Serverless computing allows you to run applications without managing underlying servers, streamlining deployment and scaling efforts. This architecture reduces operational costs and enhances flexibility by automatically allocating resources based on demand. Explore the full article to understand how serverless solutions can transform your development strategy.
Table of Comparison
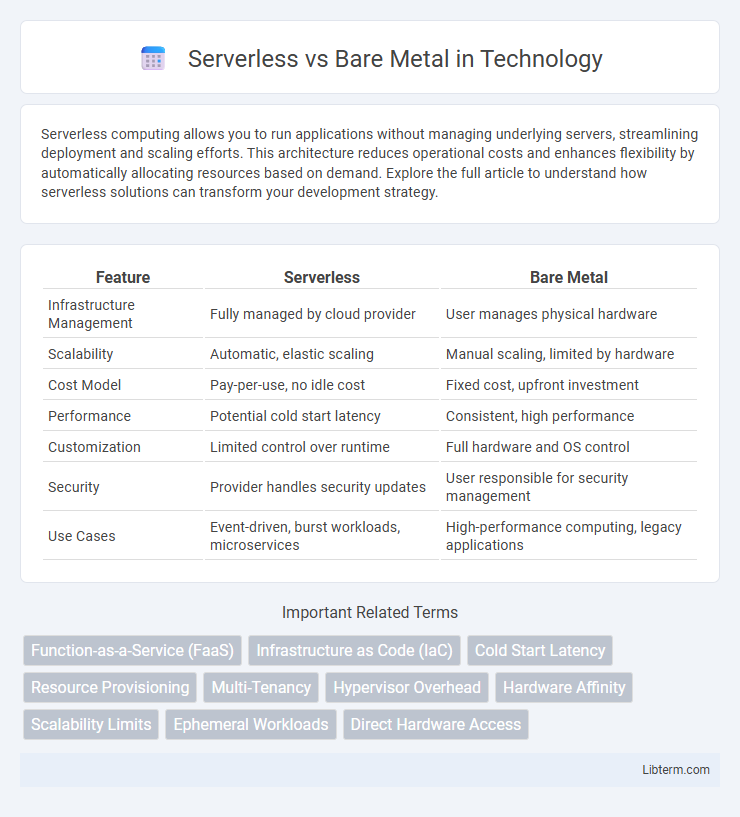
| Feature | Serverless | Bare Metal |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure Management | Fully managed by cloud provider | User manages physical hardware |
| Scalability | Automatic, elastic scaling | Manual scaling, limited by hardware |
| Cost Model | Pay-per-use, no idle cost | Fixed cost, upfront investment |
| Performance | Potential cold start latency | Consistent, high performance |
| Customization | Limited control over runtime | Full hardware and OS control |
| Security | Provider handles security updates | User responsible for security management |
| Use Cases | Event-driven, burst workloads, microservices | High-performance computing, legacy applications |
Introduction to Serverless and Bare Metal
Serverless computing allows developers to run applications without managing underlying infrastructure, automatically scaling resources based on demand and charging only for actual usage. Bare metal servers provide dedicated physical hardware, offering maximum control, performance, and security without virtualization overhead. Choosing between serverless and bare metal depends on workload requirements, with serverless suited for dynamic, event-driven applications and bare metal ideal for high-performance, resource-intensive tasks.
Key Differences Between Serverless and Bare Metal
Serverless computing eliminates the need for infrastructure management by automatically scaling resources based on demand, while bare metal involves dedicated physical servers offering full control and customization. Serverless platforms charge based on actual usage, optimizing cost efficiency, whereas bare metal requires upfront investment and ongoing maintenance expenses. Performance in bare metal is typically more consistent due to dedicated hardware, contrasting with serverless environments where resource sharing may introduce latency.
Performance Comparison: Serverless vs Bare Metal
Bare Metal servers deliver superior raw performance with direct access to hardware resources, eliminating virtualization overhead and providing consistent low-latency computing ideal for resource-intensive applications. Serverless platforms offer scalable, event-driven execution with rapid deployment but introduce latency due to cold starts and shared infrastructure, potentially impacting real-time performance. For workloads demanding predictable, high-performance throughput and low latency, Bare Metal remains the optimal choice, whereas Serverless suits dynamic scaling and cost-efficiency in variable or intermittent workloads.
Cost Efficiency and Pricing Models
Serverless computing offers a pay-as-you-go pricing model, charging based on actual compute time and resource usage, which often reduces costs by eliminating the need for overprovisioning. In contrast, bare metal servers require fixed costs for dedicated hardware, including maintenance and upfront capital expenses, making them less flexible but potentially more cost-effective for consistent, heavy workloads. Cost efficiency in serverless is optimized for variable or unpredictable workloads, while bare metal suits predictable, high-intensity applications where full resource control is critical.
Scalability and Resource Management
Serverless architectures automatically scale resources based on demand, enabling efficient handling of variable workloads without manual intervention. Bare metal servers provide dedicated hardware resources, allowing for precise resource allocation but require manual scaling and management. Serverless platforms optimize resource utilization through dynamic provisioning, whereas bare metal offers consistent performance at the cost of flexibility in scalability.
Security Considerations and Best Practices
Serverless environments abstract infrastructure management, reducing attack surface by limiting OS and network access compared to bare metal servers which require comprehensive patching and configuration to prevent vulnerabilities. Implementing strict IAM policies, encrypting data at rest and in transit, and continuous monitoring are essential security best practices in serverless architectures, while bare metal demands robust isolation, regular hardware audits, and network segmentation to mitigate risks. Both models necessitate proactive threat detection, but serverless benefits from cloud provider security frameworks, whereas bare metal relies heavily on in-house security protocols and physical security controls.
Deployment and Maintenance Complexity
Serverless deployment significantly reduces maintenance complexity by abstracting infrastructure management, enabling automatic scaling and seamless updates without manual intervention. In contrast, bare metal deployment demands extensive manual configuration, continuous hardware management, and hands-on scaling efforts, increasing operational overhead. Serverless environments optimize rapid deployment cycles while bare metal provides granular control at the cost of higher complexity in maintenance and deployment processes.
Ideal Use Cases for Serverless
Serverless computing excels in applications with variable or unpredictable workloads, such as event-driven architectures, microservices, and real-time data processing, due to its automatic scaling and cost-efficiency. It is ideal for startups and small teams aiming to reduce infrastructure management overhead while accelerating deployment cycles. High-throughput, short-duration tasks like APIs, chatbots, and IoT device interactions benefit from serverless platforms like AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, and Google Cloud Functions.
When to Choose Bare Metal Solutions
Choose bare metal solutions for workloads demanding maximum performance, low latency, and full hardware control, such as high-frequency trading, scientific simulations, or gaming servers. Enterprises requiring dedicated resources for compliance, security, or custom hardware configurations benefit from bare metal's isolation and customization capabilities. Bare metal is optimal when predictable, consistent performance is critical, avoiding the overhead and variability inherent in virtualized or serverless environments.
Future Trends in Serverless and Bare Metal Computing
Future trends in serverless computing emphasize enhanced scalability, improved cost efficiency, and tighter integration with AI and machine learning workloads, enabling developers to focus more on code and less on infrastructure management. Meanwhile, bare metal computing advances with greater hardware customization, increased performance for latency-sensitive applications, and stronger security measures, catering to industries requiring direct hardware access and deterministic resource allocation. Hybrid approaches combining serverless flexibility with bare metal control are emerging to meet diverse enterprise demands and optimize workload deployment.
Serverless Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com