Manual testing involves carefully evaluating software by executing test cases without automation tools to identify defects and ensure functionality meets requirements. This hands-on approach allows testers to observe user interface behavior and validate user experience directly, making it essential for exploratory and usability testing. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your understanding of manual testing strategies and best practices.
Table of Comparison
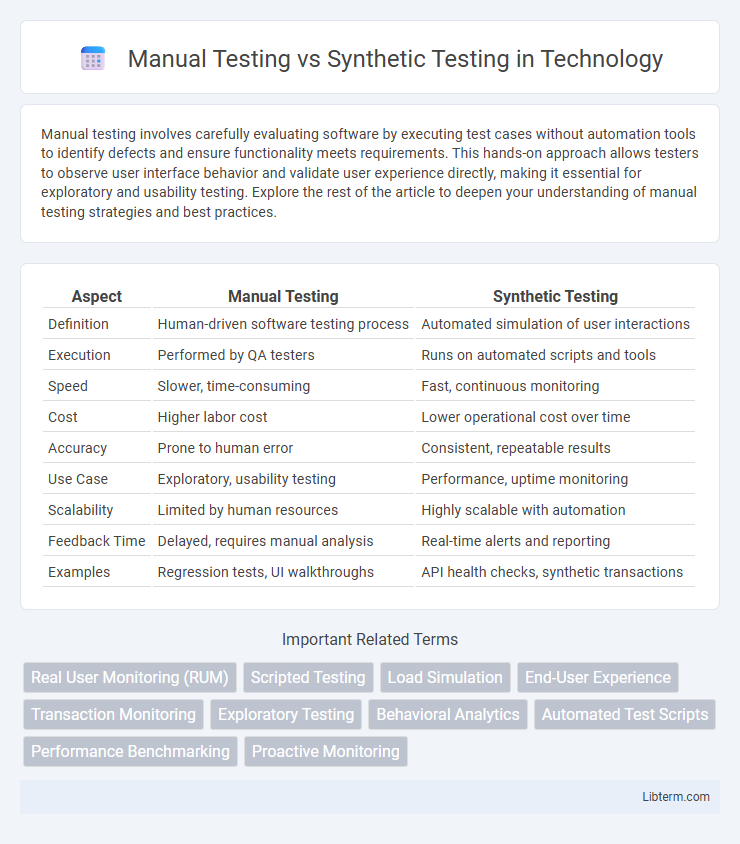
| Aspect | Manual Testing | Synthetic Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Human-driven software testing process | Automated simulation of user interactions |
| Execution | Performed by QA testers | Runs on automated scripts and tools |
| Speed | Slower, time-consuming | Fast, continuous monitoring |
| Cost | Higher labor cost | Lower operational cost over time |
| Accuracy | Prone to human error | Consistent, repeatable results |
| Use Case | Exploratory, usability testing | Performance, uptime monitoring |
| Scalability | Limited by human resources | Highly scalable with automation |
| Feedback Time | Delayed, requires manual analysis | Real-time alerts and reporting |
| Examples | Regression tests, UI walkthroughs | API health checks, synthetic transactions |
Introduction to Manual Testing and Synthetic Testing
Manual testing involves human testers executing test cases without automation tools, ensuring real-time feedback and intuitive assessment of software functionality. Synthetic testing uses automated scripts to simulate user interactions and monitor system performance, enabling continuous and consistent evaluation of application behavior. Both methods serve critical roles in quality assurance, balancing human insight and automated efficiency for comprehensive software validation.
Key Differences Between Manual and Synthetic Testing
Manual testing involves human testers executing test cases without automation tools, allowing for exploratory and ad-hoc testing that identifies user experience issues and unexpected bugs. Synthetic testing uses automated scripts to simulate user interactions and monitor system performance continuously, providing consistent and repeatable results for uptime and response time analysis. Key differences include manual testing's reliance on human judgment and flexibility versus synthetic testing's emphasis on automation, scalability, and real-time monitoring through pre-scripted scenarios.
Definitions: What is Manual Testing?
Manual testing is the process where testers execute test cases without using automation tools, relying on human observation to identify defects or unexpected behaviors in software applications. It involves validating functionality, usability, and overall user experience by manually interacting with the system under test. This approach is essential for exploratory testing, ad-hoc testing, and scenarios requiring human judgment beyond automated scripts.
Definitions: What is Synthetic Testing?
Synthetic testing is a proactive monitoring technique that simulates user interactions with an application or system to identify performance issues and ensure availability before real users are affected. It involves scripted tests running continuously or at scheduled intervals from various locations to replicate critical business transactions, validating functionality and response times. This method complements manual testing by providing automated, consistent, and repeatable assessments outside of actual user activity.
Advantages of Manual Testing
Manual testing offers the advantage of human intuition and flexibility, enabling testers to detect subtle user experience issues and unexpected behavior that automated synthetic tests may overlook. It allows for exploratory testing, providing real-time feedback and adapting test cases dynamically to evolving software requirements. Manual testing is especially valuable in complex scenarios where user interactions and subjective assessments are critical for quality assurance.
Advantages of Synthetic Testing
Synthetic testing offers consistent, repeatable monitoring of application performance and availability by simulating user interactions from multiple global locations. It enables early detection of issues before real users are affected, ensuring proactive maintenance and faster troubleshooting. This automated approach reduces reliance on manual intervention, saving time and resources while delivering precise, actionable insights.
Limitations and Challenges of Manual Testing
Manual testing faces significant limitations such as human error, inconsistency, and inefficiency when handling repetitive or large-scale test cases. The process is time-consuming and lacks scalability, making it challenging to achieve comprehensive coverage in complex software environments. Manual testing also struggles with limited test repeatability and slower feedback cycles compared to automated synthetic testing solutions.
Limitations and Challenges of Synthetic Testing
Synthetic testing faces limitations such as potential inaccuracies in simulating real user behavior, which can lead to incomplete assessment of application performance under real-world conditions. The challenge of maintaining and updating synthetic scripts to keep pace with frequent application changes often results in increased operational overhead and possible false positives. Furthermore, synthetic testing cannot capture spontaneous user interactions or unforeseen issues, limiting its effectiveness in detecting all types of performance bottlenecks or usability problems.
Choosing the Right Testing Approach: Manual vs Synthetic
Selecting the appropriate testing approach depends on the specific goals and context of the project. Manual testing excels in exploratory scenarios where human intuition uncovers unexpected issues, while synthetic testing provides automated, continuous monitoring of application performance and availability. Evaluating factors like test frequency, resource availability, and the need for real-time insights guides the decision between manual and synthetic testing methodologies.
Conclusion: Manual Testing or Synthetic Testing?
Manual testing provides human insight and adaptability, essential for exploratory testing and identifying subjective user experience issues, while synthetic testing offers automated, consistent, and scalable monitoring to detect performance and availability problems proactively. The choice depends on specific goals: prioritize manual testing for nuanced usability feedback and synthetic testing for continuous, real-time system health checks. Combining both approaches yields comprehensive quality assurance and operational reliability.
Manual Testing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com