Secure Enclave is a dedicated security coprocessor integrated into Apple devices, designed to handle sensitive data such as encryption keys, passwords, and biometric information. It operates independently from the main processor to ensure data protection even if the device's operating system is compromised. Explore the rest of this article to understand how Secure Enclave enhances your device's security and privacy.
Table of Comparison
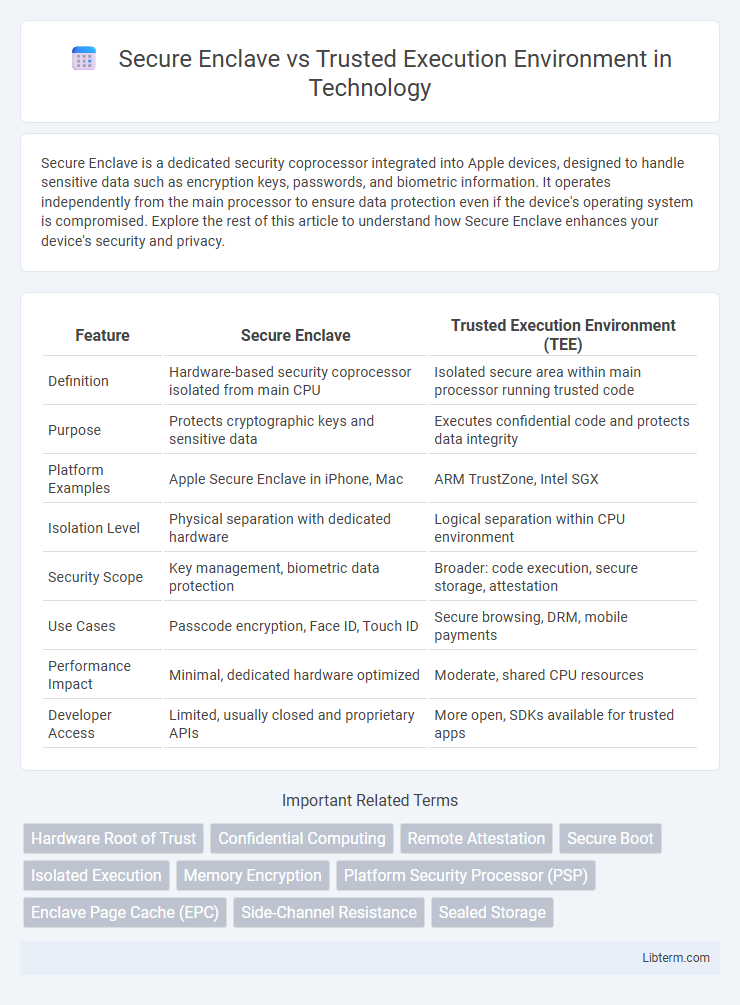
| Feature | Secure Enclave | Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hardware-based security coprocessor isolated from main CPU | Isolated secure area within main processor running trusted code |
| Purpose | Protects cryptographic keys and sensitive data | Executes confidential code and protects data integrity |
| Platform Examples | Apple Secure Enclave in iPhone, Mac | ARM TrustZone, Intel SGX |
| Isolation Level | Physical separation with dedicated hardware | Logical separation within CPU environment |
| Security Scope | Key management, biometric data protection | Broader: code execution, secure storage, attestation |
| Use Cases | Passcode encryption, Face ID, Touch ID | Secure browsing, DRM, mobile payments |
| Performance Impact | Minimal, dedicated hardware optimized | Moderate, shared CPU resources |
| Developer Access | Limited, usually closed and proprietary APIs | More open, SDKs available for trusted apps |
Introduction to Secure Enclave and Trusted Execution Environment
Secure Enclave is a hardware-based security feature embedded within Apple devices, designed to provide an isolated environment for sensitive data processing like encryption keys and biometric information. Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) is a separate, secure area within a device's main processor that runs trusted applications, protecting them from the regular operating system vulnerabilities. Both Secure Enclave and TEE enhance data security by isolating critical operations but differ in implementation and platform specificity.
Defining Secure Enclave: Key Features and Architecture
Secure Enclave is a dedicated security coprocessor integrated into Apple devices, designed to provide a physically isolated environment for processing sensitive data such as encryption keys and biometric information. Its architecture includes a separate processor, secure boot process, and encrypted memory, ensuring data remains protected even if the main operating system is compromised. Key features include hardware-based key management, secure boot verification, and on-device cryptographic operations that prevent external tampering and unauthorized access.
What is a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE)?
A Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) is a secure area within a main processor that runs code in an isolated, trusted environment to protect sensitive data and operations from unauthorized access or tampering. TEEs use hardware-based isolation, typically found in ARM TrustZone or Intel SGX architectures, to enable secure execution of cryptographic functions and protect digital assets such as encryption keys and biometric information. Unlike Secure Enclaves, which are specific implementations like Apple's Secure Enclave Processor, TEEs provide a broader framework for secure computing on various platforms.
Core Differences Between Secure Enclave and TEE
Secure Enclave is a hardware-based key manager isolated within Apple processors, designed exclusively for iOS and macOS devices, providing a dedicated secure area for cryptographic operations and biometric data. Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) is a more generalized secure area embedded in various processors across multiple platforms, offering a safe environment for running trusted applications isolated from the main operating system. The core difference lies in Secure Enclave's proprietary Apple ecosystem integration and hardware design, whereas TEE supports broader device compatibility with standardized security frameworks like ARM TrustZone.
Security Mechanisms: How Each Protects Sensitive Data
Secure Enclave uses a dedicated coprocessor with encrypted memory, isolating cryptographic operations from the main processor to safeguard sensitive data. Trusted Execution Environment leverages hardware-based isolation within the main CPU, enabling secure execution of trusted applications alongside an untrusted operating system. Both employ encryption, secure boot, and attestation mechanisms to ensure data integrity and confidentiality during processing.
Hardware vs Software Implementation: A Comparative Analysis
Secure Enclave, a hardware-based isolated security subsystem found in Apple devices, offers dedicated cryptographic operations and secure key storage, ensuring robust protection against software attacks. Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) operates as a secure area within the main processor, often implemented via software extensions like ARM TrustZone, enabling a trusted platform for sensitive computations while sharing hardware resources with the OS. The hardware implementation of Secure Enclave provides stronger physical isolation compared to the hybrid hardware-software nature of TEEs, leading to enhanced resistance against sophisticated hardware and side-channel attacks.
Use Cases and Real-World Applications
Secure Enclave provides hardware-based encryption and isolation mainly for protecting sensitive data like biometric information and cryptographic keys within Apple devices, ensuring secure authentication and payment processing. Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) supports a broader range of secure applications by isolating code execution for tasks such as digital rights management, secure mobile payments, and enterprise data protection across various platforms including ARM TrustZone. Both technologies enhance device security, with Secure Enclave specializing in user-centric privacy and TEE enabling versatile secure computing environments for diverse industry needs.
Performance Impact: Efficiency and Resource Consumption
Secure Enclave offers highly efficient performance by isolating sensitive tasks within dedicated hardware, minimizing resource consumption and maintaining low latency for cryptographic operations. Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) provides a broader range of secure computing capabilities but typically consumes more system resources due to its integration with the main processor and broader security management. The efficiency of Secure Enclave is optimized for specific security functions, while TEEs balance performance and flexibility, often resulting in higher overhead.
Industry Adoption and Vendor Support
Secure Enclave technology, prominently adopted by Apple, offers robust hardware-level isolation for sensitive data, gaining widespread support in the consumer electronics sector. Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) solutions, such as ARM TrustZone, enjoy broad industry adoption across mobile, IoT, and enterprise hardware, backed by extensive vendor ecosystems including Qualcomm, Intel, and Samsung. Vendor support for TEEs often involves comprehensive software development kits and integration tools, enabling scalable security across diverse platforms compared to the more proprietary nature of Secure Enclave implementations.
Choosing the Right Technology for Your Security Needs
Secure Enclave offers a hardware-based isolated environment, ideal for safeguarding sensitive data like biometric information and cryptographic keys in consumer devices. Trusted Execution Environment provides a more flexible, firmware-driven solution across various platforms, suitable for enterprise applications requiring versatile security controls and trusted app execution. Select Secure Enclave for enhanced protection in mobile ecosystems or opt for Trusted Execution Environment when prioritizing broad compatibility and enterprise-level security integration.
Secure Enclave Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com