Edge computing processes data closer to the source rather than relying on centralized data centers, reducing latency and bandwidth use. This technology enhances real-time decision-making and supports applications such as IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, and smart cities. Discover how edge computing can transform your digital infrastructure by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
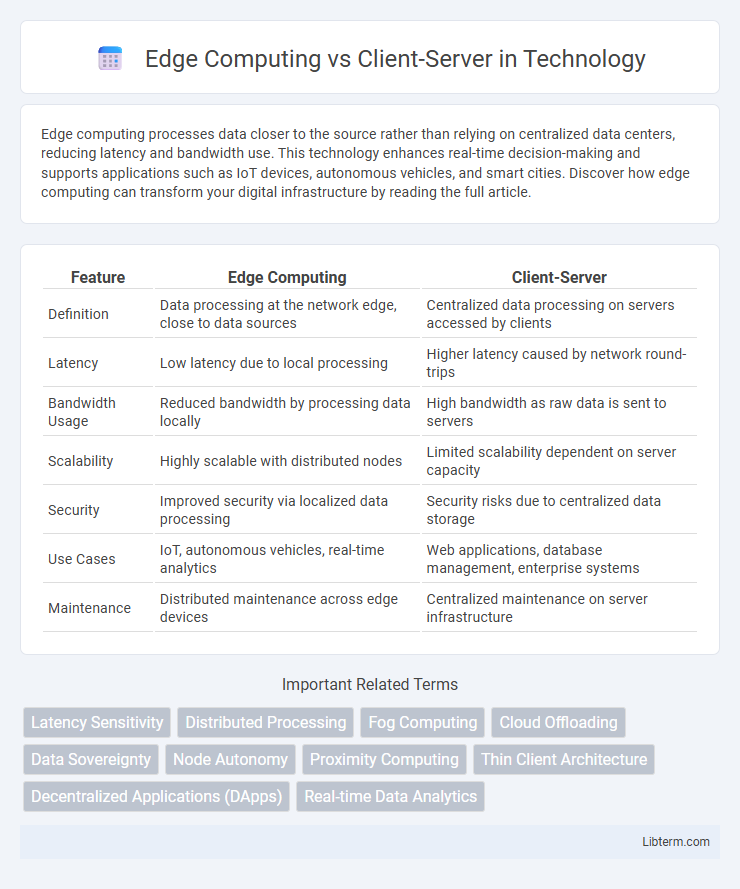
| Feature | Edge Computing | Client-Server |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Data processing at the network edge, close to data sources | Centralized data processing on servers accessed by clients |
| Latency | Low latency due to local processing | Higher latency caused by network round-trips |
| Bandwidth Usage | Reduced bandwidth by processing data locally | High bandwidth as raw data is sent to servers |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with distributed nodes | Limited scalability dependent on server capacity |
| Security | Improved security via localized data processing | Security risks due to centralized data storage |
| Use Cases | IoT, autonomous vehicles, real-time analytics | Web applications, database management, enterprise systems |
| Maintenance | Distributed maintenance across edge devices | Centralized maintenance on server infrastructure |
Introduction to Edge Computing and Client-Server Models
Edge computing processes data near the source, reducing latency and bandwidth usage by handling tasks on local devices or edge servers. The client-server model centralizes data processing on remote servers, requiring constant communication between clients and servers over networks. Edge computing enhances real-time analytics and IoT applications, while client-server models remain essential for centralized data management and complex processing.
Core Concepts: Edge Computing Explained
Edge computing processes data near the source of generation, reducing latency and bandwidth use compared to traditional client-server models that rely on centralized data centers. Core concepts include decentralized processing, real-time analytics, and enhanced security through local data handling. This paradigm improves efficiency for IoT devices and applications requiring instant responsiveness.
Core Concepts: Understanding the Client-Server Architecture
Client-server architecture is a distributed computing model where clients request services and servers provide resources or responses over a network. This model separates tasks between service providers (servers) and service requesters (clients), enabling centralized processing and resource management. Edge computing extends this paradigm by decentralizing data processing, bringing computational power closer to the client devices to reduce latency and bandwidth use.
Performance Comparison: Latency and Speed
Edge computing significantly reduces latency by processing data closer to the source, minimizing the delay often experienced in client-server architectures that rely on centralized servers. This proximity enables faster data processing and real-time analytics, making edge computing ideal for applications requiring immediate response times, such as autonomous vehicles and IoT devices. In contrast, client-server models may suffer from network congestion and longer round-trip times, impacting speed and overall performance in latency-sensitive environments.
Scalability and Flexibility Differences
Edge computing enhances scalability by distributing data processing closer to the source, reducing latency and bandwidth usage compared to traditional client-server models reliant on centralized servers. This decentralized architecture allows for greater flexibility, enabling real-time decision-making and adaptive resource allocation across diverse and geographically dispersed devices. Client-server systems often face bottlenecks and limited scalability due to reliance on fixed infrastructure, whereas edge computing supports dynamic scaling tailored to varying workload demands and network conditions.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Edge computing enhances security and privacy by processing data locally on devices or edge servers, reducing exposure to centralized data breaches common in client-server models. Sensitive data remains closer to its source, minimizing latency and the risk of interception during transmission to central servers. While client-server architectures rely on robust central security measures, edge computing demands distributed security protocols to protect multiple, often heterogeneous, endpoints from potential attacks.
Network Dependency and Reliability
Edge computing reduces network dependency by processing data locally on devices or nearby edge nodes, enhancing reliability in environments with intermittent or limited connectivity. In contrast, the client-server model relies heavily on constant network access to a centralized server, making it vulnerable to disruptions and latency issues. Edge computing offers improved responsiveness and fault tolerance by minimizing reliance on distant data centers.
Cost Implications: Edge vs Client-Server
Edge computing reduces latency and bandwidth costs by processing data locally on edge devices, minimizing the need for constant communication with central servers. Client-server models often incur higher expenses due to centralized data storage and processing, leading to increased infrastructure and maintenance costs. The decentralized nature of edge computing enables scalable cost-efficient solutions, particularly in IoT and real-time analytics applications.
Real-World Use Cases and Applications
Edge computing excels in real-world applications requiring low latency and real-time data processing, such as autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and industrial IoT, by processing data near the source instead of relying on centralized servers. Client-server architecture remains prevalent in applications demanding centralized data management and robust security, including online banking, enterprise software, and e-commerce platforms. Selecting between edge computing and client-server models depends on specific use cases, with edge optimizing for speed and locality, while client-server prioritizes centralized control and resource management.
Future Trends and Evolution of Both Models
Edge computing is evolving toward decentralized architectures that enhance real-time data processing and reduce latency by processing information closer to data sources, driven by IoT expansion and 5G networks. Client-server models continue to optimize centralized data management and security but face challenges scaling with increasing data volumes and the demand for instantaneous responsiveness. Future trends indicate hybrid systems integrating edge and client-server approaches to leverage edge's immediacy and client-server's robust resource management for scalable, efficient computing environments.
Edge Computing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com