Colocation offers businesses the advantage of housing their servers in data centers with enhanced security, reliable power, and high-speed connectivity, ensuring optimal uptime and performance. By choosing colocation, Your infrastructure benefits from scalable resources and professional maintenance without the overhead costs of managing a private facility. Explore the rest of the article to discover how colocation can transform your IT strategy.
Table of Comparison
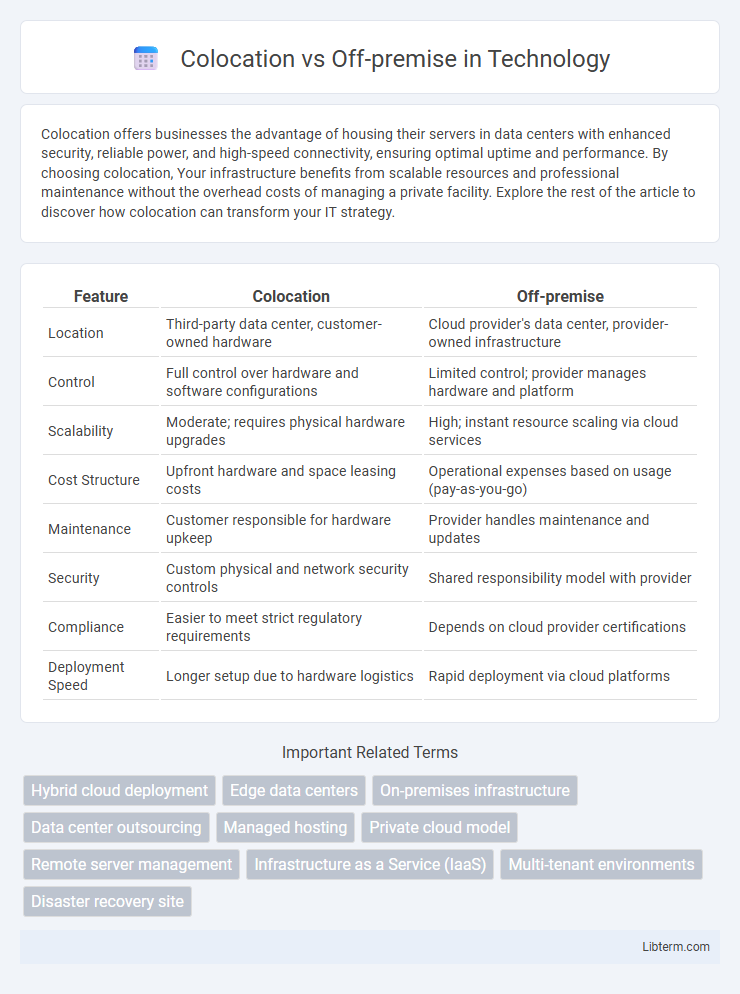
| Feature | Colocation | Off-premise |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Third-party data center, customer-owned hardware | Cloud provider's data center, provider-owned infrastructure |
| Control | Full control over hardware and software configurations | Limited control; provider manages hardware and platform |
| Scalability | Moderate; requires physical hardware upgrades | High; instant resource scaling via cloud services |
| Cost Structure | Upfront hardware and space leasing costs | Operational expenses based on usage (pay-as-you-go) |
| Maintenance | Customer responsible for hardware upkeep | Provider handles maintenance and updates |
| Security | Custom physical and network security controls | Shared responsibility model with provider |
| Compliance | Easier to meet strict regulatory requirements | Depends on cloud provider certifications |
| Deployment Speed | Longer setup due to hardware logistics | Rapid deployment via cloud platforms |
Introduction to Colocation and Off-Premise Solutions
Colocation involves housing physical servers and hardware in a third-party data center, providing enhanced security, reliable power, and network connectivity while maintaining control over the equipment. Off-premise solutions, such as cloud services, eliminate the need for physical infrastructure on-site by hosting data and applications remotely, offering scalability and flexible resource allocation. Both approaches optimize IT operations by balancing control, cost, and access to advanced technology environments.
Defining Colocation: Key Features and Benefits
Colocation involves housing privately-owned servers and networking equipment in a third-party data center, ensuring enhanced physical security, reliable power supply, and robust connectivity. Key features include shared infrastructure with controlled access, redundant systems for uptime assurance, and scalable space options tailored to client needs. Businesses benefit from reduced operational costs, expert facility management, and improved disaster recovery capabilities compared to traditional off-premise hosting.
Understanding Off-Premise Solutions
Off-premise solutions involve hosting IT infrastructure at a third-party data center, allowing businesses to leverage advanced security, scalability, and managed services without the need for on-site maintenance. These solutions reduce capital expenditures by shifting to a subscription or pay-as-you-go model, optimizing operational costs. Off-premise data centers offer enhanced disaster recovery options and compliance with industry standards, making them ideal for organizations seeking flexibility and robust uptime guarantees.
Cost Comparison: Colocation vs Off-Premise
Colocation typically involves fixed upfront costs for hardware and data center space rental, while off-premise cloud solutions operate on a pay-as-you-go model, with variable expenses based on usage. Colocation can offer lower long-term costs for organizations with stable, predictable workloads due to economies of scale in space and power. Off-premise services reduce capital expenditures but may incur higher operational expenses over time, especially with increasing data transfer and storage demands.
Security Considerations in Both Models
Colocation offers physical security advantages by allowing direct access control, surveillance systems, and tailored security protocols within a dedicated data center space, ensuring compliance with stringent regulatory standards. Off-premise cloud solutions implement advanced cybersecurity measures including encryption, multi-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring managed by third-party providers, reducing the risk of local breaches but increasing reliance on vendor trust and shared security responsibility models. Both models require robust disaster recovery plans and regular security audits to mitigate risks from cyber threats, physical intrusions, and data loss effectively.
Scalability and Flexibility: Which is Better?
Colocation offers physical control and dedicated space, allowing businesses to scale by adding hardware on-site, but flexibility is limited by fixed rack space and power constraints. Off-premise solutions provide greater scalability through on-demand resource allocation and quick adjustments without hardware investment, enhancing operational flexibility. For dynamic growth and rapid scaling, off-premise cloud infrastructures outperform colocation's static capacity limitations.
Operational Control and Management Differences
Colocation offers businesses physical ownership of hardware while outsourcing data center infrastructure, allowing greater operational control over servers, configurations, and maintenance. Off-premise cloud solutions provide managed services with limited direct access to hardware, placing infrastructure management responsibilities on the provider. This distinction impacts flexibility in customization, security protocols, and response times, with colocation enabling hands-on management and off-premise favoring convenience and scalability.
Compliance and Regulatory Implications
Colocation facilities offer enterprises enhanced control over hardware while ensuring compliance with industry-specific regulations such as HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI DSS through customizable security measures and audit support. Off-premise cloud services provide scalability and ease of compliance management by leveraging provider certifications and automated compliance tools, reducing the burden on internal teams. Understanding the regulatory environment and data sovereignty requirements is critical when choosing between colocation and off-premise solutions to maintain legal adherence and mitigate compliance risks.
Use Cases: When to Choose Colocation or Off-Premise
Colocation is ideal for businesses needing full control over hardware while benefiting from a secure, high-availability data center environment, making it suitable for enterprises with strict compliance requirements or legacy systems. Off-premise cloud solutions are best for organizations seeking scalability, rapid deployment, and cost efficiency without the burden of physical infrastructure management, often favored by startups and companies with fluctuating workloads. Hybrid strategies combining both models are increasingly adopted to optimize performance, security, and cost based on specific workload characteristics and business priorities.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Model for Your Business
Selecting the right data hosting model depends on your business's specific needs for control, security, and scalability. Colocation offers enhanced physical security and complete hardware control ideal for companies with IT expertise, while off-premise cloud solutions provide flexible, cost-effective scalability with less onsite management. Evaluate factors such as budget, compliance requirements, and IT staffing capabilities to determine the optimal solution for your organization's operational goals.
Colocation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com