Version control enables efficient management of code changes, ensuring that every modification is tracked and reversible, which enhances collaboration and minimizes errors. It supports multiple contributors by keeping a detailed history of updates and facilitating conflict resolution during simultaneous edits. Explore this article to understand how version control can streamline your development workflow and safeguard your projects.
Table of Comparison
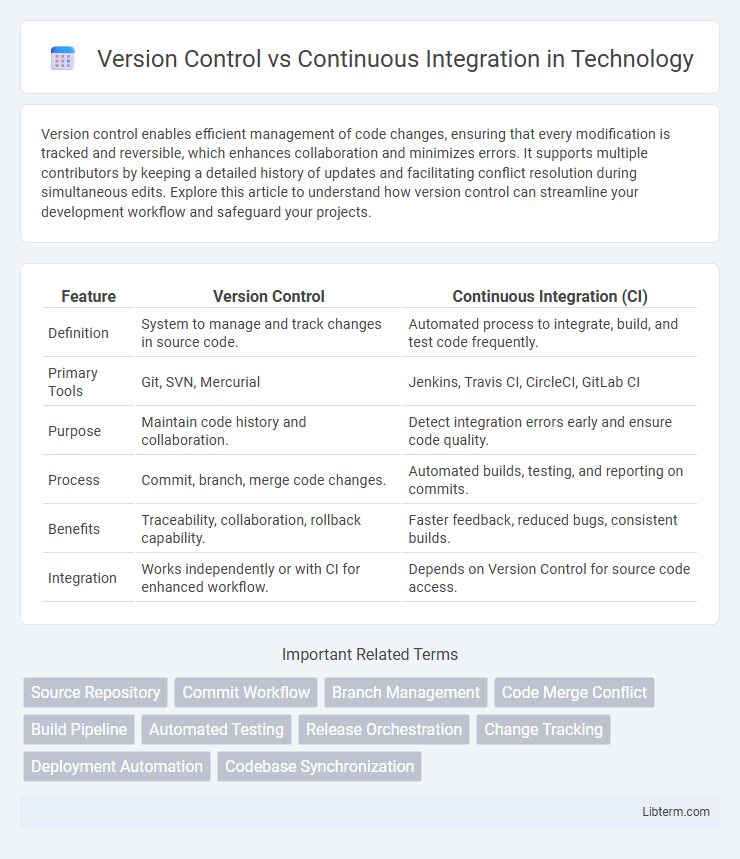
| Feature | Version Control | Continuous Integration (CI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | System to manage and track changes in source code. | Automated process to integrate, build, and test code frequently. |
| Primary Tools | Git, SVN, Mercurial | Jenkins, Travis CI, CircleCI, GitLab CI |
| Purpose | Maintain code history and collaboration. | Detect integration errors early and ensure code quality. |
| Process | Commit, branch, merge code changes. | Automated builds, testing, and reporting on commits. |
| Benefits | Traceability, collaboration, rollback capability. | Faster feedback, reduced bugs, consistent builds. |
| Integration | Works independently or with CI for enhanced workflow. | Depends on Version Control for source code access. |
Introduction to Version Control and Continuous Integration
Version control systems like Git track and manage changes to source code, enabling collaboration and maintaining a history of project development. Continuous Integration (CI) automates the process of merging code changes, running tests, and deploying builds to ensure software quality and faster delivery. Integrating version control with CI tools such as Jenkins or GitLab CI streamlines development workflows and reduces integration issues.
Key Differences Between Version Control and Continuous Integration
Version control systems manage and track changes in source code, enabling collaboration and historical record-keeping of software development. Continuous integration automates the merging of code changes and runs automated tests to ensure software functionality and quality after every integration. Key differences include version control focusing on code management while continuous integration emphasizes automated testing and build processes to detect errors early in the development cycle.
Importance of Version Control in Modern Software Development
Version control is essential in modern software development as it enables developers to track changes, collaborate effectively, and maintain a comprehensive history of code revisions. It supports branching and merging techniques that facilitate parallel development and reduce conflicts, enhancing overall productivity. Integrating version control with continuous integration systems ensures automated testing and deployment, improving software quality and delivery speed.
Role of Continuous Integration in Agile Workflows
Continuous Integration (CI) plays a critical role in Agile workflows by automating the process of integrating code changes frequently, which ensures early detection of defects and reduces integration risks. Unlike Version Control systems that manage and track changes to source code, CI platforms build, test, and validate code continuously, enabling faster feedback and higher code quality. This seamless integration accelerates Agile iterations, facilitates collaboration, and supports rapid delivery cycles in software development projects.
How Version Control Systems Work
Version Control Systems (VCS) manage changes to source code by tracking modifications, enabling multiple developers to collaborate efficiently. They store code in repositories, allowing users to commit changes, create branches for parallel development, and merge updates to integrate features or fixes. VCS like Git provide detailed history logs and conflict resolution tools that streamline collaboration and maintain code integrity throughout the software lifecycle.
Core Benefits of Continuous Integration
Continuous Integration (CI) automates the merging and testing of code changes, significantly reducing integration issues and accelerating development cycles. It ensures early detection of defects through frequent automated builds and tests, enhancing software quality and stability. CI supports rapid feedback and collaboration among development teams, leading to more reliable and consistent code delivery compared to traditional Version Control systems alone.
Popular Tools for Version Control and Continuous Integration
Git remains the most popular version control system, widely adopted for its distributed architecture and robust branching capabilities, with platforms like GitHub and GitLab enhancing collaboration. For continuous integration, Jenkins leads due to its extensive plugin ecosystem, while CircleCI and Travis CI offer cloud-based solutions that streamline automated testing and deployment pipelines. Integrating Git repositories with CI tools like Jenkins or GitLab CI/CD ensures seamless code versioning and automated build processes, accelerating software delivery cycles.
Integrating Version Control with CI Pipelines
Integrating version control systems like Git with continuous integration (CI) pipelines enables automated build and test processes triggered by code changes, improving development efficiency and code quality. By linking commits and branches to CI tools such as Jenkins or GitLab CI, teams can ensure consistent code validation and faster detection of integration issues. This seamless integration supports collaborative workflows and accelerates release cycles by maintaining a robust, up-to-date codebase.
Common Challenges and Best Practices
Version control and continuous integration often face challenges such as merge conflicts, inconsistent testing environments, and inadequate integration frequency. Best practices include frequent commits with descriptive messages, automated testing pipelines, and maintaining a shared repository to ensure code consistency. Implementing branch strategies like GitFlow and regularly reviewing integration logs helps mitigate risks and maintain code quality.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Team
Selecting the right approach between version control and continuous integration depends on your team's collaboration needs and development workflow. Version control systems like Git provide robust code management and history tracking, essential for coordinated teamwork. Continuous integration tools automate testing and merging processes, enhancing code quality and deployment speed, making them ideal for teams pursuing agile and DevOps practices.
Version Control Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com