Endpoint security protects your devices from cyber threats by monitoring and managing network access points such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets. It employs advanced encryption, malware detection, and real-time threat intelligence to safeguard sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. Explore the rest of the article to learn how you can strengthen your security posture and protect your digital environment effectively.
Table of Comparison
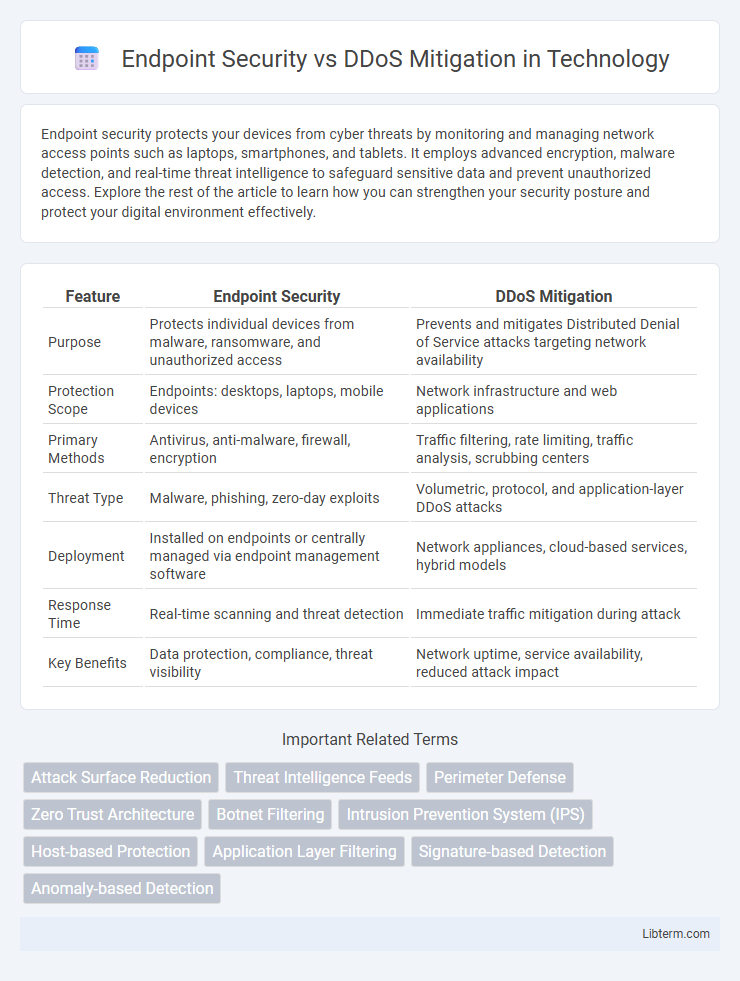
| Feature | Endpoint Security | DDoS Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Protects individual devices from malware, ransomware, and unauthorized access | Prevents and mitigates Distributed Denial of Service attacks targeting network availability |
| Protection Scope | Endpoints: desktops, laptops, mobile devices | Network infrastructure and web applications |
| Primary Methods | Antivirus, anti-malware, firewall, encryption | Traffic filtering, rate limiting, traffic analysis, scrubbing centers |
| Threat Type | Malware, phishing, zero-day exploits | Volumetric, protocol, and application-layer DDoS attacks |
| Deployment | Installed on endpoints or centrally managed via endpoint management software | Network appliances, cloud-based services, hybrid models |
| Response Time | Real-time scanning and threat detection | Immediate traffic mitigation during attack |
| Key Benefits | Data protection, compliance, threat visibility | Network uptime, service availability, reduced attack impact |
Understanding Endpoint Security
Endpoint security is a critical cybersecurity measure designed to protect individual devices such as laptops, smartphones, and desktops from malware, ransomware, and unauthorized access. It involves deploying antivirus software, firewalls, and advanced threat detection systems directly on endpoints to detect and neutralize security threats before they infiltrate the wider network. By securing endpoints, organizations can reduce vulnerabilities that Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) mitigation solutions alone cannot address, ensuring comprehensive protection against both device-level and network-level attacks.
What is DDoS Mitigation?
DDoS mitigation refers to the process of detecting, preventing, and responding to Distributed Denial of Service attacks that aim to overwhelm networks, servers, or services with malicious traffic. It involves specialized techniques such as traffic filtering, rate limiting, and deployment of scrubbing centers to ensure continuous availability and minimize service disruption. Effective DDoS mitigation solutions help maintain website performance and protect infrastructure from large-scale cyber threats targeting network resources.
Key Differences Between Endpoint Security and DDoS Mitigation
Endpoint security protects individual devices such as computers, smartphones, and tablets by preventing malware, unauthorized access, and data breaches, focusing on device-level threat detection and response. DDoS mitigation targets network-level attacks by identifying and blocking distributed denial-of-service traffic designed to overwhelm servers, ensuring availability and uptime of online services. The key difference lies in endpoint security's focus on safeguarding device integrity versus DDoS mitigation's role in maintaining network service continuity during large-scale traffic attacks.
Threat Landscape: Endpoints vs Network Attacks
Endpoint security primarily defends individual devices such as laptops, smartphones, and IoT gadgets against malware, ransomware, and phishing exploits that target user-level vulnerabilities. DDoS mitigation focuses on protecting network infrastructure by detecting and blocking massive volumes of malicious traffic aimed at overwhelming servers, thereby preventing service outages. The threat landscape reveals endpoints are susceptible to intricate, targeted breaches exploiting software flaws and user behavior, while network attacks rely on large-scale traffic surges designed to disrupt availability on a broader, infrastructure level.
Techniques Used in Endpoint Security
Endpoint security employs advanced techniques such as antivirus and anti-malware software, behavioral analysis, and endpoint detection and response (EDR) to protect devices from unauthorized access and cyber threats. Techniques include application whitelisting, device control, and encryption to secure sensitive data and prevent malware infections. These methods differ from DDoS mitigation, which primarily focuses on network traffic filtering, rate limiting, and traffic rerouting to defend against distributed denial-of-service attacks.
Common Methods of DDoS Mitigation
Common methods of DDoS mitigation include traffic filtering, rate limiting, and deploying web application firewalls (WAFs) to detect and block malicious traffic targeting network resources. Cloud-based DDoS protection services and content delivery networks (CDNs) are often used to absorb and disperse attack traffic, preventing infrastructure overload. Endpoint security, while crucial for protecting individual devices from malware and unauthorized access, does not address large-scale volumetric or protocol-based attacks characteristic of DDoS threats.
When to Prioritize Endpoint Security
Prioritize endpoint security when the primary threat involves malware, phishing attacks, or unauthorized access to sensitive data on devices such as laptops, smartphones, and desktops. Endpoint security is critical in environments with remote workers or BYOD policies, as it protects against device-level vulnerabilities and data breaches. Deploy endpoint security solutions before focusing on DDoS mitigation when internal device protection and data integrity are at higher risk than network-based denial-of-service attacks.
Scenarios Requiring DDoS Mitigation
Scenarios requiring DDoS mitigation typically involve large-scale, distributed attacks aimed at overwhelming network resources, such as web servers, cloud services, or critical infrastructure, to cause service disruptions and downtime. Enterprises hosting customer-facing applications, online retailers during high traffic events, and financial institutions managing real-time transactions are especially vulnerable to volumetric, protocol, and application layer DDoS attacks. Unlike endpoint security, which targets device-level threats like malware and unauthorized access, DDoS mitigation focuses on traffic filtering, rate limiting, and anomaly detection to maintain network availability under attack conditions.
Integrating Endpoint Security with DDoS Solutions
Integrating endpoint security with DDoS mitigation enhances overall network defense by combining device-level protection and attack traffic filtration, ensuring continuous monitoring and rapid response across all access points. Endpoint security tools detect malicious activity on devices, while DDoS solutions identify and block volumetric traffic floods targeting network infrastructure, reducing vulnerability to multi-vector attacks. This unified approach streamlines threat intelligence sharing and automated incident response, minimizing disruption and improving resilience against sophisticated cyber threats.
Best Practices for Comprehensive Cyber Defense
Endpoint security emphasizes protecting individual devices through antivirus software, firewalls, and regular patch management to prevent malware infections and unauthorized access. DDoS mitigation involves detecting and filtering malicious traffic using firewalls, intrusion prevention systems, and cloud-based scrubbing services to maintain network availability during attacks. Combining endpoint security best practices with proactive DDoS mitigation strategies establishes a comprehensive cyber defense framework that safeguards both device integrity and network resilience.
Endpoint Security Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com