Server-based architecture centralizes computing resources on dedicated servers, enabling efficient data management, improved security, and easier maintenance across a network. This setup supports scalability and robust performance for businesses handling large volumes of information. Explore the rest of the article to discover how server-based solutions can enhance your IT infrastructure.
Table of Comparison
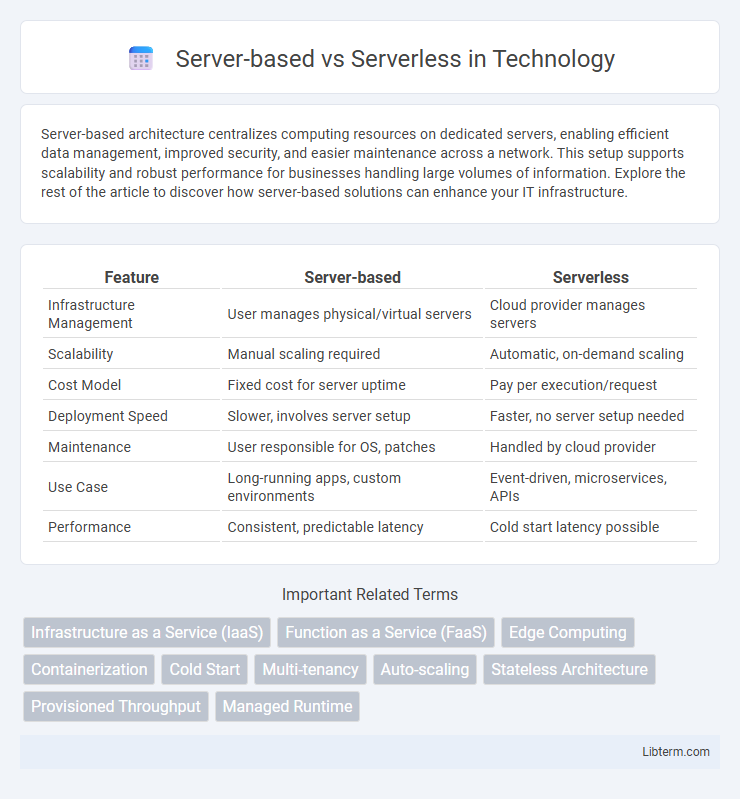
| Feature | Server-based | Serverless |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure Management | User manages physical/virtual servers | Cloud provider manages servers |
| Scalability | Manual scaling required | Automatic, on-demand scaling |
| Cost Model | Fixed cost for server uptime | Pay per execution/request |
| Deployment Speed | Slower, involves server setup | Faster, no server setup needed |
| Maintenance | User responsible for OS, patches | Handled by cloud provider |
| Use Case | Long-running apps, custom environments | Event-driven, microservices, APIs |
| Performance | Consistent, predictable latency | Cold start latency possible |
Introduction to Server-Based and Serverless Architectures
Server-based architectures rely on dedicated physical or virtual servers to host applications and manage resources, requiring active management of infrastructure, security, and scalability. Serverless architectures abstract server management by utilizing cloud provider services where code execution is event-driven and resources automatically scale based on demand. This shift enables developers to focus on writing business logic rather than maintaining underlying servers, optimizing operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Key Differences Between Server-Based and Serverless
Server-based architectures require physical or virtual servers to manage and deploy applications, offering full control over infrastructure but demanding ongoing maintenance and scalability planning. Serverless computing eliminates server management by automatically allocating resources based on demand, allowing developers to focus solely on code while scaling seamlessly and charging only for actual usage. Key differences include infrastructure management, cost efficiency, scalability, and deployment speed, with serverless providing dynamic resource allocation and reduced operational overhead compared to traditional server-based systems.
How Server-Based Architecture Works
Server-based architecture relies on dedicated physical or virtual servers to host applications, manage data processing, and handle client requests through a fixed infrastructure. Each server in this model requires manual configuration, scaling, and maintenance, often involving load balancers and web servers to distribute traffic and ensure reliability. The architecture provides predictable performance but demands continuous resource management and capacity planning to accommodate varying workloads.
How Serverless Architecture Works
Serverless architecture operates by outsourcing server management and infrastructure maintenance to cloud providers, allowing developers to deploy functions that automatically scale based on demand. Execution is event-driven, where individual functions are triggered by specific requests, reducing idle resource usage and lowering costs. This model abstracts away server provisioning, enabling rapid development cycles and seamless scalability without manual intervention.
Pros and Cons of Server-Based Solutions
Server-based solutions offer greater control over hardware and software configurations, allowing customization to meet specific application requirements. They provide reliable performance for consistent workloads but require ongoing maintenance, updates, and scalability management, which can increase operational costs. Security responsibilities also fall heavily on in-house teams, potentially posing risks if not managed effectively.
Pros and Cons of Serverless Solutions
Serverless solutions offer automatic scaling, reduced infrastructure management, and cost efficiency by charging only for actual usage, making them ideal for variable workloads and rapid prototyping. However, they can suffer from cold start latency, limited execution duration, and potential vendor lock-in, which may impact performance and flexibility. Security responsibilities shift to the provider, but developers must still manage application-level vulnerabilities and integration complexities.
Cost Comparison: Server-Based vs Serverless
Server-based architectures incur fixed costs related to hardware, maintenance, and continuous resource allocation, often leading to higher expenses during low traffic periods. Serverless computing offers a pay-as-you-go pricing model that scales automatically with demand, reducing costs during idle times and optimizing resource usage. Analyzing total cost of ownership reveals serverless solutions can significantly lower operational expenses for variable workloads compared to traditional server-based setups.
Security Considerations in Server-Based vs Serverless
Server-based architectures require robust physical and network security measures to protect dedicated servers from unauthorized access and potential breaches, whereas serverless computing shifts security responsibilities to cloud providers, reducing the burden of infrastructure management but introducing reliance on their security protocols. Serverless environments emphasize secure function permissions, API gateway configurations, and proper management of environment variables to prevent vulnerabilities. Both models demand vigilant monitoring and implementation of identity and access management (IAM) policies to ensure data protection and compliance.
Ideal Use Cases for Each Architecture
Server-based architecture is ideal for applications requiring full control over the server environment, such as legacy systems, complex transaction processing, and workloads with predictable, steady traffic. Serverless architecture excels in event-driven applications, microservices, and rapid scaling scenarios where demand is unpredictable or highly variable, reducing infrastructure management overhead. Enterprises with strict compliance, security requirements, or long-running processes typically favor server-based solutions, while startups and agile teams benefit from the cost-efficiency and flexibility of serverless platforms like AWS Lambda or Azure Functions.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Project
Choosing between server-based and serverless architectures depends on your project's scalability, control, and cost requirements. Server-based solutions offer full control and customization, ideal for complex applications needing consistent performance and security. Serverless platforms excel in handling variable workloads with automatic scaling and reduced operational overhead, making them perfect for startups or projects with unpredictable traffic patterns.
Server-based Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com