BIOS password serves as a crucial security feature that restricts unauthorized access to your computer's firmware settings, protecting system integrity and sensitive data. It helps prevent malicious changes at the hardware level, ensuring only authorized users can modify boot configurations or hardware setup. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to set, reset, and manage your BIOS password effectively.
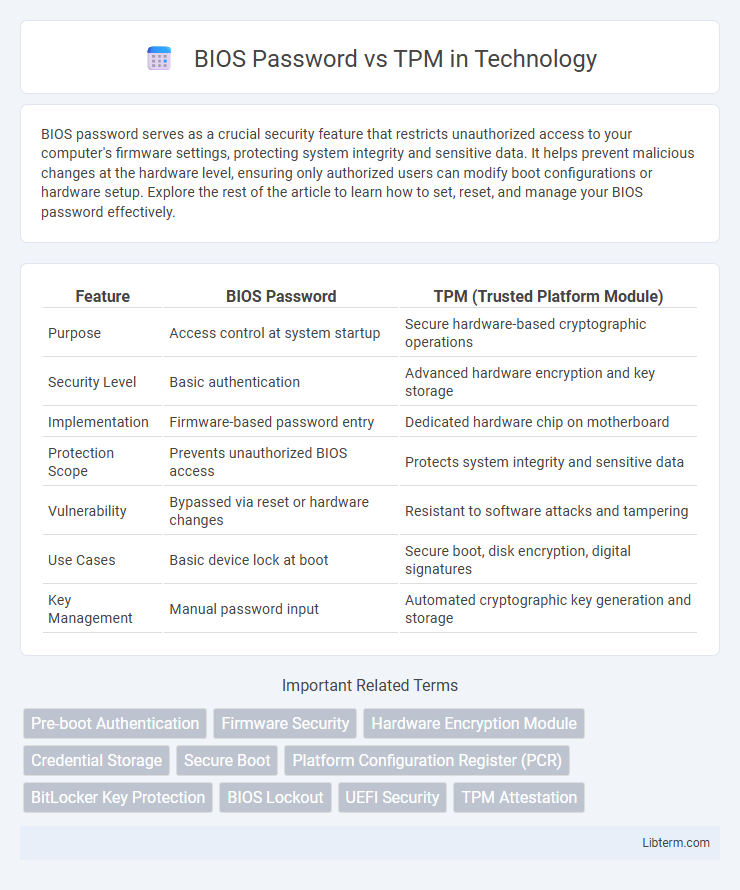
Table of Comparison
| Feature | BIOS Password | TPM (Trusted Platform Module) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Access control at system startup | Secure hardware-based cryptographic operations |
| Security Level | Basic authentication | Advanced hardware encryption and key storage |
| Implementation | Firmware-based password entry | Dedicated hardware chip on motherboard |
| Protection Scope | Prevents unauthorized BIOS access | Protects system integrity and sensitive data |
| Vulnerability | Bypassed via reset or hardware changes | Resistant to software attacks and tampering |
| Use Cases | Basic device lock at boot | Secure boot, disk encryption, digital signatures |
| Key Management | Manual password input | Automated cryptographic key generation and storage |
Introduction to BIOS Password and TPM
BIOS Password is a security feature that restricts unauthorized access to a computer's firmware settings, preventing changes to hardware configuration and boot sequence. Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a dedicated cryptographic processor that enhances security by securely storing encryption keys, passwords, and digital certificates. BIOS Password protects at the hardware setup level, while TPM focuses on secure data storage and encryption, both playing pivotal roles in safeguarding system integrity and user data.
What Is a BIOS Password?
A BIOS password is a security feature set within the motherboard firmware that restricts unauthorized access to the computer's BIOS settings and prevents the system from booting without the correct password. It protects critical configurations such as boot sequence and hardware settings but does not encrypt data on the hard drive. Unlike TPM (Trusted Platform Module), which provides hardware-based encryption and platform integrity verification, a BIOS password primarily serves as a gatekeeper for firmware access control.
Understanding TPM (Trusted Platform Module)
The Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a specialized hardware chip designed to enhance computer security by securely storing cryptographic keys and ensuring platform integrity. Unlike BIOS passwords that restrict system access at startup, TPM enables advanced features such as hardware-based encryption, secure boot, and integrity measurement, providing robust protection against firmware attacks. TPM plays a critical role in modern cybersecurity frameworks by enabling device authentication and safeguarding sensitive data at the hardware level.
Key Differences Between BIOS Password and TPM
BIOS Password is a user-created code that restricts access to the computer's firmware settings during startup, primarily preventing unauthorized BIOS configuration changes. TPM (Trusted Platform Module) is a hardware-based security chip that securely stores cryptographic keys and enhances platform integrity by enabling features like disk encryption and hardware authentication. The key difference lies in BIOS Password offering basic firmware access control, whereas TPM provides advanced hardware-level security for encryption and system integrity verification.
Security Functions of BIOS Password
BIOS password enhances security by restricting unauthorized access to the system firmware settings, preventing changes to boot sequences and hardware configurations. It serves as a first line of defense against physical tampering by requiring authentication before the operating system loads. Unlike TPM, which provides hardware-based cryptographic functions, BIOS password specifically controls access to the BIOS interface, protecting critical system-level settings from unauthorized modifications.
TPM’s Role in Modern Device Security
TPM (Trusted Platform Module) enhances device security by providing hardware-based cryptographic functions that protect encryption keys, user credentials, and system integrity against unauthorized access and tampering. Unlike BIOS passwords, which only restrict basic access during boot, TPM enables secure boot processes, disk encryption (such as BitLocker), and trusted attestation to ensure the device's software environment remains uncompromised. Modern security frameworks rely heavily on TPM for safeguarding sensitive data and enabling advanced authentication mechanisms beyond what BIOS passwords can offer.
Strengths and Limitations of BIOS Password
BIOS passwords provide a straightforward layer of hardware-level security by restricting unauthorized access to the system BIOS settings, effectively preventing unauthorized changes to boot order or firmware configurations; however, their strength is limited as they can often be bypassed or reset by physically accessing the motherboard or removing the CMOS battery. In contrast, TPM (Trusted Platform Module) offers a more robust cryptographic approach by securely storing encryption keys and ensuring hardware-based security that resists tampering and unauthorized access at a deeper level. BIOS passwords lack the advanced encryption and integrity verification features found in TPM, making them more vulnerable to sophisticated attacks despite their ease of implementation and management.
TPM Advantages and Potential Vulnerabilities
TPM (Trusted Platform Module) enhances security by providing hardware-based encryption and secure storage of cryptographic keys, making it more resistant to software attacks compared to BIOS passwords that rely solely on firmware protection. TPM supports secure boot and platform integrity verification, which prevents unauthorized firmware or OS modification, whereas BIOS passwords can be bypassed through physical access or reset methods. However, TPM faces potential vulnerabilities such as firmware exploits or side-channel attacks that can compromise its security if not properly managed or updated.
Choosing Between BIOS Password and TPM
Choosing between BIOS password and TPM depends on the security needs of a system; BIOS password restricts unauthorized boot access while TPM provides hardware-based encryption and integrity checks. TPM enhances protection by securely storing cryptographic keys, enabling features like BitLocker and secure boot, which BIOS password alone cannot achieve. For comprehensive security, leveraging TPM is preferable, but BIOS password remains a simple first-layer defense against unauthorized access.
Combining BIOS Password and TPM for Enhanced Security
Combining a BIOS password with TPM (Trusted Platform Module) significantly enhances system security by requiring both user authentication and hardware-level encryption. The BIOS password restricts unauthorized access to the system setup, preventing changes to boot settings, while TPM securely stores cryptographic keys essential for hardware-based encryption and platform integrity verification. This dual-layer protection mitigates risks such as unauthorized firmware alterations and unauthorized access to encrypted data, ensuring comprehensive defense against firmware attacks and data breaches.
BIOS Password Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com