Data masking protects sensitive information by replacing original data with realistic but fictional values, ensuring privacy during software testing or data analysis. It helps organizations comply with data protection regulations while minimizing the risk of data breaches. Discover how data masking can safeguard your information and enhance security in the full article.
Table of Comparison
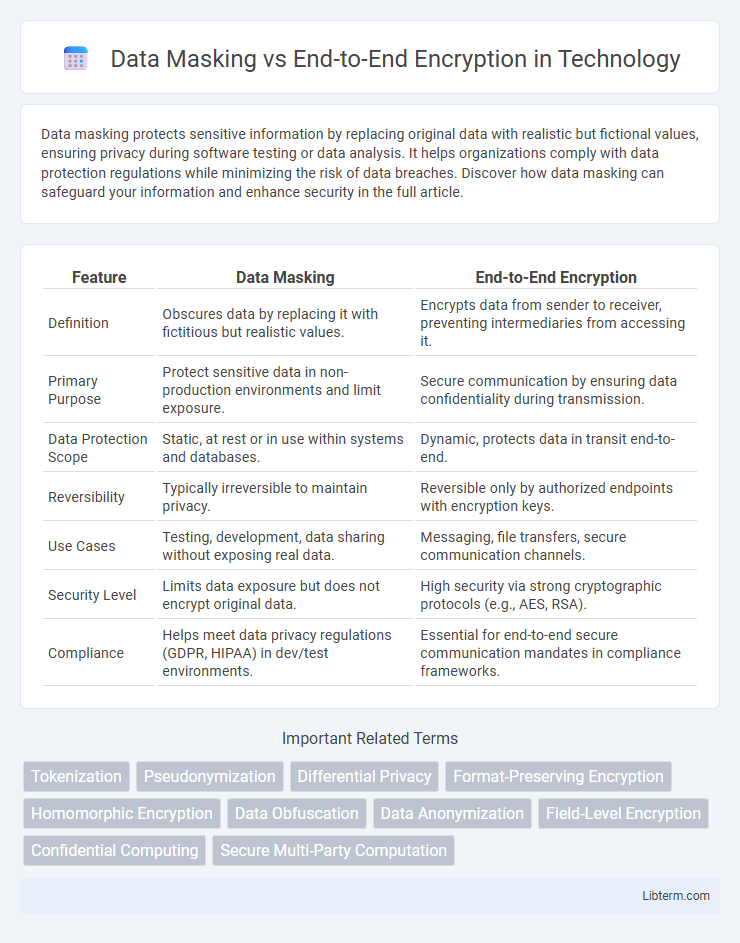
| Feature | Data Masking | End-to-End Encryption |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Obscures data by replacing it with fictitious but realistic values. | Encrypts data from sender to receiver, preventing intermediaries from accessing it. |
| Primary Purpose | Protect sensitive data in non-production environments and limit exposure. | Secure communication by ensuring data confidentiality during transmission. |
| Data Protection Scope | Static, at rest or in use within systems and databases. | Dynamic, protects data in transit end-to-end. |
| Reversibility | Typically irreversible to maintain privacy. | Reversible only by authorized endpoints with encryption keys. |
| Use Cases | Testing, development, data sharing without exposing real data. | Messaging, file transfers, secure communication channels. |
| Security Level | Limits data exposure but does not encrypt original data. | High security via strong cryptographic protocols (e.g., AES, RSA). |
| Compliance | Helps meet data privacy regulations (GDPR, HIPAA) in dev/test environments. | Essential for end-to-end secure communication mandates in compliance frameworks. |
Introduction to Data Masking and End-to-End Encryption
Data masking hides sensitive data by replacing original information with obfuscated values, ensuring data privacy during use or testing without exposing real data. End-to-end encryption secures data by encoding it from the sender directly to the intended recipient, preventing unauthorized access during transmission and storage. Both techniques protect sensitive information but apply different methods and scopes within data security frameworks.
Key Differences Between Data Masking and End-to-End Encryption
Data masking obscures sensitive information by replacing original data with fictitious yet realistic values, ensuring confidentiality in non-production environments, while end-to-end encryption secures data by converting it into unreadable ciphertext during transmission and storage, only decryptable by authorized recipients. Data masking primarily serves to protect data privacy during testing and development, whereas end-to-end encryption safeguards data integrity and confidentiality across communication channels. Key differences include their application scope, with masking applied to data at rest and testing scenarios, and encryption applied for secure data in transit and at rest, emphasizing different security objectives.
Core Principles of Data Masking
Data masking obscures sensitive information by replacing original data with realistic but fictitious values, ensuring privacy while maintaining data utility for non-production environments. It focuses on preserving data format and structure to support testing and analytics without exposing actual data, minimizing risk during data sharing or analysis. Core principles include deterministic masking for consistent results, reversible or irreversible methods depending on use case, and compliance with data protection regulations.
Core Principles of End-to-End Encryption
End-to-End Encryption (E2EE) ensures that data is encrypted on the sender's device and only decrypted on the recipient's device, preventing intermediaries from accessing the information. This core principle relies on cryptographic key pairs, where only the communicating parties hold the private keys necessary for decryption, maintaining data confidentiality and integrity across the transmission path. Unlike Data Masking, which obfuscates data for testing or privacy by altering values, E2EE secures actual data in transit and at rest without exposing it in any readable form to unauthorized users.
Use Cases for Data Masking
Data masking is primarily used to protect sensitive data in non-production environments such as development, testing, and training, ensuring that realistic but obfuscated data is available without exposing confidential information. It is essential for compliance in industries like healthcare, finance, and retail, where privacy regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS require masking of personally identifiable information (PII) and payment data in datasets accessed by developers or analysts. Unlike end-to-end encryption, which secures data during transmission and storage, data masking offers a controlled approach to anonymizing data within internal workflows while maintaining usability for analysis and software testing.
Use Cases for End-to-End Encryption
End-to-End Encryption (E2EE) is essential for securing sensitive communications in healthcare, financial services, and messaging apps, ensuring data remains confidential from sender to recipient. Unlike data masking, which obscures data for testing and development environments, E2EE protects data in transit and storage, preventing interception by unauthorized parties. This encryption method is widely used in secure email, instant messaging, and payment processing to maintain data integrity and privacy.
Advantages and Limitations of Data Masking
Data masking enhances data security by obfuscating sensitive information, allowing safe use of data in non-secure environments without exposing original values, which is essential for development and testing phases. It prevents unauthorized access to critical data but does not protect data in transit or at rest, making it less comprehensive than end-to-end encryption. Limitations of data masking include the risk of data utility loss due to altered data and the complexity of maintaining mask consistency across dynamic datasets.
Pros and Cons of End-to-End Encryption
End-to-End Encryption (E2EE) ensures that data is encrypted on the sender's device and only decrypted on the recipient's device, providing robust protection against interception and unauthorized access throughout data transmission. Its primary advantage lies in privacy assurance, making it ideal for sensitive communications like financial transactions and personal messaging, but challenges include increased computational overhead and complexity in key management. A notable drawback is the limitation on data processing by intermediaries, which can hinder functionalities such as data analytics or compliance monitoring in enterprise environments.
When to Choose Data Masking Over End-to-End Encryption
Data masking is preferred when organizations need to protect sensitive data in non-production environments or share data with external parties without exposing real information, ensuring usability by obfuscating data while maintaining format and type. It is ideal for testing, development, and training where realistic but non-sensitive data is required, reducing risks of data breaches without the computational overhead of encryption. End-to-end encryption, however, is better suited for securing data in transit or storage, guaranteeing confidentiality by rendering data unreadable to unauthorized users.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Data Protection Strategy
Selecting the right data protection strategy depends on the specific use case and regulatory requirements. Data masking is ideal for creating realistic, anonymized datasets for testing or analytics without exposing sensitive information. End-to-end encryption ensures data confidentiality during transmission and storage, providing strong security for communication and compliance-critical environments.
Data Masking Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com