Webhooks provide a powerful way to automate communication between different web services by sending real-time data updates triggered by specific events. This enables seamless integration and instant notification without requiring constant polling, boosting efficiency and responsiveness in your applications. Discover how webhooks can transform your workflows by exploring the detailed insights in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
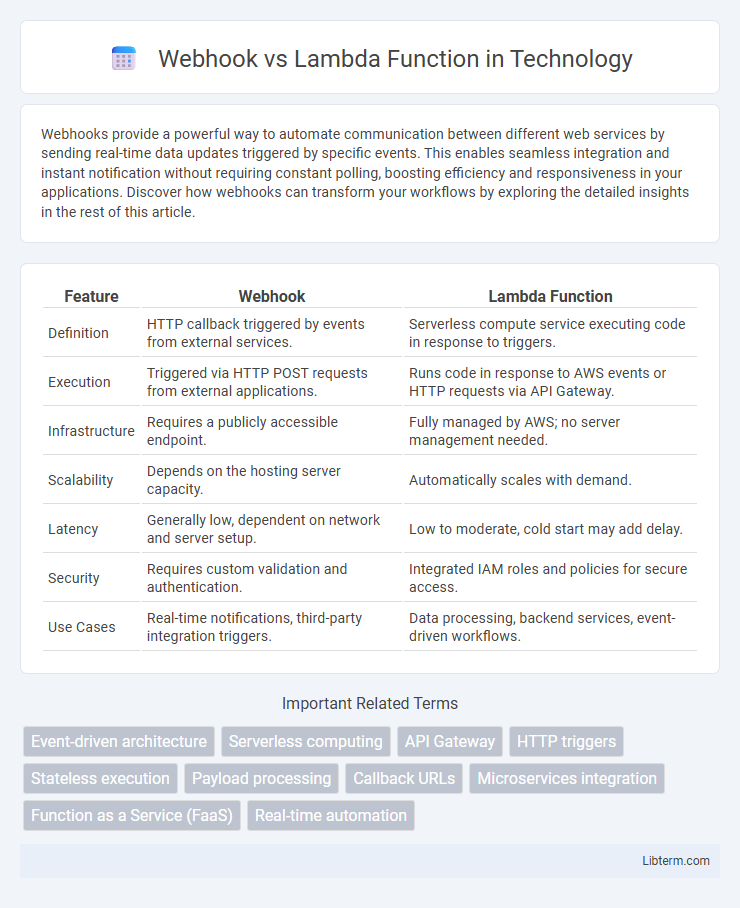
| Feature | Webhook | Lambda Function |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | HTTP callback triggered by events from external services. | Serverless compute service executing code in response to triggers. |
| Execution | Triggered via HTTP POST requests from external applications. | Runs code in response to AWS events or HTTP requests via API Gateway. |
| Infrastructure | Requires a publicly accessible endpoint. | Fully managed by AWS; no server management needed. |
| Scalability | Depends on the hosting server capacity. | Automatically scales with demand. |
| Latency | Generally low, dependent on network and server setup. | Low to moderate, cold start may add delay. |
| Security | Requires custom validation and authentication. | Integrated IAM roles and policies for secure access. |
| Use Cases | Real-time notifications, third-party integration triggers. | Data processing, backend services, event-driven workflows. |
Introduction to Webhooks and Lambda Functions
Webhooks are user-defined HTTP callbacks triggered by specific events, enabling real-time data transfer between applications without polling. Lambda functions are serverless compute services that execute code in response to events, offering scalable and cost-effective function execution without managing servers. Both enable event-driven architectures, but webhooks primarily facilitate event notifications, while Lambda functions handle event processing and automation.
Key Differences Between Webhooks and Lambda Functions
Webhooks are user-defined HTTP callbacks triggered by specific events, primarily used for real-time notifications and event-driven integrations. Lambda functions are serverless compute services that execute code in response to triggers such as HTTP requests, database changes, or other AWS services, offering greater flexibility and scalability. Unlike webhooks that rely on external systems to send events, Lambda functions can perform complex processing and interact directly with AWS resources without managing servers.
How Webhooks Work
Webhooks operate by sending real-time HTTP POST requests to a predefined URL whenever a specific event occurs, enabling seamless communication between different services. They rely on event-driven architecture, where the source system pushes data automatically to the target endpoint without polling. This mechanism allows instant data synchronization and automation across web applications.
How Lambda Functions Work
Lambda functions operate as serverless compute services triggered by events such as API calls, database updates, or file uploads. These functions automatically execute code in response to specific triggers without the need to manage underlying infrastructure, enabling scalable and cost-efficient processing. By running code only when needed, Lambda functions reduce operational overhead and integrate seamlessly with various AWS services for real-time event handling.
Use Cases for Webhooks
Webhooks are ideal for real-time event notifications, enabling applications to respond instantly to specific triggers such as payment completions, form submissions, or system alerts. They streamline workflows by pushing data to external services or APIs without polling, facilitating seamless integrations with third-party platforms like Slack, GitHub, and Stripe. Webhooks excel in scenarios requiring immediate data synchronization, automated notifications, and lightweight event-driven architecture.
Use Cases for Lambda Functions
Lambda functions excel in use cases involving serverless computing where event-driven execution is critical, such as real-time data processing, automated backups, and dynamic content generation. They enable seamless integration with AWS services like S3, DynamoDB, and API Gateway to trigger scalable, low-latency operations without provisioning or managing servers. Common scenarios include executing code in response to file uploads, database modifications, or API requests, offering efficient resource utilization and cost savings in cloud environments.
Security Considerations for Webhooks and Lambda
Webhooks require strict validation of incoming requests through methods like HMAC signatures and IP whitelisting to prevent spoofing and unauthorized access. AWS Lambda functions benefit from integrated IAM roles that enforce granular permissions and execution policies, minimizing the risk of privilege escalation. Both methods should implement encryption for data in transit and detailed logging for monitoring and forensic analysis.
Scalability and Performance Comparison
Webhook architecture relies on HTTP callbacks that trigger actions in real-time but may face scalability challenges under high request volumes due to server limitations. Lambda functions, managed by cloud providers like AWS, automatically scale in response to workload, ensuring consistent performance even during traffic spikes. This serverless model reduces latency and operational overhead, making Lambda functions more efficient for scalable, event-driven applications.
Choosing Between Webhook and Lambda Function
Choosing between a webhook and a Lambda function depends on the specific use case and architecture requirements. Webhooks excel in event-driven scenarios where external services trigger real-time HTTP callbacks, offering simplicity and immediate response. Lambda functions provide greater flexibility with scalable, serverless compute capabilities ideal for complex processing, integration with AWS services, and handling asynchronous workloads.
Conclusion: Which Solution Fits Your Needs?
Webhook integration offers real-time event-driven communication ideal for lightweight, external service interactions, while AWS Lambda excels in serverless, scalable computing for complex workflows within the AWS ecosystem. Choosing between a webhook and Lambda function depends on application architecture, latency sensitivity, and processing complexity. For minimal infrastructure management and dynamic scaling, Lambda is preferred; for straightforward notifications or third-party API triggers, webhooks provide a simpler, cost-effective solution.
Webhook Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com