Security audits assess your organization's systems, policies, and procedures to identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with industry standards. Regular audits help mitigate risks, protect sensitive data, and improve overall cybersecurity posture. Explore the full article to learn how a thorough security audit can safeguard your business.
Table of Comparison
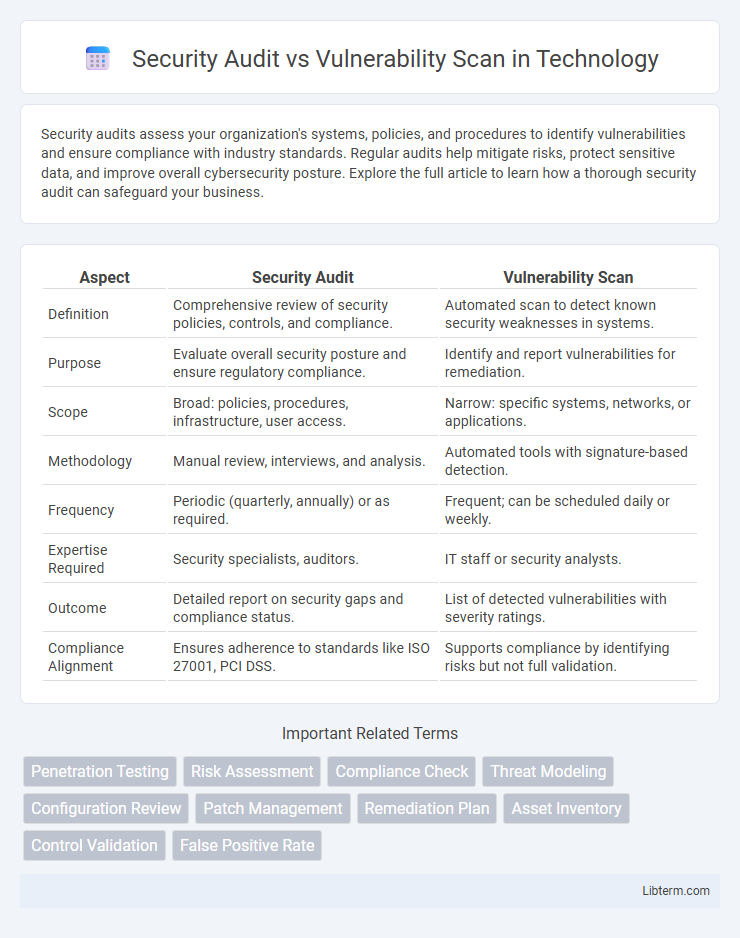
| Aspect | Security Audit | Vulnerability Scan |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Comprehensive review of security policies, controls, and compliance. | Automated scan to detect known security weaknesses in systems. |
| Purpose | Evaluate overall security posture and ensure regulatory compliance. | Identify and report vulnerabilities for remediation. |
| Scope | Broad: policies, procedures, infrastructure, user access. | Narrow: specific systems, networks, or applications. |
| Methodology | Manual review, interviews, and analysis. | Automated tools with signature-based detection. |
| Frequency | Periodic (quarterly, annually) or as required. | Frequent; can be scheduled daily or weekly. |
| Expertise Required | Security specialists, auditors. | IT staff or security analysts. |
| Outcome | Detailed report on security gaps and compliance status. | List of detected vulnerabilities with severity ratings. |
| Compliance Alignment | Ensures adherence to standards like ISO 27001, PCI DSS. | Supports compliance by identifying risks but not full validation. |
Introduction: Understanding Security Audits and Vulnerability Scans
Security audits involve a comprehensive evaluation of an organization's security policies, procedures, and controls to ensure compliance and identify potential risks. Vulnerability scans use automated tools to detect known weaknesses and vulnerabilities in systems, networks, or applications. Combining both approaches strengthens overall security posture by addressing both policy effectiveness and technical vulnerabilities.
Defining Security Audit
A Security Audit is a comprehensive evaluation of an organization's information systems, policies, and procedures to assess compliance with security standards and identify potential risks. It involves a structured review process conducted by internal or external auditors who examine security controls, configurations, and access management. Unlike a Vulnerability Scan that automatically detects security weaknesses, a Security Audit provides an in-depth analysis that includes risk assessment and recommendations for remediation.
What is a Vulnerability Scan?
A vulnerability scan is an automated process that identifies security weaknesses within a network, system, or application by detecting known vulnerabilities and misconfigurations. It uses specialized software tools to examine devices, operating systems, and applications for security flaws that could be exploited by attackers. Unlike a security audit, which involves a comprehensive and manual review of security policies, controls, and procedures, a vulnerability scan provides a snapshot of technical vulnerabilities to facilitate timely remediation.
Key Differences Between Security Audits and Vulnerability Scans
Security audits provide a comprehensive evaluation of an organization's security policies, procedures, and technical controls, ensuring alignment with compliance standards and risk management objectives. Vulnerability scans focus on automated detection of known security weaknesses in systems and networks, identifying potential entry points for cyberattacks without assessing overall security posture. Key differences include scope, depth, and methodology: security audits are manual, thorough, and compliance-driven, while vulnerability scans are automated, surface-level, and threat-focused tools.
Scope and Depth of Analysis
Security audits involve comprehensive evaluations of an organization's security policies, procedures, and controls, assessing compliance with industry standards and regulatory requirements. Vulnerability scans focus on automated identification of known security weaknesses in systems and networks, providing a broader but shallower analysis limited to detectable vulnerabilities. While security audits deliver in-depth insights through manual reviews and interviews, vulnerability scans offer rapid detection across numerous assets without deep contextual understanding.
Frequency and Timing Considerations
Security audits are typically conducted periodically, such as annually or biannually, to provide a comprehensive evaluation of an organization's overall security posture. Vulnerability scans occur more frequently, often weekly or monthly, to identify new threats and weaknesses in real-time or near real-time. Timing the security audit to align with regulatory requirements and major system updates ensures thorough assessment, while frequent vulnerability scans facilitate proactive risk management and rapid remediation.
Tools and Techniques Used
Security audits employ comprehensive methodologies, including manual code reviews, configuration assessments, and policy compliance checks, utilizing tools such as Nessus, Qualys, and manual penetration testing frameworks like Metasploit. Vulnerability scans primarily rely on automated software tools such as OpenVAS, Nexpose, and Rapid7 to identify known security flaws by scanning systems against updated vulnerability databases. Techniques in security audits emphasize thorough analysis and expert evaluation, whereas vulnerability scans focus on rapid detection of vulnerabilities using signature-based detection methods.
When to Choose a Security Audit
Security audits should be chosen when organizations require a comprehensive evaluation of their security policies, procedures, and controls to ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations like ISO 27001 or HIPAA. These audits provide in-depth analysis, including risk assessment and penetration testing, enabling identification and remediation of complex vulnerabilities beyond the scope of automated scans. Security audits are ideal before major software deployments, during regulatory reviews, or when a thorough governance and risk management assessment is necessary.
When to Opt for a Vulnerability Scan
Opt for a vulnerability scan when the goal is to identify and prioritize potential security weaknesses quickly across networks, systems, or applications, typically in routine or automated assessments. Vulnerability scans are best suited for continuous monitoring, compliance checks, and early detection of common threats without the depth or manual intervention required in security audits. This approach allows organizations to maintain baseline security hygiene and address emerging vulnerabilities before escalating to more comprehensive security audits.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Approach for Your Organization
Choosing between a security audit and a vulnerability scan depends on your organization's specific risk profile, compliance requirements, and cybersecurity goals. Security audits provide comprehensive assessments including policy reviews and process evaluations, ideal for regulatory compliance and strategic security improvements. Vulnerability scans offer automated and frequent detection of technical weaknesses, useful for ongoing threat identification and rapid remediation efforts.
Security Audit Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com