On-premises solutions offer businesses direct control over their IT infrastructure, enhancing security and customization options tailored to specific organizational needs. These systems require physical hardware management and significant upfront investment but provide greater data privacy compared to cloud alternatives. Discover how on-premises deployments can benefit your company by exploring our in-depth analysis.
Table of Comparison
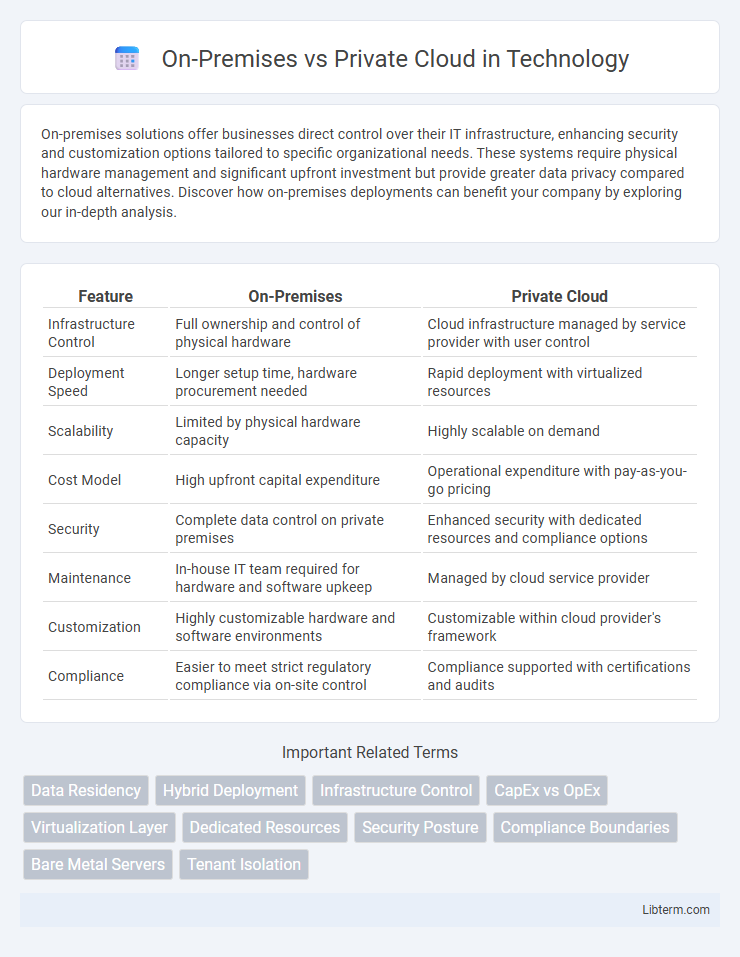
| Feature | On-Premises | Private Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure Control | Full ownership and control of physical hardware | Cloud infrastructure managed by service provider with user control |
| Deployment Speed | Longer setup time, hardware procurement needed | Rapid deployment with virtualized resources |
| Scalability | Limited by physical hardware capacity | Highly scalable on demand |
| Cost Model | High upfront capital expenditure | Operational expenditure with pay-as-you-go pricing |
| Security | Complete data control on private premises | Enhanced security with dedicated resources and compliance options |
| Maintenance | In-house IT team required for hardware and software upkeep | Managed by cloud service provider |
| Customization | Highly customizable hardware and software environments | Customizable within cloud provider's framework |
| Compliance | Easier to meet strict regulatory compliance via on-site control | Compliance supported with certifications and audits |
Introduction to On-Premises and Private Cloud
On-premises infrastructure involves hosting servers and data within a company's physical facilities, offering direct control over hardware, security, and compliance. Private cloud leverages virtualization and cloud technologies to provide a dedicated environment hosted either internally or by third-party providers, combining scalability with enhanced security. Both models emphasize data sovereignty and tailored resource management but differ in flexibility and operational overhead.
Key Differences Between On-Premises and Private Cloud
On-premises infrastructure requires organizations to maintain physical hardware and software within their own facilities, providing full control over data security and customization. Private cloud environments offer scalable, virtualized resources hosted either on-site or by a third-party provider, enabling flexible access and improved disaster recovery capabilities. Key differences include capital expenditure versus operational expenditure models, maintenance responsibilities, and the agility to quickly scale resources based on demand.
Infrastructure and Deployment Models
On-Premises infrastructure entails hosting servers and hardware within an organization's physical location, offering direct control, customization, and security but requiring significant capital investment and maintenance. Private Cloud deployment models utilize virtualized resources hosted either on-premises or by third-party providers, enabling scalability, automation, and improved resource utilization while maintaining exclusive access and compliance controls. Choosing between On-Premises and Private Cloud depends on factors such as workload sensitivity, budget constraints, and desired agility in infrastructure management.
Security and Compliance Considerations
On-premises deployments provide organizations with direct control over physical security measures and data access, enabling strict adherence to industry-specific compliance requirements such as HIPAA or PCI DSS. Private cloud environments offer enhanced scalability and automation while incorporating robust security frameworks, encryption, and compliance certifications tailored to regulatory standards like GDPR. Evaluating risk management, data residency, and audit capabilities is critical to determining the optimal solution for securing sensitive information and maintaining regulatory compliance.
Cost Analysis and Budget Implications
On-premises infrastructure requires significant upfront capital expenditures for hardware, software licenses, and physical space, leading to higher initial costs but predictable ongoing maintenance expenses. Private cloud solutions operate on a subscription or pay-as-you-go model, reducing capital outlays and offering scalable resource allocation that aligns operational costs with actual usage. Budget implications favor private cloud for organizations seeking flexible spending and reduced total cost of ownership (TCO), while on-premises setups may be cost-effective for long-term, stable workloads with predictable demand.
Scalability and Flexibility Comparison
On-premises infrastructure offers limited scalability due to fixed physical resources, requiring significant capital investment and time for upgrades. Private cloud environments provide dynamic scalability with on-demand resource allocation, enabling rapid adaptation to fluctuating workloads and business needs. Flexibility in private clouds is enhanced by automation and virtualization, while on-premises systems often require manual configuration and longer deployment cycles.
Performance and Reliability Factors
On-premises infrastructure provides direct control over hardware and networking, often resulting in lower latency and consistent performance tailored to specific workloads. Private cloud environments offer scalable resources and automated management, enhancing reliability through built-in redundancy and failover mechanisms. Performance variability in private clouds can occur due to resource sharing and virtualization overhead, while on-premises systems require dedicated maintenance to sustain uptime and prevent hardware failures.
Management and Maintenance Requirements
On-premises systems demand that organizations manage and maintain all hardware, software, and infrastructure internally, requiring dedicated IT staff and resources for regular updates, patches, and troubleshooting. Private cloud environments shift some management responsibilities to the cloud provider, offering automated maintenance, scalability, and streamlined updates while still providing control over security and compliance. The choice impacts operational overhead, with on-premises requiring more hands-on management versus the more managed services approach of private cloud solutions.
Use Cases and Industry Applications
On-premises infrastructure is favored by industries requiring maximum control and compliance, such as government agencies and financial institutions, for sensitive data processing and regulatory adherence. Private cloud environments offer scalable, secure solutions ideal for healthcare providers and enterprises managing dynamic workloads and collaboration across distributed teams. Manufacturing and retail sectors benefit from hybrid models leveraging on-premises systems for legacy applications while utilizing private clouds for data analytics and customer engagement platforms.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
Choosing the right solution for your business depends on factors like control, security, scalability, and budget. On-premises infrastructure offers maximum control and enhanced security by maintaining data onsite, ideal for industries with strict compliance requirements. Private cloud provides flexible scalability, cost efficiency, and managed services, making it suitable for growing businesses seeking agility without sacrificing data privacy.
On-Premises Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com