Protocol Buffer offers a compact, efficient binary format for data serialization, enabling faster transmission and reduced storage compared to JSON's text-based structure. JSON remains widely used for its simplicity and readability, making it ideal for web APIs and human-readable configurations. Explore the full article to understand which format best suits your application's needs.
Table of Comparison
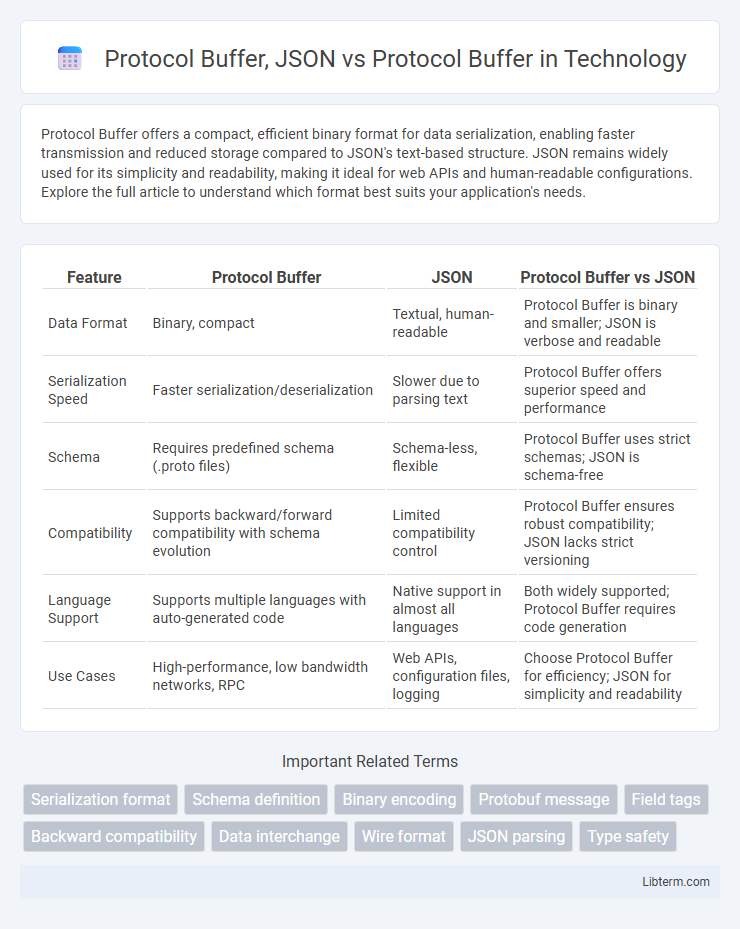
| Feature | Protocol Buffer | JSON | Protocol Buffer vs JSON |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Format | Binary, compact | Textual, human-readable | Protocol Buffer is binary and smaller; JSON is verbose and readable |
| Serialization Speed | Faster serialization/deserialization | Slower due to parsing text | Protocol Buffer offers superior speed and performance |
| Schema | Requires predefined schema (.proto files) | Schema-less, flexible | Protocol Buffer uses strict schemas; JSON is schema-free |
| Compatibility | Supports backward/forward compatibility with schema evolution | Limited compatibility control | Protocol Buffer ensures robust compatibility; JSON lacks strict versioning |
| Language Support | Supports multiple languages with auto-generated code | Native support in almost all languages | Both widely supported; Protocol Buffer requires code generation |
| Use Cases | High-performance, low bandwidth networks, RPC | Web APIs, configuration files, logging | Choose Protocol Buffer for efficiency; JSON for simplicity and readability |
Introduction to Data Serialization
Protocol Buffer is a language-neutral, platform-neutral data serialization format developed by Google, designed for efficient and compact encoding of structured data. Compared to JSON, Protocol Buffers offer faster serialization and deserialization speeds with smaller message sizes due to their binary format, which reduces bandwidth and storage requirements. JSON is human-readable and widely supported, making it ideal for simple data interchange, whereas Protocol Buffers excel in performance-critical applications requiring schema enforcement and backward compatibility.
Understanding Protocol Buffers
Protocol Buffers (Protobuf) offer a compact and efficient serialization format compared to JSON, enabling faster data transmission and reduced message size. Unlike JSON's text-based structure, Protobuf uses a binary format that requires predefined schemas for data serialization, ensuring strict type safety and compatibility across different languages. Understanding Protocol Buffers involves mastering schema definition using .proto files and leveraging generated code for optimized, cross-platform data exchange in distributed systems.
What is JSON?
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data interchange format widely used for its simplicity and human readability in transmitting structured data between a server and web applications. Unlike Protocol Buffer, which is a compact binary serialization format designed for efficient data encoding, JSON uses a text-based format with key-value pairs making it easy to read and debug but less efficient in terms of size and parsing speed. JSON's compatibility with most programming languages and its support for nested data structures make it a popular choice for APIs and configuration files.
Key Differences Between Protocol Buffers and JSON
Protocol Buffers use a compact binary format, resulting in faster serialization and smaller message sizes compared to JSON's text-based format. Protocol Buffers require a predefined schema (.proto files) for data structure enforcement, whereas JSON is schema-less and more flexible but less efficient. Protocol Buffers excel in performance-critical applications, transmitting structured data with strong typing, while JSON favors readability and ease of use in web APIs.
Performance Comparison: Protocol Buffers vs JSON
Protocol Buffers outperform JSON in both serialization speed and data size efficiency, making them ideal for performance-critical applications. Protocol Buffers encode data into a compact binary format, significantly reducing payload size and improving transmission speed compared to JSON's verbose text-based structure. Benchmark tests show Protocol Buffers can serialize and deserialize data up to 10 times faster than JSON while consuming less bandwidth and processing power.
Data Size and Efficiency
Protocol Buffer offers significantly smaller data sizes compared to JSON, making it highly efficient for data serialization and transmission in bandwidth-constrained environments. Unlike JSON's text-based format, Protocol Buffer uses a compact binary encoding that reduces payload size and accelerates parsing speed. This efficiency is critical for applications requiring fast, low-latency communication and optimized storage usage.
Schema and Type Safety
Protocol Buffers offer strict schema enforcement, ensuring type safety through predefined message structures compiled into efficient binary formats. JSON lacks a formal schema, making it flexible but prone to runtime type errors and inconsistencies in data representation. The strong typing and schema validation of Protocol Buffers enable more reliable data serialization and deserialization compared to JSON's text-based, schema-less approach.
Language and Platform Support
Protocol Buffer offers extensive language and platform support including C++, Java, Python, Go, and many others, enabling seamless integration across diverse development environments. JSON is universally supported by virtually all programming languages and platforms, making it highly accessible for web development and data interchange. Protocol Buffer's compact binary format and strong schema ensure efficient serialization, while JSON's text-based format provides ease of use and human readability.
Use Cases: When to Choose Protocol Buffers Over JSON
Protocol Buffers excel in use cases requiring efficient serialization, compact data representation, and high-speed communication, making them ideal for microservices, mobile applications, and large-scale data storage. JSON is preferred for human-readable data interchange, easy debugging, and web APIs, but Protocol Buffers outperform JSON in scenarios demanding lower bandwidth and faster parsing in distributed systems or IoT devices. Choose Protocol Buffers when performance, schema evolution, and backward compatibility are critical, especially in environments with constrained resources or complex data structures.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Data Serialization Format
Protocol Buffer offers significantly faster serialization and smaller message size compared to JSON, making it ideal for high-performance applications and environments with limited bandwidth or storage. JSON provides better human readability and ease of use, which is advantageous for web services and scenarios requiring quick debugging or direct data inspection. Choosing the right data serialization format depends on the trade-off between performance efficiency with Protocol Buffer and the flexibility and accessibility of JSON.
Protocol Buffer, JSON Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com