Platform as a Service (PaaS) offers a cloud-based environment where developers can build, deploy, and manage applications without worrying about underlying infrastructure. It streamlines software development by providing pre-configured tools and scalability options that enhance productivity and reduce time to market. Explore the rest of the article to discover how PaaS can transform Your development workflow and accelerate innovation.
Table of Comparison
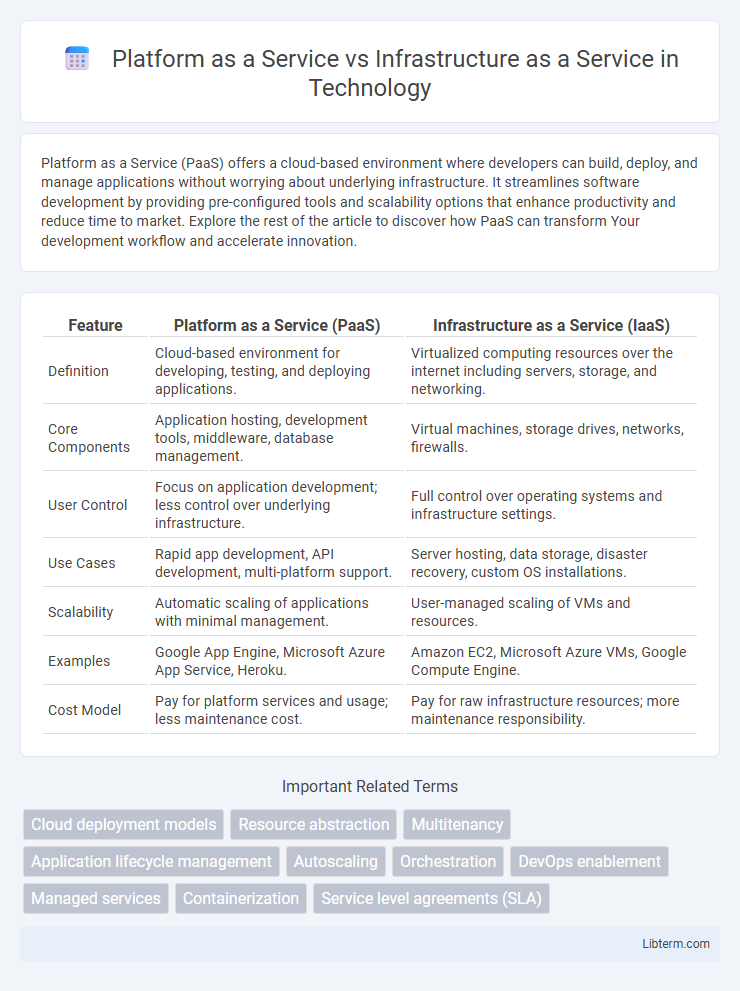
| Feature | Platform as a Service (PaaS) | Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cloud-based environment for developing, testing, and deploying applications. | Virtualized computing resources over the internet including servers, storage, and networking. |
| Core Components | Application hosting, development tools, middleware, database management. | Virtual machines, storage drives, networks, firewalls. |
| User Control | Focus on application development; less control over underlying infrastructure. | Full control over operating systems and infrastructure settings. |
| Use Cases | Rapid app development, API development, multi-platform support. | Server hosting, data storage, disaster recovery, custom OS installations. |
| Scalability | Automatic scaling of applications with minimal management. | User-managed scaling of VMs and resources. |
| Examples | Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure App Service, Heroku. | Amazon EC2, Microsoft Azure VMs, Google Compute Engine. |
| Cost Model | Pay for platform services and usage; less maintenance cost. | Pay for raw infrastructure resources; more maintenance responsibility. |
Introduction to Cloud Computing Models
Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) represent core cloud computing models offering distinct levels of abstraction and control. IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, enabling users to manage servers, storage, and networking while retaining middleware and applications control. PaaS delivers a fully managed environment for application development and deployment, abstracting infrastructure management to enhance developer productivity and scalability.
Defining Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Platform as a Service (PaaS) provides a comprehensive cloud environment allowing developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without handling underlying infrastructure components like servers or storage. PaaS delivers pre-configured development tools, middleware, and runtime environments, accelerating software development and enabling seamless collaboration. Unlike Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), which offers raw computing resources, PaaS abstracts hardware and operating systems, emphasizing application lifecycle management.
Explaining Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) delivers virtualized computing resources over the internet, including servers, storage, and networking. IaaS enables businesses to scale infrastructure on-demand without investing in physical hardware, providing flexibility and cost efficiency. Key providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform offer extensive IaaS solutions with features such as automated backups, load balancing, and customizable configurations.
Key Differences Between PaaS and IaaS
Platform as a Service (PaaS) offers a managed environment for application development, providing tools, middleware, and runtime without the need to manage underlying infrastructure. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) delivers virtualized computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking, allowing users to configure and control operating systems and applications. The key difference lies in PaaS abstracting infrastructure management to focus on development, while IaaS offers granular control over infrastructure components for maximum flexibility.
Use Cases for Platform as a Service
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is ideal for developers focusing on application development, testing, and deployment without managing underlying infrastructure, enabling rapid innovation and scalability. Use cases include building custom web and mobile applications, integrating APIs, and managing databases within a controlled environment that supports continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines. In contrast, Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) offers virtualized computing resources, suitable for organizations needing complete control over hardware and software stacks for workloads like hosting websites or running enterprise applications.
Use Cases for Infrastructure as a Service
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides scalable virtualized computing resources over the internet, making it ideal for businesses needing flexible server capacity, storage, and networking without the overhead of physical hardware management. Common use cases include disaster recovery solutions, where rapid resource allocation is critical, and hosting high-traffic websites or applications requiring dynamic scalability. Enterprises also leverage IaaS for developing and testing new applications in virtual environments, streamlining deployment while controlling costs.
Pros and Cons of PaaS
Platform as a Service (PaaS) offers streamlined application development with built-in tools, automated scaling, and reduced management overhead, enabling faster deployment of software solutions. However, PaaS can present limitations such as reduced customization, potential vendor lock-in, and dependency on the provider's uptime and security protocols. Compared to Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), which provides flexible control over virtualized computing resources, PaaS prioritizes ease of use and developer productivity over granular infrastructure management.
Pros and Cons of IaaS
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) offers scalable computing resources such as virtual machines, storage, and networking, providing businesses with flexible control over their IT infrastructure without the need to manage physical hardware. Pros of IaaS include rapid scalability, cost-effectiveness through pay-as-you-go pricing models, and greater customization for specific application needs. Cons involve potential security vulnerabilities requiring robust management, dependency on internet connectivity, and the complexity of maintaining and configuring virtual infrastructure compared to the more abstracted Platform as a Service (PaaS) model.
Choosing the Right Model: PaaS vs IaaS
Choosing between Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) depends on the level of control and management required; PaaS offers a complete development environment with managed infrastructure ideal for rapid application development and deployment, while IaaS provides raw computing resources allowing more customization and control over virtual machines, storage, and networking. Organizations prioritizing speed, scalability, and reduced operational burden often prefer PaaS, whereas those needing granular resource configuration and flexible infrastructure management lean towards IaaS. Evaluating specific business needs, technical expertise, and the desired degree of infrastructure maintenance is essential for selecting the optimal cloud service model.
Future Trends in Cloud Service Models
Future trends in cloud service models emphasize greater integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities within Platform as a Service (PaaS), enabling developers to build smarter, more adaptive applications with streamlined workflows. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is evolving toward enhanced automation and scalability, leveraging edge computing and hybrid cloud architectures to support latency-sensitive applications and multi-cloud strategies. Both models are expected to adopt advanced security features like zero-trust frameworks and confidential computing to address growing concerns around data privacy and compliance.
Platform as a Service Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com