Multi-cloud deployment enables organizations to leverage multiple cloud service providers, maximizing flexibility, performance, and cost-efficiency by distributing workloads across platforms. This approach enhances redundancy and minimizes the risk of vendor lock-in, ensuring better disaster recovery and optimized resource allocation. Discover how your business can benefit from a tailored multi-cloud strategy by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
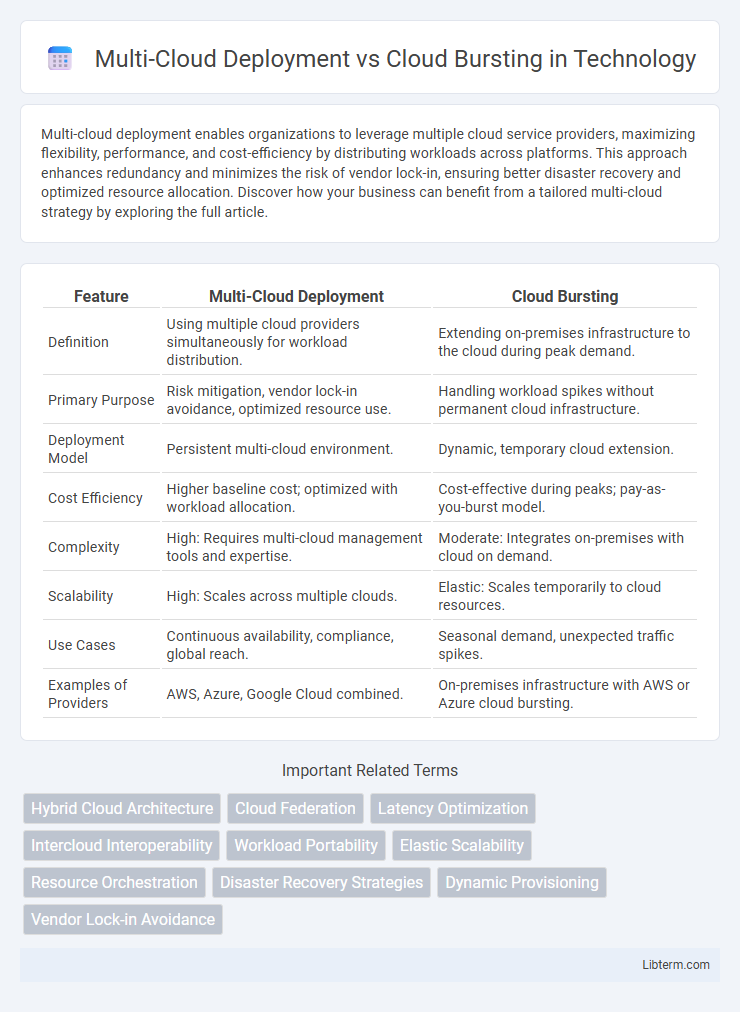
| Feature | Multi-Cloud Deployment | Cloud Bursting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Using multiple cloud providers simultaneously for workload distribution. | Extending on-premises infrastructure to the cloud during peak demand. |
| Primary Purpose | Risk mitigation, vendor lock-in avoidance, optimized resource use. | Handling workload spikes without permanent cloud infrastructure. |
| Deployment Model | Persistent multi-cloud environment. | Dynamic, temporary cloud extension. |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher baseline cost; optimized with workload allocation. | Cost-effective during peaks; pay-as-you-burst model. |
| Complexity | High: Requires multi-cloud management tools and expertise. | Moderate: Integrates on-premises with cloud on demand. |
| Scalability | High: Scales across multiple clouds. | Elastic: Scales temporarily to cloud resources. |
| Use Cases | Continuous availability, compliance, global reach. | Seasonal demand, unexpected traffic spikes. |
| Examples of Providers | AWS, Azure, Google Cloud combined. | On-premises infrastructure with AWS or Azure cloud bursting. |
Introduction to Multi-Cloud Deployment and Cloud Bursting
Multi-cloud deployment refers to the strategic use of multiple cloud service providers to optimize performance, enhance redundancy, and avoid vendor lock-in. Cloud bursting is a dynamic scaling technique where an application's workload extends from a private cloud to a public cloud during peak demand to maintain performance and cost-efficiency. Both approaches leverage different clouds to improve resource utilization and flexibility in cloud infrastructure management.
Defining Multi-Cloud Deployment
Multi-cloud deployment involves distributing applications and workloads across multiple cloud service providers simultaneously to enhance redundancy, optimize performance, and avoid vendor lock-in. This strategy leverages the unique strengths and pricing models of different clouds, ensuring high availability and flexibility. Unlike cloud bursting, which temporarily offloads traffic to a public cloud during spikes, multi-cloud deployment maintains a persistent presence across several clouds for strategic operational advantages.
Understanding Cloud Bursting
Cloud bursting enables organizations to handle sudden spikes in workload by dynamically extending their private cloud capacity to a public cloud, ensuring seamless scalability and cost efficiency. Unlike multi-cloud deployment, which involves distributing workloads across multiple cloud providers for resilience or optimization, cloud bursting specifically acts as a failover mechanism during peak demand. This approach optimizes resource utilization and minimizes latency by maintaining baseline operations in a private cloud while leveraging public cloud resources only when necessary.
Key Differences Between Multi-Cloud Deployment and Cloud Bursting
Multi-cloud deployment involves using multiple cloud service providers simultaneously to distribute workloads and improve redundancy, while cloud bursting allows an application to run in a private cloud or data center and burst into a public cloud during peak demand. Multi-cloud strategies optimize cost, risk management, and vendor flexibility by leveraging diverse platforms, whereas cloud bursting primarily focuses on scaling resources dynamically to handle traffic spikes. Key differences include multi-cloud's permanent utilization of multiple clouds for varied purposes versus cloud bursting's temporary, event-driven expansion of resources based on demand.
Benefits of Multi-Cloud Deployment
Multi-cloud deployment enhances resilience by distributing workloads across multiple cloud providers, reducing dependency on a single vendor and mitigating risks like outages or data loss. It optimizes performance and cost-efficiency by enabling businesses to select the best services and pricing from different clouds tailored to specific workload requirements. This strategy also improves compliance and data sovereignty by leveraging regional data centers aligned with regulatory mandates.
Advantages of Cloud Bursting Strategies
Cloud bursting strategies enable businesses to handle peak workloads efficiently by dynamically extending applications from private to public clouds, ensuring optimal resource utilization without over-provisioning. This approach reduces costs by leveraging elastic cloud resources only when necessary, providing scalability and flexibility. Cloud bursting also enhances disaster recovery and performance by distributing workloads across multiple environments based on demand.
Common Use Cases for Multi-Cloud Architectures
Multi-cloud deployment is commonly used for workload distribution across multiple cloud providers to enhance redundancy and avoid vendor lock-in, supporting applications such as global content delivery and disaster recovery. It enables organizations to leverage specialized services from different clouds, optimizing performance for data analytics, machine learning, and enterprise resource planning systems. In contrast, cloud bursting is primarily employed for handling peak workloads by extending on-premises data center capacity to a public cloud for temporary scalability during high-demand periods.
Typical Scenarios for Cloud Bursting Adoption
Cloud bursting is typically adopted in scenarios with highly variable workloads, such as e-commerce platforms facing seasonal traffic spikes or research institutions conducting intensive, time-sensitive data analysis. Businesses use cloud bursting to maintain on-premises infrastructure for base workloads while dynamically extending capacity to public clouds during peak demand, optimizing cost and performance. This approach prevents over-provisioning, allowing seamless handling of unpredictable surges without permanent investment in additional local resources.
Challenges and Risks: Multi-Cloud vs Cloud Bursting
Multi-cloud deployment faces challenges such as increased complexity in managing multiple platforms, potential data consistency issues, and higher operational costs due to disparate cloud environments. Cloud bursting introduces risks including latency problems, security vulnerabilities during workload transfers, and dependency on seamless integration between private and public clouds. Ensuring reliable performance and robust security remains critical for both strategies, requiring sophisticated monitoring and management tools.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Your Business
Multi-cloud deployment involves using multiple cloud providers simultaneously to optimize performance, avoid vendor lock-in, and enhance redundancy, making it suitable for businesses requiring diverse workloads and high availability. Cloud bursting enables on-premises or private cloud infrastructures to overflow into public clouds during peak demand, offering cost-effective scalability for variable workloads with unpredictable spikes. Selecting the right strategy depends on your business needs for flexibility, workload patterns, budget constraints, and long-term IT goals.
Multi-Cloud Deployment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com