Manual deployment allows precise control over the release process, enabling you to manage updates and configuration changes directly on each server or environment. This approach is essential for small-scale projects or when automated systems are unavailable, providing flexibility and minimizing risks with hands-on intervention. Explore the full article to understand best practices and optimize your manual deployment strategy effectively.
Table of Comparison
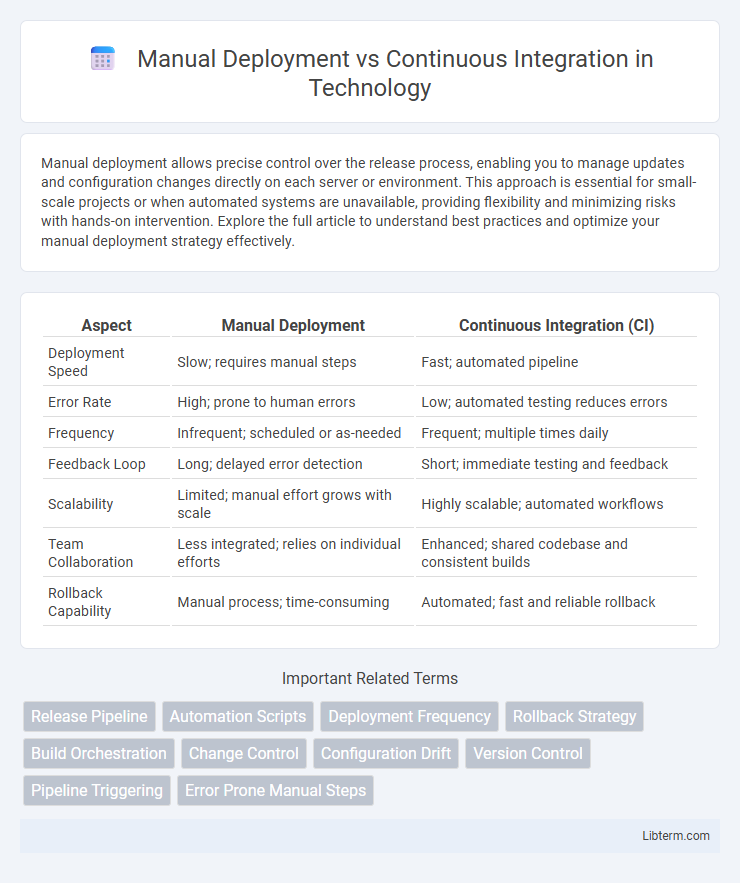
| Aspect | Manual Deployment | Continuous Integration (CI) |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment Speed | Slow; requires manual steps | Fast; automated pipeline |
| Error Rate | High; prone to human errors | Low; automated testing reduces errors |
| Frequency | Infrequent; scheduled or as-needed | Frequent; multiple times daily |
| Feedback Loop | Long; delayed error detection | Short; immediate testing and feedback |
| Scalability | Limited; manual effort grows with scale | Highly scalable; automated workflows |
| Team Collaboration | Less integrated; relies on individual efforts | Enhanced; shared codebase and consistent builds |
| Rollback Capability | Manual process; time-consuming | Automated; fast and reliable rollback |
Introduction to Deployment Strategies
Manual deployment involves directly transferring code to production environments, often relying on developer intervention and specific timing, leading to potential human errors and slower release cycles. Continuous Integration (CI) automates the building, testing, and merging of code changes, ensuring faster and more reliable deployment processes through automated validation. Deployment strategies leveraging CI enable consistent software delivery, reduce integration conflicts, and enhance overall development team productivity.
Understanding Manual Deployment
Manual deployment involves directly transferring application files and configurations from a developer's local environment to production servers without automation tools. This process can increase the risk of human errors, inconsistencies, and longer deployment times compared to continuous integration systems. Understanding manual deployment is essential for appreciating its limitations and the benefits offered by automated CI/CD pipelines.
What is Continuous Integration?
Continuous Integration (CI) is a software development practice where developers frequently merge their code changes into a shared repository, triggering automated builds and tests to detect integration issues early. This process enhances code quality by identifying bugs and conflicts quickly, reducing the risk of integration problems during deployment. CI tools like Jenkins, Travis CI, and CircleCI streamline this workflow, enabling faster and more reliable software delivery compared to manual deployment methods.
Key Differences Between Manual Deployment and CI
Manual deployment involves manually transferring code to production environments, often resulting in slower release cycles and higher risk of human error. Continuous Integration (CI) automates code integration and testing, ensuring frequent, reliable updates and faster detection of issues. Key differences include automation level, speed of deployment, and consistency in error handling and testing processes.
Pros and Cons of Manual Deployment
Manual deployment offers greater control and flexibility, allowing developers to tailor each step to specific needs and address unique environment issues in real time. However, it is prone to human error, time-consuming, and less efficient than automated methods, potentially leading to inconsistent deployments and delayed releases. The lack of automation also hinders scalability and continuous feedback, making it challenging to maintain frequent updates in fast-paced development environments.
Advantages of Continuous Integration
Continuous Integration (CI) significantly enhances development workflows by automatically integrating code changes, reducing integration conflicts, and enabling faster issue detection compared to manual deployment. CI pipelines improve software quality through automated testing and consistent builds, resulting in more reliable and stable releases. This approach accelerates delivery timelines and supports continuous feedback, fostering better collaboration among development teams.
Common Challenges in Manual Deployment
Manual deployment often faces challenges such as human error, which can lead to inconsistent environments and unpredictable outcomes. The process typically consumes significant time and resources due to repetitive tasks and lack of automation. Maintaining clear documentation and coordination among teams is difficult, increasing the risk of deployment failures and delayed releases.
How Continuous Integration Enhances Workflow
Continuous Integration (CI) significantly enhances workflow by automating the build, test, and deployment processes, reducing manual errors commonly associated with manual deployment. By integrating code changes frequently and validating them through automated tests, CI accelerates feedback loops, enabling faster detection and resolution of issues. This automated approach improves collaboration among development teams, streamlines code integration, and ensures higher software quality and delivery speed.
Choosing the Right Deployment Strategy
Selecting the right deployment strategy depends on project size, team expertise, and release frequency. Manual deployment offers control and flexibility for small projects with infrequent updates but risks human error and slower delivery cycles. Continuous Integration streamlines code integration, automates testing, and accelerates deployment, making it ideal for agile teams requiring rapid, reliable releases.
Future Trends in Deployment Practices
Future trends in deployment practices emphasize the shift from manual deployment to continuous integration (CI) due to increasing demand for automation, speed, and reliability. Continuous integration platforms like Jenkins, GitLab CI, and CircleCI enable frequent code integration and automated testing, significantly reducing human error and deployment time. Emerging technologies such as AI-driven deployment automation and serverless architecture are expected to further transform deployment workflows by enhancing scalability and predictive error detection.
Manual Deployment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com