VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) technology enables network segmentation by logically grouping devices even if they are not physically connected, enhancing security and reducing broadcast traffic. By isolating sensitive data and optimizing bandwidth, VLANs improve network performance and management flexibility. Explore the rest of the article to understand how VLANs can optimize your network infrastructure.
Table of Comparison
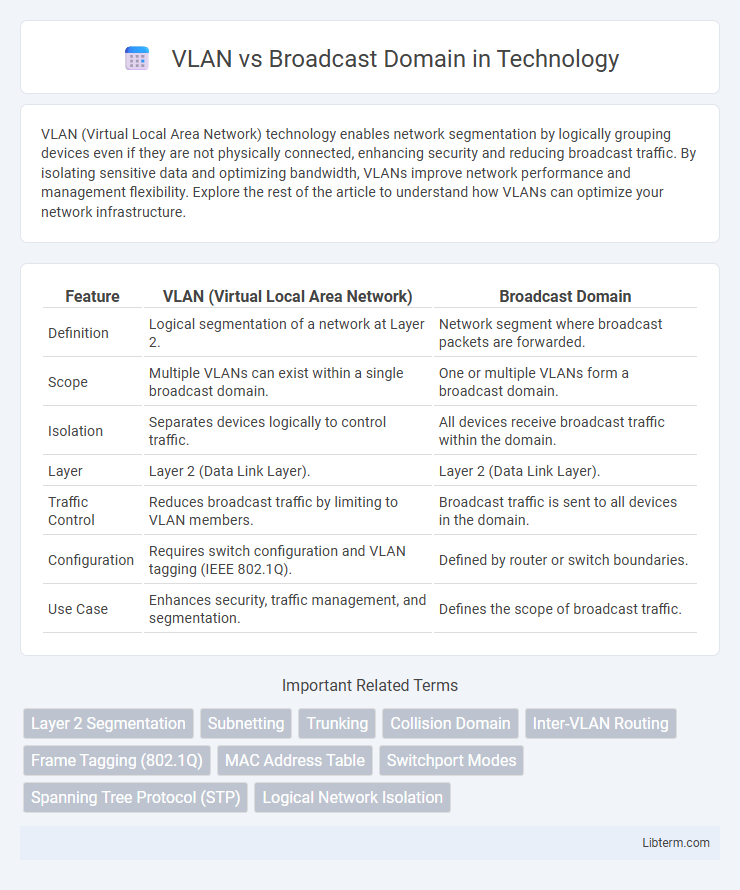
| Feature | VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) | Broadcast Domain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Logical segmentation of a network at Layer 2. | Network segment where broadcast packets are forwarded. |
| Scope | Multiple VLANs can exist within a single broadcast domain. | One or multiple VLANs form a broadcast domain. |
| Isolation | Separates devices logically to control traffic. | All devices receive broadcast traffic within the domain. |
| Layer | Layer 2 (Data Link Layer). | Layer 2 (Data Link Layer). |
| Traffic Control | Reduces broadcast traffic by limiting to VLAN members. | Broadcast traffic is sent to all devices in the domain. |
| Configuration | Requires switch configuration and VLAN tagging (IEEE 802.1Q). | Defined by router or switch boundaries. |
| Use Case | Enhances security, traffic management, and segmentation. | Defines the scope of broadcast traffic. |
Overview of VLAN and Broadcast Domain
A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) segments a physical network into multiple logical networks, enhancing security and traffic management by isolating broadcast traffic within each VLAN. A broadcast domain defines a network segment where a broadcast frame is forwarded to all devices without crossing routers, typically limited by router boundaries or VLANs. VLANs effectively control broadcast domains by confining broadcast traffic, reducing congestion, and improving network efficiency.
Key Definitions: VLAN and Broadcast Domain
A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is a network segmentation technology that divides a physical network into multiple logically separated networks, enhancing security and reducing broadcast traffic. A Broadcast Domain refers to a logical division of a computer network where all nodes can reach each other by broadcast at the data link layer, typically bounded by routers or VLANs. VLANs effectively create separate broadcast domains within the same physical network infrastructure, isolating broadcast traffic to improve network performance and security.
How VLANs Segment Network Traffic
VLANs segment network traffic by logically dividing a single physical network into multiple distinct broadcast domains, isolating traffic within each VLAN to reduce congestion and improve security. Each VLAN operates as a separate subnet, preventing broadcast frames from crossing VLAN boundaries and thereby limiting the scope of broadcast traffic. Network switches use VLAN tagging (IEEE 802.1Q) to ensure data frames are properly segmented and directed only to devices within the same VLAN, enhancing overall network performance and management.
The Role of Broadcast Domains in Networking
Broadcast domains are network segments where a broadcast frame sent by any device is received by all devices within the same domain, enabling efficient local communication. VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) partition a physical network into multiple isolated broadcast domains, reducing unnecessary traffic and improving security. Proper segmentation using VLANs minimizes broadcast storms and enhances overall network performance by containing broadcasts within defined boundaries.
VLANs and Broadcast Domains: Relationship Explained
VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) create separate broadcast domains by segmenting a physical network into multiple logical networks, limiting broadcast traffic to devices within the same VLAN. Each VLAN functions as an independent broadcast domain, enhancing network efficiency and security by reducing unnecessary broadcasts and isolating traffic. Understanding the relationship between VLANs and broadcast domains is crucial for designing scalable, optimized networks that manage traffic flow effectively.
Advantages of Using VLANs for Broadcast Domain Control
VLANs provide significant advantages for broadcast domain control by segmenting a physical network into multiple logical networks, which limits broadcast traffic to each VLAN and reduces unnecessary load on devices. This segmentation improves network performance, enhances security by isolating sensitive data, and simplifies network management through more efficient use of IP addressing. VLANs also enable flexible network design and easier troubleshooting compared to traditional flat broadcast domains.
Common Applications of VLANs in Modern Networks
VLANs segment a single physical network into multiple logical broadcast domains, improving network efficiency and security by restricting broadcast traffic to specific VLANs. Common applications of VLANs include isolating sensitive data by creating separate VLANs for departments such as finance and HR, enhancing Voice over IP (VoIP) performance through dedicated voice VLANs, and simplifying network management in large enterprises by grouping users based on function or location. VLANs also support scalable network architectures by enabling easier moves, adds, and changes without physical rewiring.
Typical Challenges of Managing Broadcast Domains
Managing broadcast domains presents challenges such as excessive broadcast traffic leading to network congestion and reduced performance, which VLANs help mitigate by segmenting networks logically. Without proper VLAN configuration, broadcast storms can propagate across devices, overwhelming network resources and causing latency issues. Ensuring VLAN tagging consistency and inter-VLAN routing further complicates maintaining isolated broadcast domains while supporting necessary communication.
VLAN Configuration Best Practices
VLAN configuration best practices include assigning each VLAN a unique IP subnet to segment broadcast domains effectively, reducing unnecessary traffic and enhancing network performance. Use VLAN pruning on trunk links to limit VLAN traffic to only necessary switches, minimizing broadcast domain size and improving security. Implement VLAN access control lists (VACLs) and consistently document VLAN IDs and purposes to maintain clear network management and avoid misconfigurations.
VLAN vs Broadcast Domain: Summary and Key Takeaways
A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) segments a physical network into multiple logical networks, isolating broadcast domains to enhance network efficiency and security. Each VLAN acts as a separate broadcast domain, preventing broadcast traffic from flooding other VLANs, thus reducing network congestion and improving performance. Implementing VLANs allows precise control over traffic flow and isolation within a switch, optimizing resource use and simplifying network management.
VLAN Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com