Real-time processing enables immediate data analysis and response, crucial for applications requiring instant decision-making such as financial trading, autonomous vehicles, and live monitoring systems. This technology minimizes latency by processing information as it is received, ensuring timely actions and enhancing operational efficiency. Explore the rest of the article to understand how real-time processing can revolutionize your workflows and improve performance.
Table of Comparison
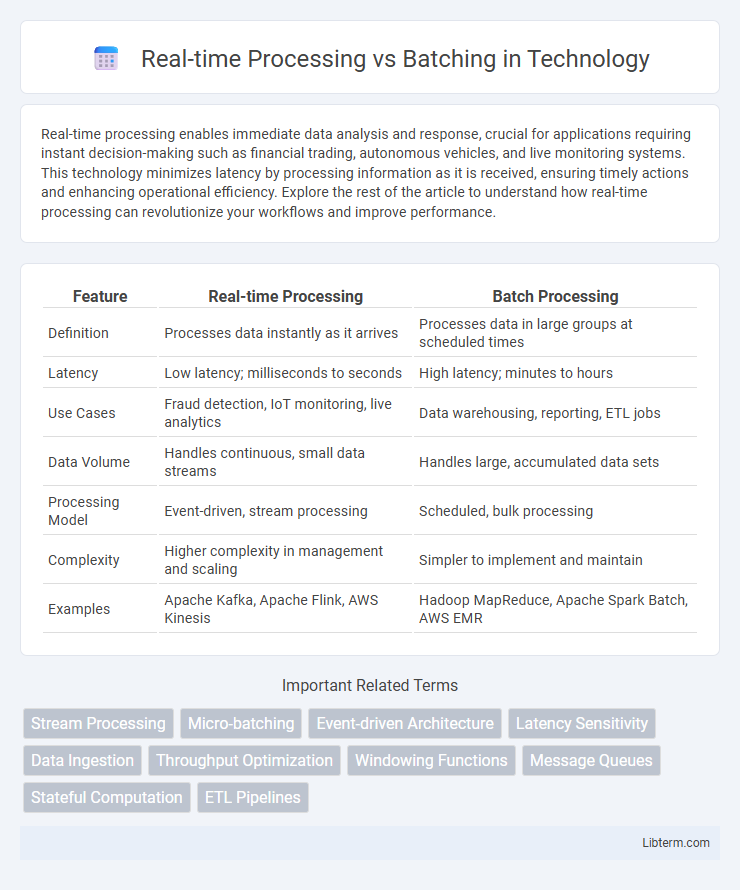
| Feature | Real-time Processing | Batch Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Processes data instantly as it arrives | Processes data in large groups at scheduled times |
| Latency | Low latency; milliseconds to seconds | High latency; minutes to hours |
| Use Cases | Fraud detection, IoT monitoring, live analytics | Data warehousing, reporting, ETL jobs |
| Data Volume | Handles continuous, small data streams | Handles large, accumulated data sets |
| Processing Model | Event-driven, stream processing | Scheduled, bulk processing |
| Complexity | Higher complexity in management and scaling | Simpler to implement and maintain |
| Examples | Apache Kafka, Apache Flink, AWS Kinesis | Hadoop MapReduce, Apache Spark Batch, AWS EMR |
Introduction to Real-time Processing and Batching
Real-time processing involves the continuous input, processing, and output of data with minimal latency, enabling immediate decision-making and responsiveness. Batching processes large volumes of data collected over a period, executing computations in scheduled intervals to optimize resource usage and throughput. The choice between real-time processing and batching depends on application requirements such as latency sensitivity, data volume, and system complexity.
Core Concepts and Definitions
Real-time processing involves the immediate analysis and handling of data as it is generated, enabling instant insights and actions critical for applications like fraud detection and live monitoring. Batching processes large volumes of data collected over a period, optimizing resource use and throughput for tasks such as report generation and data warehousing. The core difference lies in latency, with real-time systems prioritizing minimal delay and batching systems maximizing processing efficiency through scheduled execution.
Key Differences Between Real-time and Batch Processing
Real-time processing handles data instantly as it arrives, enabling immediate analysis and decision-making, while batch processing collects data over a period and processes it all at once. Real-time systems prioritize low latency and continuous input, ideal for applications like fraud detection and live monitoring. Batch processing excels in handling large volumes of data efficiently, often used in scenarios like payroll or report generation where time sensitivity is lower.
Use Cases for Real-time Processing
Real-time processing excels in use cases requiring immediate data analysis and response, such as fraud detection in financial transactions, live monitoring of industrial equipment for predictive maintenance, and dynamic content personalization on digital platforms. Enterprises leverage real-time processing to enhance customer experience by providing instant recommendations, alerts, and decision-making capabilities. This approach supports critical operations in healthcare, telecommunications, and emergency response systems where latency must be minimized.
Applications of Batch Processing
Batch processing excels in applications where large volumes of data require periodic processing, such as payroll systems, billing cycles, and data warehousing. It enables efficient handling of high-throughput tasks by grouping data into sequential batches, ensuring resource optimization and cost-effectiveness. Industries like finance, retail, and telecommunications rely heavily on batch processing for end-of-day transaction reconciliation and report generation.
Performance Considerations
Real-time processing offers low-latency data handling essential for time-sensitive applications such as fraud detection and live analytics, delivering immediate insights by processing streaming data continuously. Batching processes large volumes of data at scheduled intervals, optimizing throughput and resource utilization but introducing latency unsuitable for scenarios requiring instant decisions. Choosing between real-time processing and batching depends on application performance requirements, data velocity, and the trade-off between latency and system complexity.
Scalability and Resource Management
Real-time processing enables scalable, low-latency data handling by processing data streams instantly, efficiently using resources to accommodate fluctuating workloads. Batching processes large volumes of data periodically, optimizing resource utilization by aggregating tasks, but may face challenges scaling under time-critical demands. Effective resource management in real-time systems relies on dynamic allocation and parallelism, while batching benefits from predictable scheduling and resource provisioning.
Data Consistency and Reliability
Real-time processing ensures low-latency data handling, providing immediate insights essential for time-sensitive applications, but it poses challenges in maintaining data consistency due to the continuous stream of incoming data. Batching processes data in large chunks at scheduled intervals, delivering higher consistency and reliability through controlled, repeatable operations while potentially increasing latency. Systems requiring strict transactional integrity often favor batching, whereas those prioritizing instant responsiveness lean towards real-time solutions with mechanisms to mitigate consistency trade-offs.
Cost Implications
Real-time processing often incurs higher costs due to the need for continuous data ingestion, low-latency infrastructure, and complex event handling, which require more advanced hardware and software resources. In contrast, batching leverages scheduled, bulk data processing that optimizes resource utilization and reduces operational expenses by minimizing continuous compute demands. Organizations must evaluate workload patterns and latency requirements to balance cost efficiency against the urgency of data delivery in their processing strategy.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Needs
Real-time processing delivers immediate data insights by continuously analyzing incoming streams, ideal for applications requiring instant decision-making such as fraud detection or live monitoring. Batching processes large volumes of data in scheduled intervals, optimizing resource efficiency and complexity for tasks like historical trend analysis or reporting. Selecting the right approach depends on your latency requirements, data volume, computational resources, and specific business objectives.
Real-time Processing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com