DevOps integrates development and operations to accelerate software delivery while ensuring high-quality releases through continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) practices. It fosters collaboration, automates workflows, and enhances system reliability to meet evolving business goals efficiently. Discover how adopting DevOps can transform Your organization's IT strategy by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
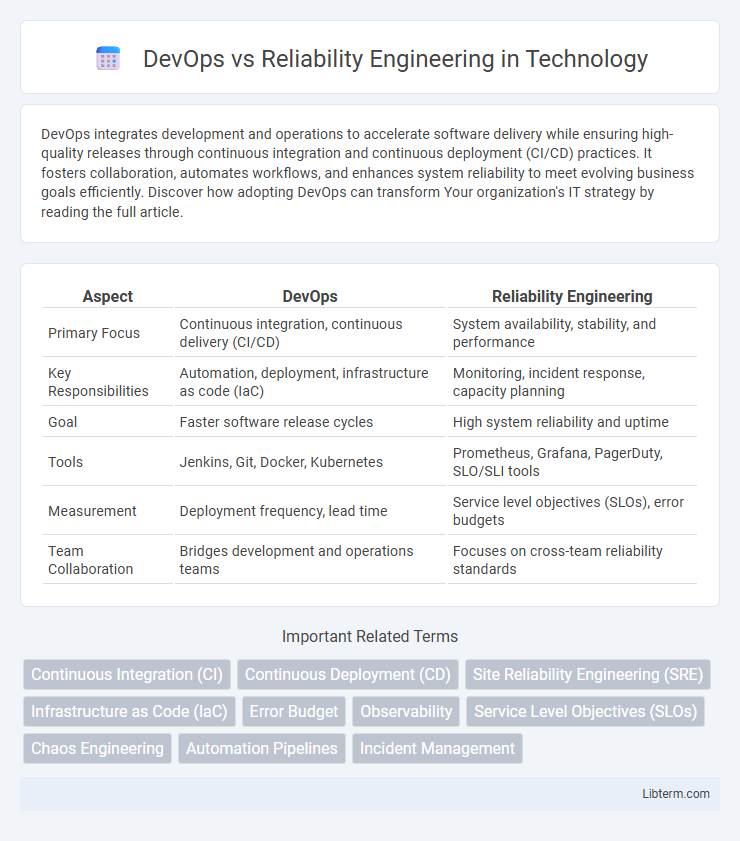
| Aspect | DevOps | Reliability Engineering |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Continuous integration, continuous delivery (CI/CD) | System availability, stability, and performance |
| Key Responsibilities | Automation, deployment, infrastructure as code (IaC) | Monitoring, incident response, capacity planning |
| Goal | Faster software release cycles | High system reliability and uptime |
| Tools | Jenkins, Git, Docker, Kubernetes | Prometheus, Grafana, PagerDuty, SLO/SLI tools |
| Measurement | Deployment frequency, lead time | Service level objectives (SLOs), error budgets |
| Team Collaboration | Bridges development and operations teams | Focuses on cross-team reliability standards |
Understanding DevOps: Principles and Practices
DevOps emphasizes collaboration between development and operations teams to accelerate software delivery through automation, continuous integration, and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. Key principles include infrastructure as code (IaC), monitoring, and feedback loops to enable rapid, reliable releases and iterative improvements. By fostering a culture of shared responsibility and transparency, DevOps enhances operational efficiency and reduces the time to market while maintaining system stability.
What is Reliability Engineering? Key Concepts
Reliability Engineering focuses on ensuring systems perform consistently over time by identifying and mitigating potential failures through rigorous testing, monitoring, and analysis of failure modes. Key concepts include fault tolerance, failure rate, mean time between failures (MTBF), and system availability, all aimed at maximizing uptime and minimizing downtime. It complements DevOps by emphasizing long-term operational stability and continuous improvement of system dependability.
Goals and Objectives: DevOps vs Reliability Engineering
DevOps focuses on accelerating software delivery through continuous integration, continuous deployment, and collaboration between development and operations teams to improve efficiency and reduce time to market. Reliability Engineering aims to ensure system stability, availability, and fault tolerance by implementing monitoring, incident response, and reliability best practices like SRE (Site Reliability Engineering). While both emphasize automation and quality, DevOps targets speed and agility, whereas Reliability Engineering prioritizes system resilience and consistent performance.
Core Responsibilities: DevOps Engineers vs Reliability Engineers
DevOps engineers primarily focus on automating software delivery pipelines, continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD), and infrastructure as code (IaC) to accelerate development cycles and improve collaboration between development and operations teams. Reliability engineers concentrate on system stability, monitoring, incident response, and developing fault-tolerant architectures to ensure high availability and minimize downtime. Both roles emphasize automation and collaboration but differ in the balance of development speed versus operational resilience.
Toolchains and Technologies Used
DevOps leverages continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI, and CircleCI alongside containerization platforms such as Docker and Kubernetes to automate software delivery and infrastructure management. Reliability Engineering emphasizes observability stacks including Prometheus for metrics, Grafana for visualization, and distributed tracing tools like Jaeger to ensure system resilience and uptime. Both disciplines integrate cloud services from AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud, but Reliability Engineering prioritizes incident response and service level objectives (SLOs) through specialized tools like PagerDuty and SRE-focused automation frameworks.
Collaboration and Team Dynamics
DevOps emphasizes continuous collaboration between development and operations teams to accelerate software delivery and improve system reliability. Reliability Engineering focuses on embedding resilience and fault tolerance directly into system design through cross-functional team efforts. Both disciplines leverage shared responsibility and proactive communication to enhance operational efficiency and minimize downtime.
Incident Management and Response
DevOps integrates automated incident management and rapid response workflows to accelerate deployment cycles while maintaining system stability. Reliability Engineering emphasizes proactive incident response planning, root cause analysis, and resilience engineering to minimize system downtime and ensure consistent service performance. Both disciplines prioritize effective communication and collaboration tools to streamline incident detection, analysis, and resolution, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Performance Measurement: Metrics and KPIs
Performance measurement in DevOps centers on deployment frequency, lead time for changes, and mean time to recovery (MTTR) as primary KPIs for assessing software delivery speed and reliability. Reliability engineering prioritizes metrics like error budget consumption, availability percentage, and service level indicators (SLIs) to ensure system stability and uptime. Both disciplines leverage monitoring tools and quantitative data analysis, but DevOps emphasizes continuous integration and delivery metrics, while reliability engineering focuses on fault tolerance and incident reduction.
Challenges and Best Practices
DevOps faces challenges in integrating continuous deployment with maintaining system stability, often requiring automation strategies and culture shifts to balance speed and quality. Reliability Engineering emphasizes fault tolerance and proactive incident management, utilizing practices like chaos engineering and thorough monitoring to enhance system resilience. Best practices in both fields include cross-functional collaboration, robust CI/CD pipelines, and extensive use of metrics to drive improvements in performance and uptime.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Organization
Choosing between DevOps and Reliability Engineering depends on your organization's goals and operational maturity. DevOps emphasizes collaboration, continuous integration, and faster deployment cycles to accelerate software delivery, while Reliability Engineering focuses on system stability, incident response, and resilience through practices like SRE (Site Reliability Engineering). Aligning your approach with business priorities, such as innovation speed or uptime requirements, ensures optimal resource allocation and improved overall performance.
DevOps Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com