Torrenting allows fast and efficient file sharing via peer-to-peer (P2P) networks, where data is distributed across multiple users rather than a single server. This method is popular for downloading large files such as movies, software, and music with reduced server load and enhanced speed. Discover how torrenting works, its legal implications, and how to stay safe by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
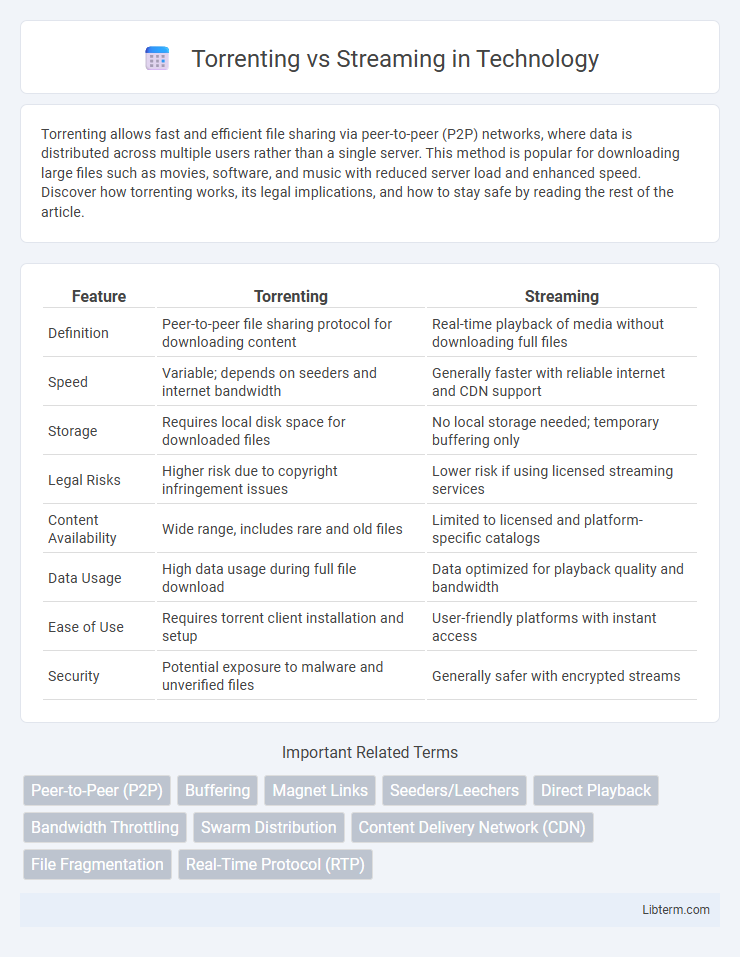
| Feature | Torrenting | Streaming |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Peer-to-peer file sharing protocol for downloading content | Real-time playback of media without downloading full files |
| Speed | Variable; depends on seeders and internet bandwidth | Generally faster with reliable internet and CDN support |
| Storage | Requires local disk space for downloaded files | No local storage needed; temporary buffering only |
| Legal Risks | Higher risk due to copyright infringement issues | Lower risk if using licensed streaming services |
| Content Availability | Wide range, includes rare and old files | Limited to licensed and platform-specific catalogs |
| Data Usage | High data usage during full file download | Data optimized for playback quality and bandwidth |
| Ease of Use | Requires torrent client installation and setup | User-friendly platforms with instant access |
| Security | Potential exposure to malware and unverified files | Generally safer with encrypted streams |
Introduction to Torrenting and Streaming
Torrenting involves downloading and sharing files via a peer-to-peer (P2P) network, allowing multiple users to upload and download parts of a file simultaneously, which can result in faster transfer speeds and reduced server load. Streaming delivers content in real-time from a centralized server to a user's device without storing the entire file locally, enabling immediate playback of videos, music, or live broadcasts. Both methods have distinct technical mechanisms and legal implications influenced by the source of the content and the user's location.
How Torrenting Works
Torrenting works by breaking large files into smaller pieces, which are shared across a peer-to-peer (P2P) network, enabling users to download and upload simultaneously. Each participant, or "peer," acts as both a downloader and an uploader, distributing fragments of the file to others, which enhances download speeds and redundancy. The process relies on a BitTorrent client to manage connections, assemble downloaded pieces, and communicate with tracker servers that coordinate the exchange of data among peers.
How Streaming Works
Streaming delivers multimedia content by continuously transmitting data packets from servers to users' devices in real-time, allowing playback to begin before the entire file is downloaded. This process relies on adaptive bitrate streaming, which adjusts video quality dynamically based on internet speed and device capabilities to reduce buffering. Content delivery networks (CDNs) play a crucial role by distributing data geographically closer to users, enhancing streaming efficiency and reducing latency.
Pros and Cons of Torrenting
Torrenting offers the advantage of accessing a vast range of content offline with high download speeds and no reliance on continuous internet connectivity. However, it carries risks such as potential exposure to malware, slower download times if seeders are limited, and possible legal issues due to copyright infringement. Users must weigh these factors against the convenience and legality of streaming services, which provide instant access but often require stable internet and may have restrictions on content use.
Pros and Cons of Streaming
Streaming offers instant access to a vast library of content without requiring downloads or storage space, making it highly convenient for users with limited device capacity. However, streaming depends heavily on a stable, high-speed internet connection, which can lead to buffering issues and degraded video quality if the connection is poor. Additionally, streaming services often require recurring subscription fees, whereas torrenting may provide content without direct costs but comes with legal and security risks.
Legal Implications: Torrenting vs Streaming
Torrenting often involves downloading files from peer-to-peer networks, which can lead to legal risks if the content is copyrighted and shared without permission. Streaming typically involves real-time access to content hosted on licensed platforms, reducing direct legal exposure but still potentially infringing copyright if the source is unlicensed. Understanding copyright laws and using authorized services is crucial to avoid legal consequences in both torrenting and streaming.
Content Availability and Selection
Torrenting offers vast content availability by enabling access to an extensive library of movies, TV shows, music, and software from around the world, often including rare and outdated titles not found on mainstream platforms. Streaming services provide a curated selection of licensed content that is easily accessible with high-quality playback but may have regional restrictions and limited catalogs compared to torrent networks. The choice between torrenting and streaming largely depends on the user's need for specific or obscure content versus convenience and legality of access.
Quality and Speed Comparison
Torrenting offers the potential for higher video quality since files are downloaded in full, allowing access to lossless or high-resolution content without buffering interruptions. Streaming depends heavily on internet speed and server bandwidth, often adjusting quality dynamically to prevent lag but potentially reducing resolution during peak times. Speed-wise, torrent downloads can be faster for large files if multiple seeds are available, while streaming provides instant playback but may suffer from buffering on slower connections.
Security and Privacy Concerns
Torrenting often exposes users to higher security risks due to peer-to-peer sharing, which can lead to IP address exposure and potential malware infections. Streaming typically offers better privacy protection since content is delivered from centralized servers, reducing the risk of direct peer exposure, but users still face data tracking by streaming platforms. Both activities require the use of VPNs to enhance anonymity and safeguard personal information from third-party surveillance and cyber threats.
Which Is Better: Torrenting or Streaming?
Torrenting offers the advantage of offline access to files and typically faster download speeds due to peer-to-peer sharing, but it requires storage space and poses higher risks of malware and copyright infringement. Streaming provides instant access to content without storage needs and is generally safer, with platforms offering high-quality video and real-time updates, though it relies heavily on stable internet connections and may involve buffering. Choosing between torrenting and streaming depends on factors such as internet speed, data limits, content availability, device storage, and legal considerations regarding copyright compliance.
Torrenting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com