Usability testing evaluates how easily users can navigate and interact with a product to identify any obstacles or areas needing improvement. This process reveals critical insights into user behavior, preferences, and pain points, ensuring your design delivers a seamless experience. Explore the rest of the article to uncover effective strategies for conducting impactful usability testing.
Table of Comparison
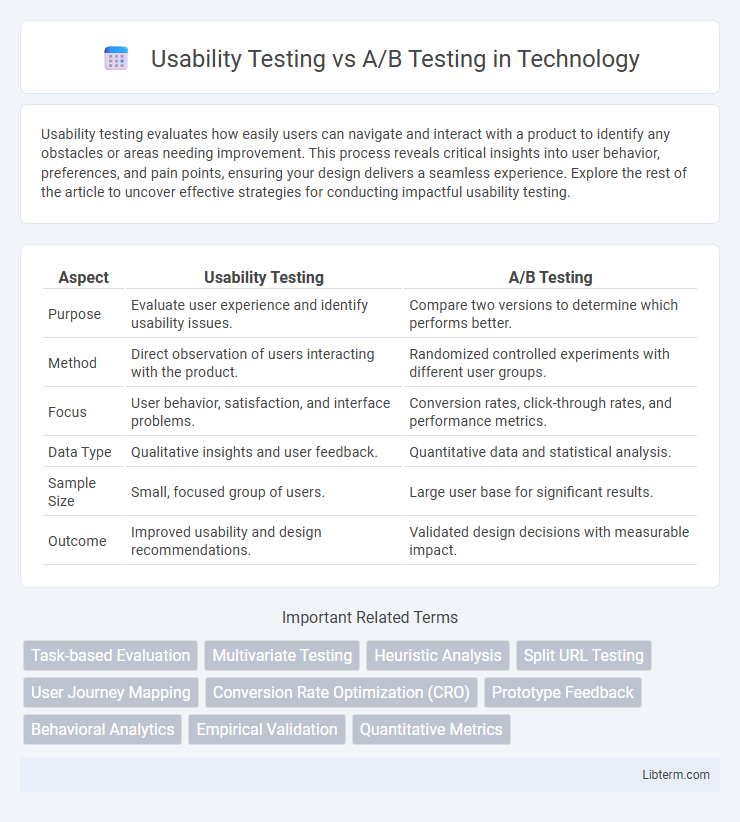
| Aspect | Usability Testing | A/B Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Evaluate user experience and identify usability issues. | Compare two versions to determine which performs better. |
| Method | Direct observation of users interacting with the product. | Randomized controlled experiments with different user groups. |
| Focus | User behavior, satisfaction, and interface problems. | Conversion rates, click-through rates, and performance metrics. |
| Data Type | Qualitative insights and user feedback. | Quantitative data and statistical analysis. |
| Sample Size | Small, focused group of users. | Large user base for significant results. |
| Outcome | Improved usability and design recommendations. | Validated design decisions with measurable impact. |
Introduction to Usability Testing and A/B Testing
Usability testing evaluates how real users interact with a product to identify pain points and improve user experience by observing tasks in a controlled environment. A/B testing compares two versions of a webpage or app by splitting traffic to determine which variation performs better based on specific metrics such as conversion rates. Both methods provide data-driven insights but usability testing focuses on qualitative feedback, while A/B testing provides quantitative results.
Definition of Usability Testing
Usability testing evaluates a product by observing real users as they interact with it, identifying usability issues and measuring user satisfaction and efficiency. This method focuses on understanding user behavior and pinpointing design flaws through direct feedback and task completion analysis. Usability testing differs from A/B testing, which compares two or more versions of a webpage or app to determine which performs better based on specific metrics like conversion rates.
Definition of A/B Testing
A/B Testing is a data-driven experiment comparing two or more variants of a webpage or app to determine which version performs better based on key metrics like click-through rates or conversions. It isolates the impact of specific changes by randomly assigning users to different versions, providing statistically significant results for optimization decisions. Unlike usability testing, which focuses on user experience issues and qualitative feedback, A/B Testing emphasizes measurable outcomes and behavior-driven performance improvements.
Key Differences Between Usability Testing and A/B Testing
Usability testing evaluates user interaction with a product to identify design issues and improve user experience, focusing on qualitative feedback and task completion rates. A/B testing compares two or more variations of a webpage or app to determine which version drives better performance metrics like conversion rates or click-through rates through quantitative data. The key difference lies in usability testing's emphasis on understanding user behavior and pain points, while A/B testing aims to optimize specific outcomes based on statistical analysis.
When to Use Usability Testing
Usability testing is essential when evaluating a product's user interface to identify pain points and improve overall user experience before full-scale launch. It is most effective during early design stages or after major feature updates to gather qualitative feedback on navigation, clarity, and functionality. Companies prioritize usability testing when understanding user behavior, preferences, and accessibility challenges is critical for increasing product adoption and satisfaction.
When to Use A/B Testing
A/B testing is ideal when comparing two or more versions of a webpage, app feature, or marketing asset to determine which one drives better user engagement or conversion rates. It excels in data-driven decision-making by providing statistically significant results through real user interactions over a defined period. Use A/B testing when you need to optimize specific design elements or content choices based on quantifiable performance metrics rather than qualitative user feedback.
Methods and Best Practices in Usability Testing
Usability testing involves observing real users as they interact with a product to identify pain points, using methods like think-aloud protocols, task analysis, and eye-tracking for qualitative insights. Best practices for usability testing emphasize recruiting representative users, creating realistic scenarios, and iterating based on feedback to enhance user experience. In contrast, A/B testing compares two variations of a design quantitatively by measuring performance metrics such as click-through rates or conversion rates to determine which version drives better results.
Methods and Best Practices in A/B Testing
Usability testing involves observing real users as they interact with a product to identify pain points and improve user experience, while A/B testing compares two or more variants of a webpage or app to measure which version performs better based on specific metrics like conversion rates or click-throughs. Best practices in A/B testing include defining clear hypotheses, segmenting target audiences, running tests for statistically significant durations, and monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) such as bounce rate and revenue per visitor. Employing proper sample sizes and avoiding multiple simultaneous changes enhances test reliability and actionable insights.
Benefits and Limitations of Each Testing Method
Usability testing provides direct insights into user behavior and identifies specific usability issues by observing real users interacting with a product, enhancing user experience and design effectiveness; however, it can be time-consuming and involve smaller sample sizes, limiting statistical significance. A/B testing enables data-driven decision making by comparing two versions of a webpage or feature to determine which performs better in real-world conditions, offering scalable results and statistical validation, but it does not reveal the underlying reasons behind user preferences or interface challenges. Combining both methods optimizes product development by leveraging usability testing's qualitative insights alongside A/B testing's quantitative performance metrics.
Choosing the Right Testing Approach for Your Product
Usability testing evaluates how real users interact with a product to identify issues and improve overall user experience, making it ideal for early-stage design validation. A/B testing compares two or more variations of a product to determine which version performs better in terms of specific metrics like conversion rates, best suited for data-driven optimization after launch. Choosing the right testing approach depends on your product development stage and goals, with usability testing focusing on qualitative feedback and A/B testing delivering quantitative performance insights.
Usability Testing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com