Effective security management involves identifying potential risks, implementing protective measures, and continuously monitoring systems to safeguard assets and information. Integrating advanced technologies and maintaining employee awareness are critical for mitigating threats and ensuring organizational resilience. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical strategies for enhancing your security management practices.
Table of Comparison
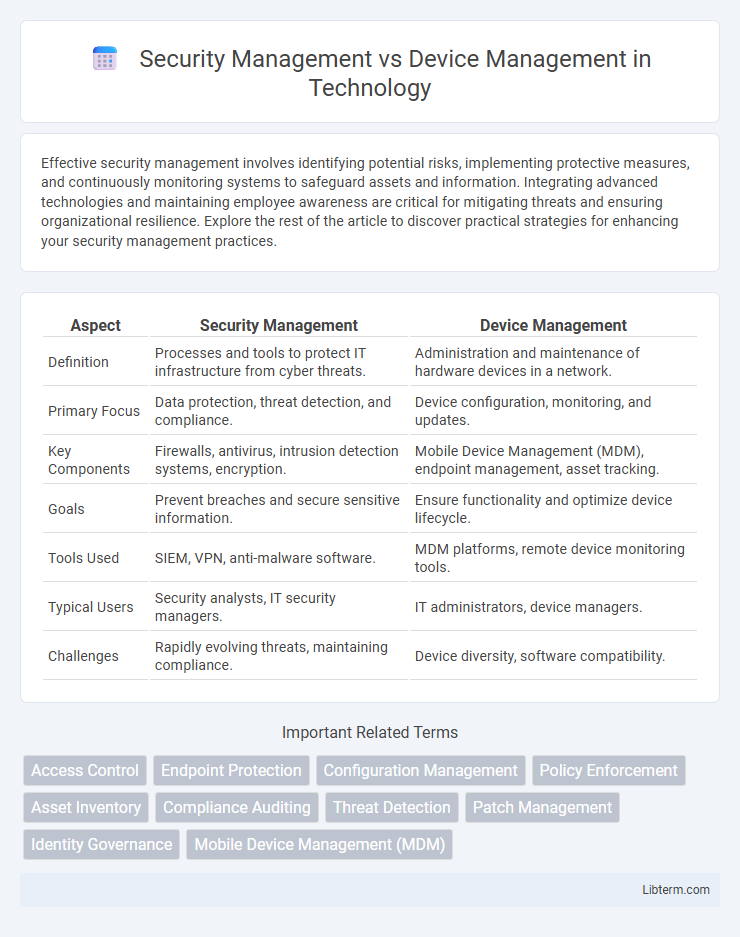
| Aspect | Security Management | Device Management |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Processes and tools to protect IT infrastructure from cyber threats. | Administration and maintenance of hardware devices in a network. |
| Primary Focus | Data protection, threat detection, and compliance. | Device configuration, monitoring, and updates. |
| Key Components | Firewalls, antivirus, intrusion detection systems, encryption. | Mobile Device Management (MDM), endpoint management, asset tracking. |
| Goals | Prevent breaches and secure sensitive information. | Ensure functionality and optimize device lifecycle. |
| Tools Used | SIEM, VPN, anti-malware software. | MDM platforms, remote device monitoring tools. |
| Typical Users | Security analysts, IT security managers. | IT administrators, device managers. |
| Challenges | Rapidly evolving threats, maintaining compliance. | Device diversity, software compatibility. |
Understanding Security Management
Security Management involves safeguarding an organization's data, networks, and systems against unauthorized access, threats, and vulnerabilities through policies, risk assessment, and continuous monitoring. It prioritizes data confidentiality, integrity, and availability while enforcing access controls and compliance with regulatory standards. Unlike Device Management, which focuses on configuring, monitoring, and maintaining hardware devices, Security Management holistically protects the IT environment from cyberattacks and internal breaches.
What is Device Management?
Device management refers to the administration and oversight of physical and virtual devices within an IT environment, ensuring optimal performance, security, and compliance. It involves tasks such as device provisioning, configuration, monitoring, software updates, and remote troubleshooting to maintain operational efficiency. Effective device management reduces the risk of security breaches by enforcing policies and managing device lifecycles across endpoints like smartphones, laptops, and IoT devices.
Key Differences Between Security and Device Management
Security management focuses on protecting systems, data, and networks from unauthorized access, threats, and vulnerabilities through policies, risk assessments, and compliance monitoring. Device management involves the deployment, configuration, monitoring, and maintenance of hardware devices such as smartphones, laptops, and IoT devices to ensure operational efficiency and consistent performance. The key difference lies in security management's goal to safeguard digital assets and enforce security protocols, whereas device management emphasizes managing the lifecycle and functionality of physical devices within an organization.
Core Functions of Security Management
Security Management focuses on protecting organizational assets by implementing risk assessment, policy enforcement, incident response, and continuous monitoring to prevent unauthorized access and cyber threats. Device Management, in contrast, primarily deals with the configuration, maintenance, and lifecycle management of hardware and software devices within a network. Core functions of Security Management include identity and access management, threat detection, vulnerability management, and compliance auditing to ensure robust defense mechanisms across IT infrastructure.
Essential Features of Device Management
Device Management emphasizes essential features like remote configuration, real-time monitoring, automated updates, and secure onboarding to maintain device integrity and operational efficiency. Security Management prioritizes threat detection, vulnerability assessment, access control, and incident response to safeguard the overall IT environment. Effective Device Management integrates asset inventory, firmware management, and compliance reporting to streamline device lifecycle and reduce operational risks.
Importance of Security Management in Modern IT
Security Management is crucial in modern IT as it safeguards sensitive data, prevents cyberattacks, and ensures regulatory compliance through continuous monitoring and risk assessment. Unlike Device Management, which focuses on configuring and maintaining hardware and software assets, Security Management addresses vulnerabilities and protects networks from increasingly sophisticated threats. Effective Security Management reduces downtime, preserves organizational reputation, and supports business continuity in an evolving digital landscape.
Role of Device Management in Enterprise Environments
Device Management plays a crucial role in enterprise environments by ensuring the proper configuration, monitoring, and maintenance of all connected hardware, which enhances operational efficiency and reduces downtime. It facilitates seamless integration of various devices, enforces compliance with corporate policies, and supports real-time updates and patch management to protect against vulnerabilities. Effective Device Management complements Security Management by providing granular control over device access and mitigating risks associated with unauthorized or compromised hardware.
Challenges in Security Management
Security management faces challenges such as evolving cyber threats, complex compliance requirements, and the need for continuous monitoring and incident response. Unlike device management, which primarily deals with inventory and configuration, security management must address vulnerability assessment, risk mitigation, and user access control. Ensuring real-time threat detection while balancing usability and data protection remains a critical and ongoing challenge.
Best Practices for Device Management
Effective device management prioritizes regular software updates, robust endpoint protection, and strict access controls to safeguard corporate assets. Implementing comprehensive asset inventory systems and real-time monitoring enhances visibility, enabling rapid detection and response to threats. Adopting automated device configuration and compliance policies ensures consistency across all devices and reduces human error, strengthening overall security posture.
Integrating Security and Device Management for Comprehensive Protection
Integrating security management and device management enhances comprehensive protection by enabling centralized control over device configurations, access policies, and threat detection. Unified platforms streamline monitoring and proactive response to vulnerabilities, ensuring consistent enforcement of security protocols across all endpoints. This holistic approach reduces gaps in defenses and improves compliance with regulatory standards through coordinated updates and incident management.
Security Management Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com