Virtual machines provide an efficient solution for running multiple operating systems simultaneously on a single physical device, enhancing resource utilization and flexibility. They isolate environments, increasing security and simplifying software testing and development. Explore the full article to understand how virtual machines can optimize your computing needs.
Table of Comparison
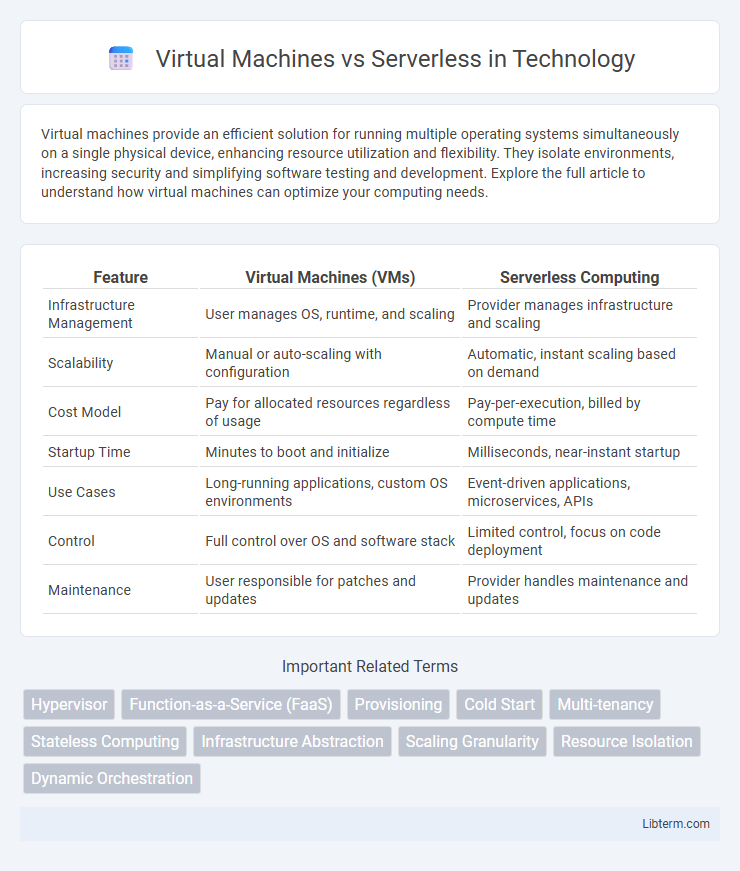
| Feature | Virtual Machines (VMs) | Serverless Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure Management | User manages OS, runtime, and scaling | Provider manages infrastructure and scaling |
| Scalability | Manual or auto-scaling with configuration | Automatic, instant scaling based on demand |
| Cost Model | Pay for allocated resources regardless of usage | Pay-per-execution, billed by compute time |
| Startup Time | Minutes to boot and initialize | Milliseconds, near-instant startup |
| Use Cases | Long-running applications, custom OS environments | Event-driven applications, microservices, APIs |
| Control | Full control over OS and software stack | Limited control, focus on code deployment |
| Maintenance | User responsible for patches and updates | Provider handles maintenance and updates |
Introduction to Virtual Machines and Serverless
Virtual Machines (VMs) provide isolated environments by virtualizing physical hardware, allowing multiple operating systems to run concurrently on a single physical server. Serverless computing abstracts server management entirely, enabling developers to deploy and execute code without provisioning or maintaining infrastructure. Understanding the differences between VMs and serverless models is crucial for optimizing resource utilization, scalability, and cost-efficiency in cloud computing environments.
Core Concepts: Virtual Machines Explained
Virtual Machines (VMs) operate by emulating hardware through a hypervisor, allowing multiple OS instances to run on a single physical server, providing isolation and dedicated resources. Each VM contains a full guest operating system, which consumes more memory and CPU compared to serverless architectures that execute code without managing underlying infrastructure. VMs excel in scenarios requiring consistent environment control, long-running processes, and applications dependent on specific OS configurations.
What is Serverless Computing?
Serverless computing enables developers to build and run applications without managing underlying infrastructure, automatically handling server provisioning, scaling, and maintenance. Unlike virtual machines that require manual configuration and resource allocation, serverless platforms use event-driven execution and charge based on actual usage, optimizing cost efficiency. Key providers of serverless services include AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, and Google Cloud Functions, which support rapid development and deployment of scalable applications.
Architecture Comparison: VM vs Serverless
Virtual Machines (VMs) provide a full operating system environment with dedicated resources, enabling complete control over the infrastructure and hosting multiple applications on a single physical server. Serverless architecture abstracts server management entirely, automatically scaling functions in response to demand and billing only for execution time, which optimizes resource utilization. Unlike VMs, serverless eliminates the need for provisioning and maintaining servers, offering event-driven execution without fixed infrastructure costs.
Cost Efficiency: Pay-as-You-Go vs Reserved Resources
Virtual machines involve reserved resources with fixed costs regardless of utilization, often leading to higher expenses during low traffic periods. Serverless platforms offer a pay-as-you-go pricing model, charging only for actual compute time and resource consumption, optimizing cost efficiency for variable workloads. This dynamic pricing minimizes idle resource costs and scales automatically to match demand, making serverless more cost-effective for unpredictable or intermittent applications.
Scalability and Resource Management
Virtual Machines offer dedicated resources and predictable performance but require manual scaling and resource allocation, which can lead to inefficiencies during variable workloads. Serverless architectures automatically scale functions based on demand, optimizing resource usage and reducing operational overhead, ideal for dynamic, unpredictable traffic patterns. The choice hinges on workload consistency and control needs, with serverless excelling in rapid scalability and cost-effective resource management.
Performance and Latency Considerations
Virtual Machines (VMs) provide dedicated resources with consistent performance, making them suitable for applications demanding predictable latency and high processing power. Serverless architectures offer scalable event-driven execution but can introduce cold start latency, impacting real-time responsiveness. Selecting between VMs and serverless hinges on balancing workload performance requirements against the acceptable latency tolerance in the deployment environment.
Security Differences: VM vs Serverless
Virtual Machines provide isolated environments with dedicated operating systems, enabling granular control over security patches and configurations, which reduces attack surfaces through strong VM-level isolation. Serverless architectures depend on cloud providers to handle security, offering automatic updates and patch management but introducing risks like shared resource vulnerabilities and less control over the underlying runtime. Security in VMs centers on managing the guest OS and hypervisor, whereas serverless security emphasizes code-level protection and dependency management within ephemeral compute containers.
Use Cases: When to Choose VMs or Serverless
Virtual Machines (VMs) are ideal for workloads requiring full control over the operating system, such as legacy applications, complex enterprise software, or custom computing environments that need consistent performance and predictable resource allocation. Serverless computing excels in event-driven architectures, microservices, and applications with variable or unpredictable workloads, offering automatic scaling and reduced infrastructure management. Choose VMs for long-running, stateful applications or when compliance and security policies mandate dedicated environments, while serverless suits rapid development cycles, cost-efficiency for intermittent tasks, and scalable APIs.
Future Trends in Cloud Computing
Future trends in cloud computing indicate a gradual shift from traditional virtual machines towards serverless architectures due to enhanced scalability, cost-efficiency, and reduced operational overhead. Serverless computing leverages function-as-a-service (FaaS) models to enable rapid deployment and execution of code without managing underlying infrastructure, driving innovation in event-driven applications and microservices. Advances in edge computing and AI integration are further pushing the adoption of serverless platforms, optimizing resource utilization and accelerating application responsiveness across distributed environments.
Virtual Machines Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com