Choosing Your Own Device (CYOD) empowers employees to select from approved devices, balancing personalization with corporate security. This approach enhances productivity while maintaining control over data protection and compliance. Discover how implementing CYOD can streamline your organization's IT strategy by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
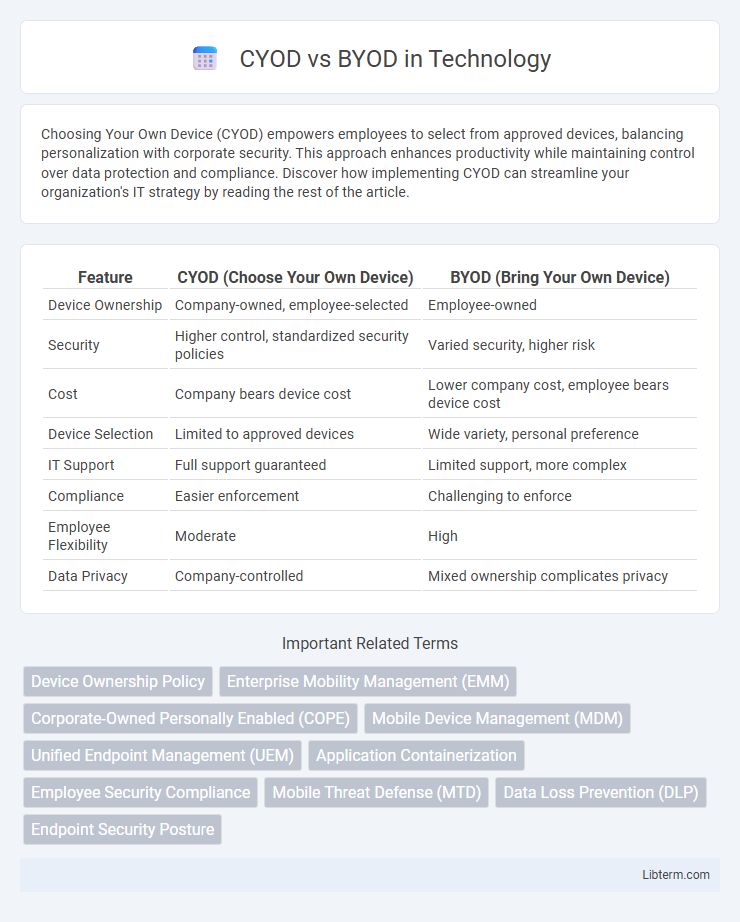
| Feature | CYOD (Choose Your Own Device) | BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) |
|---|---|---|
| Device Ownership | Company-owned, employee-selected | Employee-owned |
| Security | Higher control, standardized security policies | Varied security, higher risk |
| Cost | Company bears device cost | Lower company cost, employee bears device cost |
| Device Selection | Limited to approved devices | Wide variety, personal preference |
| IT Support | Full support guaranteed | Limited support, more complex |
| Compliance | Easier enforcement | Challenging to enforce |
| Employee Flexibility | Moderate | High |
| Data Privacy | Company-controlled | Mixed ownership complicates privacy |
Introduction to CYOD and BYOD
Choose Your Own Device (CYOD) and Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) represent two prevalent mobile device management strategies in modern workplaces. CYOD allows employees to select from a curated list of company-approved devices, ensuring security and compatibility, while BYOD permits employees to use their personal devices, offering flexibility but presenting potential security challenges. Both models impact IT policies, data protection, and user experience, with CYOD emphasizing control and BYOD prioritizing user autonomy.
Definitions: What Is CYOD? What Is BYOD?
Choose Your Own Device (CYOD) is a corporate policy allowing employees to select from a predefined list of company-approved devices, balancing security and user preference. Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) permits employees to use their personal devices for work purposes, offering flexibility but increasing potential security risks. Both approaches impact IT management, data protection, and employee productivity in distinct ways.
Key Differences Between CYOD and BYOD
Choose Your Own Device (CYOD) policies provide employees with a curated selection of company-approved devices, ensuring standardized security and easier IT management. Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies allow employees to use personal devices for work, increasing flexibility but raising significant security and compliance challenges. Key differences include control over device selection, with CYOD enhancing data protection through uniform security protocols, whereas BYOD demands robust endpoint security measures to mitigate risks from diverse device environments.
Advantages of CYOD for Businesses
Choose Your Own Device (CYOD) enhances business security by allowing companies to control the selection of devices while offering employees flexibility, reducing risks associated with unauthorized hardware. CYOD streamlines IT support and maintenance through standardized device models and software configurations, leading to lower operational costs and improved system reliability. Employee productivity benefits from CYOD as the pre-approved devices ensure compatibility with corporate applications and secure access to company resources.
Benefits of BYOD for Employees
BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) empowers employees by allowing the use of personal smartphones, tablets, and laptops, enhancing flexibility and comfort in their work environment. This approach often leads to increased productivity and job satisfaction due to familiarity with devices and personalized setups. Cost savings for employees arise from eliminating the need for additional work-specific hardware investments.
Security Implications: CYOD vs BYOD
CYOD (Choose Your Own Device) offers enhanced security by allowing IT departments to pre-select and configure devices with standardized security policies, reducing vulnerabilities related to device fragmentation. BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) introduces increased security risks due to diverse, unmanaged devices accessing corporate networks, making data protection and threat containment more complex. Endpoint security, data encryption, and consistent policy enforcement are more effectively maintained under CYOD frameworks compared to the decentralized nature of BYOD environments.
Cost Considerations and ROI Comparison
Choose Your Own Device (CYOD) often results in higher upfront costs due to standardized device procurement and management but enables better control over security and support, reducing long-term expenses. Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) lowers initial investments by leveraging employee-owned devices but can increase costs related to security vulnerabilities, IT support, and compliance risks. Evaluating the return on investment (ROI) requires analyzing total cost of ownership, including device procurement, maintenance, security measures, and productivity impacts, with CYOD typically delivering higher ROI for organizations prioritizing security and operational consistency.
User Experience and Employee Satisfaction
Choose Your Own Device (CYOD) enhances user experience by providing employees with a curated selection of company-approved devices that balance personal preference andIT security, leading to higher satisfaction through better performance and compatibility. Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) offers greater freedom and familiarity since employees use personal devices, but it may result in inconsistent user experience due to varied hardware, software, and security constraints. Employee satisfaction tends to be higher with CYOD in environments requiring robust security and standardized IT support, while BYOD appeals more to those valuing flexibility and personal device ownership.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Implementing Choose Your Own Device (CYOD) and Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) programs presents challenges such as securing diverse device environments, managing data privacy, and ensuring compliance with corporate policies. Solutions include deploying advanced mobile device management (MDM) systems, enforcing strict access controls, and offering comprehensive employee training on security protocols. Emphasizing clear policy frameworks and robust IT support helps organizations effectively balance flexibility with security in both CYOD and BYOD models.
Choosing the Right Approach: Which Model Fits Your Organization?
Choosing between CYOD (Choose Your Own Device) and BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) hinges on an organization's security needs, budget constraints, and workforce flexibility. CYOD offers greater control and standardization by allowing employees to select from pre-approved devices, reducing IT complexity and enhancing data protection. BYOD provides cost savings and user convenience but requires robust security policies to mitigate risks associated with diverse personal devices accessing corporate networks.
CYOD Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com