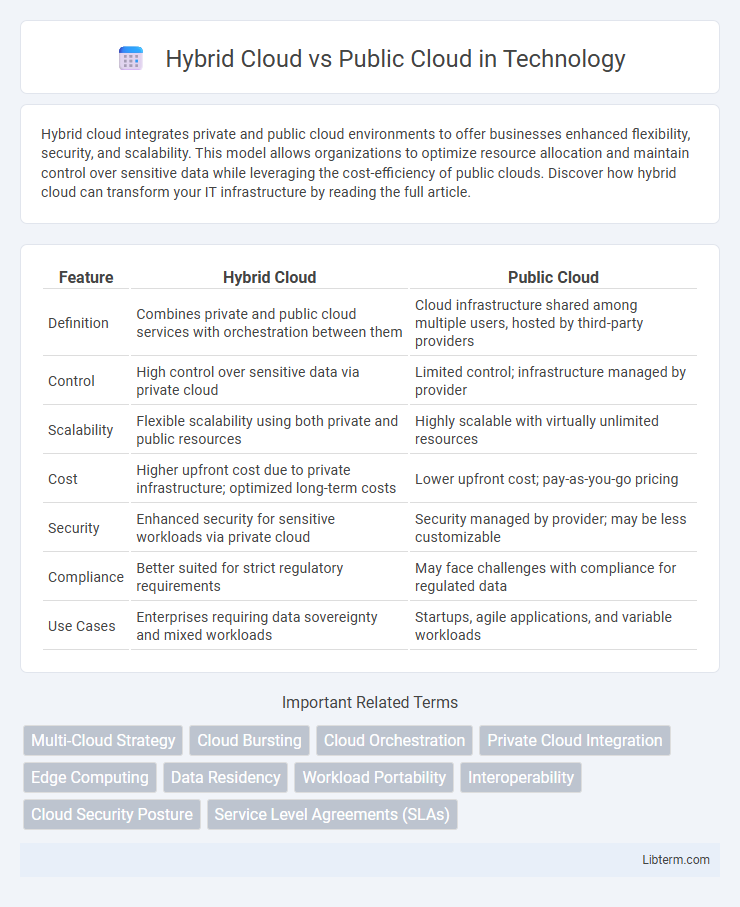
| Feature | Hybrid Cloud | Public Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines private and public cloud services with orchestration between them | Cloud infrastructure shared among multiple users, hosted by third-party providers |
| Control | High control over sensitive data via private cloud | Limited control; infrastructure managed by provider |
| Scalability | Flexible scalability using both private and public resources | Highly scalable with virtually unlimited resources |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost due to private infrastructure; optimized long-term costs | Lower upfront cost; pay-as-you-go pricing |
| Security | Enhanced security for sensitive workloads via private cloud | Security managed by provider; may be less customizable |
| Compliance | Better suited for strict regulatory requirements | May face challenges with compliance for regulated data |
| Use Cases | Enterprises requiring data sovereignty and mixed workloads | Startups, agile applications, and variable workloads |
Introduction to Cloud Computing Models
Hybrid cloud combines private and public cloud infrastructures to optimize flexibility, security, and scalability, allowing organizations to manage sensitive data on private servers while leveraging the broad resources of public clouds. Public cloud offers on-demand access to computing resources hosted by third-party providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, delivering cost efficiency and global reach. Cloud computing models vary by deployment and service types, with hybrid cloud providing a balanced approach for businesses needing control and elasticity.
Defining Public Cloud
Public cloud refers to cloud computing services offered by third-party providers over the internet, allowing multiple users to share the same infrastructure and resources. It provides scalable, on-demand access to computing power, storage, and applications, typically billed on a pay-as-you-go basis. Leading public cloud providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
What is Hybrid Cloud?
Hybrid cloud is a computing environment that combines on-premises private cloud infrastructure with public cloud services, enabling seamless data and application portability. It offers enhanced flexibility, scalability, and control by allowing workloads to move between private and public environments based on demand and compliance requirements. Enterprises leverage hybrid cloud to optimize resource utilization, improve disaster recovery, and maintain security standards while benefiting from public cloud scalability.
Key Differences Between Hybrid and Public Cloud
Hybrid cloud integrates private and public cloud environments, enabling data and applications to be shared between them for enhanced flexibility and security. Public cloud offers scalable, on-demand resources managed by third-party providers, ideal for cost efficiency and rapid deployment. Key differences include control level, with hybrid cloud providing greater governance over sensitive data, whereas public cloud emphasizes ease of access and scalability.
Security Considerations
Hybrid cloud environments offer enhanced security by enabling organizations to keep sensitive data on private infrastructure while leveraging the scalability of public clouds for less critical workloads. Public cloud providers implement robust security measures such as encryption, identity and access management, and compliance certifications, but data exposure risks increase when transferring between clouds. Comprehensive security strategies for hybrid clouds must address data sovereignty, consistent policy enforcement, and secure integration points to minimize vulnerabilities.
Cost Comparison: Hybrid Cloud vs Public Cloud
Hybrid cloud solutions typically involve higher initial capital expenditures due to the need for on-premises infrastructure alongside cloud services, leading to increased operational complexity and management costs. Public cloud models offer lower upfront costs with a pay-as-you-go pricing structure, enabling businesses to scale resources dynamically and reduce expenses related to hardware maintenance. Cost efficiency in hybrid cloud depends on workload distribution and optimization, while public cloud provides more predictable expenses with benefits for small to medium-sized enterprises seeking flexibility.
Scalability and Performance
Hybrid cloud solutions offer enhanced scalability by combining on-premises infrastructure with public cloud resources, allowing businesses to dynamically allocate workloads based on demand. Public cloud environments provide virtually unlimited scalability and high-performance computing through globally distributed data centers and advanced network architectures. Organizations leveraging hybrid cloud can optimize performance by seamlessly balancing sensitive data processing on private servers while scaling heavy workloads in the public cloud.
Use Cases and Industry Applications
Hybrid cloud offers tailored solutions for industries requiring data security and compliance, such as healthcare and finance, by combining private and public cloud benefits for sensitive workloads and scalable resources. Public cloud suits startups and e-commerce for rapid deployment and cost-efficient scaling, leveraging services like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud to handle variable traffic and computational demands. Manufacturing and retail sectors adopt hybrid cloud for integrating IoT devices and big data analytics while maintaining on-premises control over critical operations.
Choosing the Right Cloud Solution
Selecting the right cloud solution involves assessing workload sensitivity, compliance requirements, and scalability needs. Hybrid cloud offers flexibility by integrating private infrastructure with public cloud services, ideal for businesses requiring data control and dynamic resource allocation. Public cloud provides cost-effective, scalable resources with minimal management, suited for startups and applications with variable demand patterns.
Future Trends in Cloud Adoption
Hybrid cloud adoption is rapidly increasing as organizations seek to combine the scalability of public cloud services like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud with the control and security of private cloud infrastructure. Emerging trends indicate a growing emphasis on multi-cloud strategies to optimize cost efficiency, data sovereignty, and workload distribution across diverse environments. Advances in AI-driven cloud management and edge computing integration are expected to drive more seamless orchestration and real-time analytics in hybrid cloud deployments.
Hybrid Cloud Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com