Service mesh enhances microservices architecture by managing service-to-service communication, ensuring security, observability, and reliability without altering application code. It enables seamless traffic routing, load balancing, and failure recovery to improve overall system performance and resilience. Discover how integrating a service mesh can optimize Your application infrastructure by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
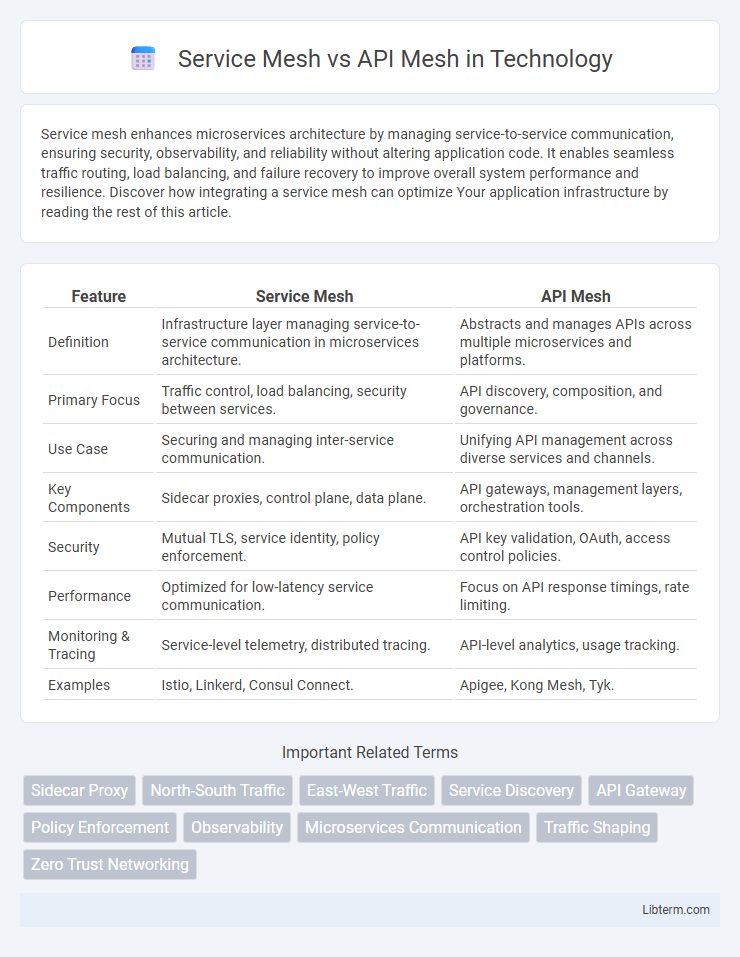
| Feature | Service Mesh | API Mesh |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Infrastructure layer managing service-to-service communication in microservices architecture. | Abstracts and manages APIs across multiple microservices and platforms. |
| Primary Focus | Traffic control, load balancing, security between services. | API discovery, composition, and governance. |
| Use Case | Securing and managing inter-service communication. | Unifying API management across diverse services and channels. |
| Key Components | Sidecar proxies, control plane, data plane. | API gateways, management layers, orchestration tools. |
| Security | Mutual TLS, service identity, policy enforcement. | API key validation, OAuth, access control policies. |
| Performance | Optimized for low-latency service communication. | Focus on API response timings, rate limiting. |
| Monitoring & Tracing | Service-level telemetry, distributed tracing. | API-level analytics, usage tracking. |
| Examples | Istio, Linkerd, Consul Connect. | Apigee, Kong Mesh, Tyk. |
Introduction to Service Mesh and API Mesh
Service Mesh is a dedicated infrastructure layer that manages service-to-service communications, providing features like traffic management, security, and observability primarily within microservices architectures. API Mesh extends this concept by focusing on the interaction and management of APIs across different services, enabling better control, monitoring, and governance of API traffic in complex distributed systems. Both technologies enhance service communication reliability but cater to different scopes--Service Mesh emphasizes internal service connectivity, while API Mesh targets API lifecycle management and integration.
Core Concepts: Understanding Service Mesh
Service Mesh is a dedicated infrastructure layer that manages service-to-service communication within microservices architectures, providing features like traffic management, security, and observability. It operates by intercepting network traffic between services through lightweight proxies, typically sidecars, enabling fine-grained control and policy enforcement without changing application code. Core concepts of Service Mesh include service discovery, load balancing, encryption, authentication, authorization, and distributed tracing to ensure reliable and secure inter-service communication.
Core Concepts: Understanding API Mesh
API Mesh centers on managing, securing, and orchestrating APIs across distributed environments by providing granular control over API traffic, analytics, and policy enforcement. Unlike Service Mesh, which handles service-to-service communication primarily at the network level, API Mesh emphasizes the lifecycle, governance, and discoverability of APIs, integrating API gateways and developer portals. Core concepts include API abstraction, versioning, and unified API management, enabling enterprises to optimize API consumption while ensuring security and compliance across hybrid and multi-cloud infrastructures.
Key Differences Between Service Mesh and API Mesh
Service Mesh primarily manages service-to-service communication within microservices architectures, providing features like traffic control, security, and observability at the network level. API Mesh extends this by focusing on API lifecycle management, including API gateway capabilities, versioning, and developer-centric controls across multiple APIs and services. Key differences include Service Mesh's emphasis on internal service communications and API Mesh's focus on external API consumption and governance.
Use Cases for Service Mesh
Service Mesh excels in managing microservices communication, providing load balancing, service discovery, and secure inter-service encryption crucial for dynamic, containerized environments. It is ideal for use cases involving complex service-to-service interactions, observability, and policy enforcement in cloud-native architectures. Organizations adopt Service Mesh to enhance resilience, streamline traffic management, and improve security in distributed applications.
Use Cases for API Mesh
API Mesh is designed to unify and manage APIs across multiple services, making it ideal for organizations with complex microservices architectures requiring streamlined API exposure and governance. It excels in use cases such as API versioning, access control, security policies enforcement, and observability across diverse API endpoints, enabling consistent and secure communication. Service Mesh primarily focuses on service-to-service communication within infrastructure, whereas API Mesh targets API lifecycle management, developer experience, and external-facing API integrations.
Architecture and Deployment Models
Service Mesh architecture centers around managing service-to-service communication within microservices environments through sidecar proxies deployed alongside application instances, providing features like traffic routing, security, and observability. API Mesh, by contrast, focuses on managing APIs at a broader scope, often incorporating centralized API gateways and control planes that facilitate unified policy enforcement, traffic management, and monitoring across diverse API endpoints. Deployment models for Service Mesh typically involve distributed sidecars operating within Kubernetes clusters, while API Mesh solutions often employ hybrid architectures combining cloud-native gateways with edge or centralized control layers for enhanced API lifecycle management.
Performance and Scalability Comparison
Service mesh enhances microservices communication by providing efficient load balancing, traffic management, and observability, resulting in optimized performance under high traffic conditions. API mesh focuses on API gateway functionalities with centralized policy enforcement and API lifecycle management, which may introduce additional latency but simplifies scalability across multiple API endpoints. In scalability terms, service mesh architectures better handle dynamic service discovery and fault tolerance, while API mesh excels in managing complex API ecosystems with consistent security and access control policies.
Security Features: Service Mesh vs API Mesh
Service Mesh provides robust security features such as mutual TLS for encrypted service-to-service communication, fine-grained access control, and traffic encryption to protect microservices within a cluster. API Mesh enhances these capabilities by securing API endpoints with advanced authentication, authorization, and threat detection specifically designed for API traffic management. Both emphasize zero-trust security principles, but API Mesh is optimized for handling complex API interactions and securing external-facing APIs beyond internal service communication.
Choosing the Right Mesh for Your Organization
Service Mesh provides robust microservice-to-microservice communication, essential for managing traffic, security, and observability within distributed applications. API Mesh extends this capability by focusing on secure, policy-driven API interactions across multiple environments, optimizing API lifecycle management and developer productivity. Choosing the right mesh depends on organizational goals: prioritize Service Mesh for internal microservices management and API Mesh for comprehensive API control across heterogeneous systems.
Service Mesh Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com