Device Authorization Grant streamlines user authentication on devices with limited input capabilities by enabling secure access without entering credentials directly. This OAuth 2.0 flow supports seamless authorization, enhancing user experience while maintaining robust security standards. Discover how this grant type can improve Your device interaction and security by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
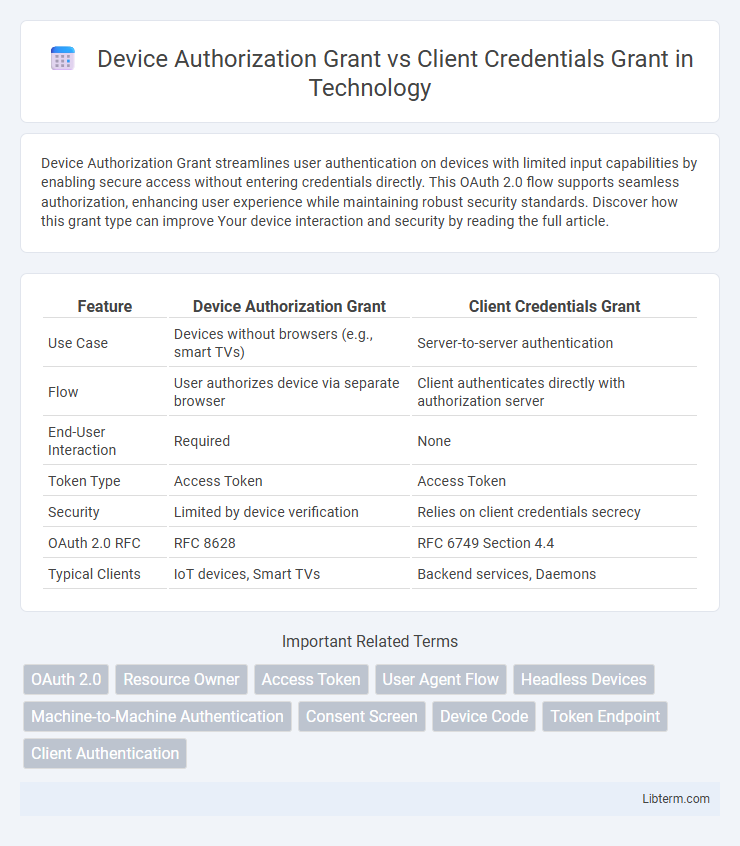
| Feature | Device Authorization Grant | Client Credentials Grant |
|---|---|---|
| Use Case | Devices without browsers (e.g., smart TVs) | Server-to-server authentication |
| Flow | User authorizes device via separate browser | Client authenticates directly with authorization server |
| End-User Interaction | Required | None |
| Token Type | Access Token | Access Token |
| Security | Limited by device verification | Relies on client credentials secrecy |
| OAuth 2.0 RFC | RFC 8628 | RFC 6749 Section 4.4 |
| Typical Clients | IoT devices, Smart TVs | Backend services, Daemons |
Introduction to OAuth 2.0 Grant Types
OAuth 2.0 grant types enable secure authorization flows tailored for different use cases. Device Authorization Grant allows users to authorize devices without input capabilities by using a secondary device for authentication. Client Credentials Grant is designed for server-to-server interactions, where applications request access tokens using their own credentials without involving a user.
Overview of Device Authorization Grant
Device Authorization Grant enables user authentication on devices with limited input capabilities by allowing users to authorize via a separate device. It involves a user code and verification URI where the user completes authorization, while the original device polls the authorization server for access tokens. This grant is essential for smart TVs, IoT devices, and other platforms lacking traditional input methods, ensuring secure and user-friendly access without exposing client credentials.
Overview of Client Credentials Grant
Client Credentials Grant is an OAuth 2.0 flow used for server-to-server authentication, enabling applications to obtain access tokens without user involvement. It requires the client to authenticate using its own credentials, typically client ID and client secret, to request an access token directly from the authorization server. This grant type is ideal for secure backend communication and automated processes where user context is unnecessary.
Key Differences Between Device Authorization and Client Credentials Grants
Device Authorization Grant enables user authentication on input-constrained devices by allowing users to authorize access through a secondary device, whereas Client Credentials Grant is designed for server-to-server authentication without user involvement. The Device Authorization Grant involves user interaction and polling mechanisms for token retrieval, contrasting with Client Credentials Grant's direct token issuance based on client identity and secret. Security considerations differ, as Device Authorization Grant accommodates untrusted clients via user consent, while Client Credentials Grant relies on secure storage of client credentials within trusted environments.
Ideal Use Cases for Device Authorization Grant
The Device Authorization Grant is ideal for devices with limited input capabilities, such as smart TVs, gaming consoles, and IoT devices, enabling users to authorize access through a separate device with an easier input method. Unlike the Client Credentials Grant, which is suited for server-to-server authentication without user involvement, the Device Authorization Grant supports user-centric authorization flows on constrained devices. This grant enhances security by requiring user interaction on a secondary device, making it well-suited for scenarios where direct device authentication is impractical.
Ideal Use Cases for Client Credentials Grant
Client Credentials Grant is ideal for server-to-server authentication where no user interaction is required, such as backend services accessing APIs or microservices communication. It excels in scenarios requiring secure, automated access to protected resources using client IDs and secrets without user context. This grant type is optimized for machine-to-machine communications, enabling efficient and scalable authentication in enterprise environments.
Security Considerations for Both Grant Types
Device Authorization Grant enhances security by enabling user authentication on a separate trusted device, minimizing the risk of credentials exposure on the input-constrained client. Client Credentials Grant relies on secure storage and management of client secrets, making it critical to protect these secrets from unauthorized access to prevent token misuse. Both grant types require robust token validation, expiration handling, and secure transmission protocols like TLS to mitigate interception and replay attacks.
Implementation Workflow Comparison
Device Authorization Grant involves a user completing authentication on a separate device after receiving a code from the first device, enabling limited-input devices to securely obtain access tokens without exposing user credentials. Client Credentials Grant requires the client application to authenticate directly with the authorization server using its own credentials, allowing server-to-server communication without user involvement. The implementation workflow of Device Authorization includes user verification via a secondary interface and polling for token retrieval, whereas Client Credentials Grant follows a straightforward token request and response cycle based on client identity validation.
Pros and Cons of Device Authorization vs Client Credentials
Device Authorization Grant offers users a streamlined login experience on input-limited devices by allowing authentication via a separate device, enhancing usability for smart TVs or IoT gadgets. However, it introduces complexity in implementation and potential delays in token acquisition compared to the Client Credentials Grant. Client Credentials Grant excels in server-to-server authentication with straightforward token exchange and lower latency but lacks user-specific context, limiting its use in scenarios requiring delegated user permissions.
Choosing the Right Grant Type for Your Application
Selecting the appropriate OAuth 2.0 grant type depends on the application's user interaction model and security requirements. Device Authorization Grant is ideal for input-constrained devices requiring user consent via secondary devices, enhancing usability without compromising security. Client Credentials Grant suits server-to-server communication where no user context exists, enabling secure, automated access to resources with client authentication.
Device Authorization Grant Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com