Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) integrates seamlessly with Agile methodologies to enhance collaboration between developers, testers, and business stakeholders by using clear, shared language to define requirements. This approach helps ensure that features are built to meet actual user needs through iterative cycles and continuous feedback. Explore the rest of the article to discover how adopting BDD within your Agile framework can streamline development and improve product quality.
Table of Comparison
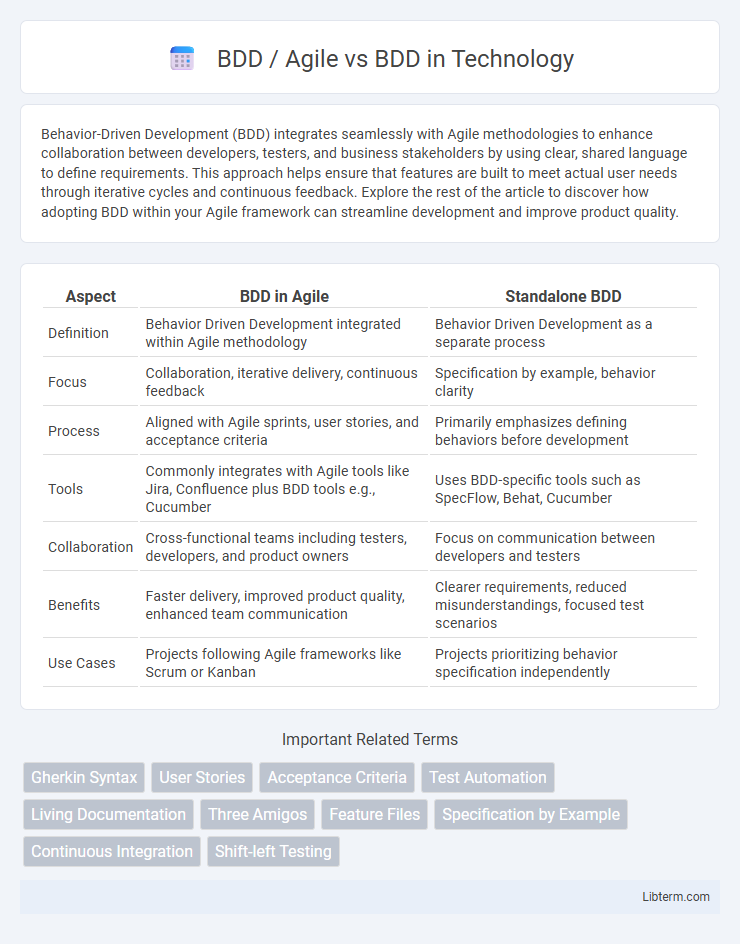
| Aspect | BDD in Agile | Standalone BDD |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Behavior Driven Development integrated within Agile methodology | Behavior Driven Development as a separate process |
| Focus | Collaboration, iterative delivery, continuous feedback | Specification by example, behavior clarity |
| Process | Aligned with Agile sprints, user stories, and acceptance criteria | Primarily emphasizes defining behaviors before development |
| Tools | Commonly integrates with Agile tools like Jira, Confluence plus BDD tools e.g., Cucumber | Uses BDD-specific tools such as SpecFlow, Behat, Cucumber |
| Collaboration | Cross-functional teams including testers, developers, and product owners | Focus on communication between developers and testers |
| Benefits | Faster delivery, improved product quality, enhanced team communication | Clearer requirements, reduced misunderstandings, focused test scenarios |
| Use Cases | Projects following Agile frameworks like Scrum or Kanban | Projects prioritizing behavior specification independently |
Understanding BDD: Core Principles
Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) centers on collaboration between developers, testers, and business stakeholders through shared examples and domain-specific language to define expected software behavior. Core principles emphasize executable specifications, ubiquitous language, and living documentation that foster clear communication and reduce ambiguity in requirements. Unlike traditional Agile, which focuses broadly on iterative delivery, BDD specifically targets bridging the gap between technical and non-technical participants to enhance requirement clarity and test automation.
The Agile Methodology: An Overview
The Agile methodology emphasizes iterative development, collaboration, and flexibility in software projects, fostering continuous delivery through short cycles called sprints. Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) integrates seamlessly with Agile by promoting clear communication via shared examples and user-centric scenarios that guide development and testing. Agile's adaptive framework supports BDD practices, enhancing alignment between stakeholders and accelerating value delivery.
BDD vs Agile: Key Differences
Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) emphasizes collaboration between developers, testers, and business stakeholders to create clear, executable specifications using a common language, enhancing communication and reducing misunderstandings. Agile is a broader project management framework focused on iterative development, flexibility, and delivering customer value through sprints and continuous feedback. Key differences include BDD's focus on specification by example and test automation, while Agile centers on adaptive planning and team collaboration for overall project management.
How BDD Complements Agile Practices
BDD enhances Agile practices by fostering clear communication through shared examples that align development with business goals. It bridges gaps between stakeholders, developers, and testers, promoting collaboration and reducing misunderstandings. By integrating testing early in the development cycle, BDD ensures continuous feedback and faster delivery of quality software.
Benefits of Implementing BDD in Agile Teams
Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) enhances Agile teams by fostering clear communication and collaboration among developers, testers, and business stakeholders through shared, understandable specifications written in natural language. This alignment reduces misunderstandings and accelerates feedback loops, enabling quicker identification and resolution of defects early in the development process. Implementing BDD in Agile workflows increases test coverage and automation efficiency, leading to higher software quality and more reliable product delivery.
Common Challenges in BDD and Agile Integration
Common challenges in integrating BDD with Agile include maintaining clear communication between developers, testers, and business stakeholders to ensure shared understanding of user stories and acceptance criteria. Adapting Agile's iterative development cycles to accommodate BDD's emphasis on executable specifications often requires continuous collaboration and frequent refinement of test scenarios. Managing the complexity of automated test maintenance while keeping pace with Agile's rapid delivery cadence can also hinder seamless BDD adoption.
Best Practices for Combining BDD with Agile
Combining BDD with Agile enhances collaboration by aligning development with business goals through clear, behavior-driven user stories expressed in Gherkin syntax. Best practices include fostering continuous communication between developers, testers, and stakeholders to ensure shared understanding and iterative feedback loops that adapt to changing requirements. Integrating automated BDD test scripts within Agile sprints accelerates validation cycles and maintains code quality while supporting rapid delivery.
Real-World Use Cases: BDD in Agile Environments
Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) enhances Agile workflows by fostering collaboration among cross-functional teams, ensuring that user stories are translated into clear, testable scenarios. Real-world Agile projects leverage BDD to bridge communication gaps between developers, testers, and business stakeholders, resulting in improved requirement clarity and faster feedback loops. Tools like Cucumber and SpecFlow integrate seamlessly with Agile sprints, enabling continuous integration and automated acceptance testing that align with business outcomes.
Tools Supporting BDD and Agile Processes
Tools supporting BDD, such as Cucumber, SpecFlow, and JBehave, enable behavior-driven development by facilitating collaboration between developers, testers, and business stakeholders through executable specifications and automated test scenarios. Agile process tools like Jira, Azure DevOps, and Rally integrate with BDD frameworks to streamline backlog management, sprint planning, and continuous integration, enhancing iterative development and feedback loops. Combining BDD tools with Agile platforms improves transparency, accelerates delivery, and ensures alignment of features with business requirements.
Future Trends: BDD and Agile Evolution
BDD and Agile continue to evolve with increasing integration of AI-driven automation and real-time collaboration tools enhancing testing accuracy and sprint efficiency. Future trends highlight the expansion of Behavior-Driven Development into model-based testing and continuous delivery pipelines, improving alignment between business stakeholders and development teams. The combined adoption of BDD and Agile methodologies drives faster feedback loops and adaptive planning, enabling more responsive and customer-focused software delivery.
BDD / Agile Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com