Backup is essential for protecting your data from unexpected loss due to hardware failure, malware attacks, or accidental deletion. Implementing a reliable backup strategy ensures that your important files are securely stored and can be quickly restored when needed. Discover effective backup solutions and best practices by reading the full article to safeguard your digital information.
Table of Comparison
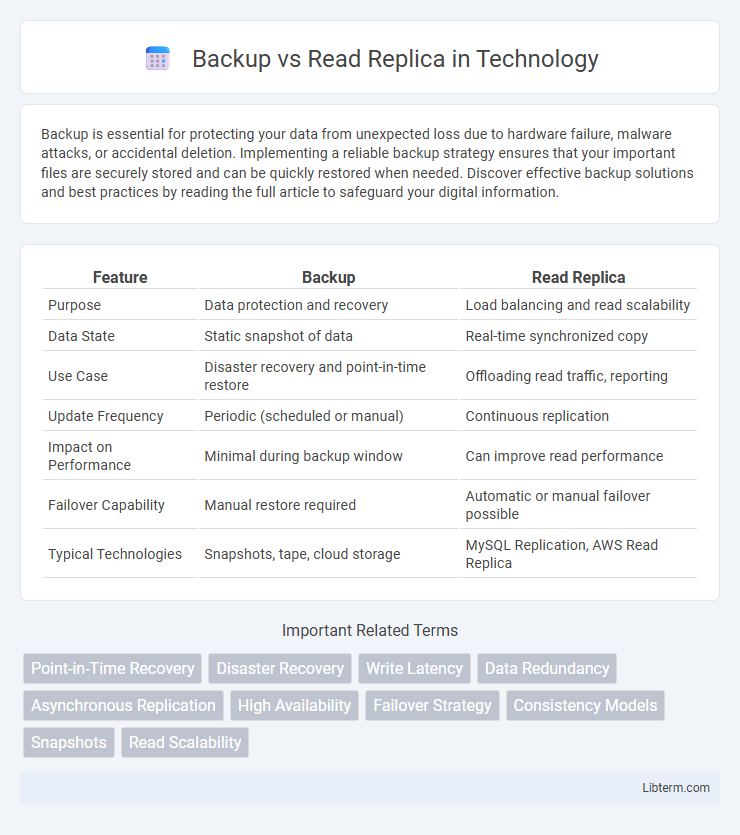
| Feature | Backup | Read Replica |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Data protection and recovery | Load balancing and read scalability |
| Data State | Static snapshot of data | Real-time synchronized copy |
| Use Case | Disaster recovery and point-in-time restore | Offloading read traffic, reporting |
| Update Frequency | Periodic (scheduled or manual) | Continuous replication |
| Impact on Performance | Minimal during backup window | Can improve read performance |
| Failover Capability | Manual restore required | Automatic or manual failover possible |
| Typical Technologies | Snapshots, tape, cloud storage | MySQL Replication, AWS Read Replica |
Understanding Backup and Read Replica: Key Definitions
Backup involves creating a complete copy of data at a specific point in time to ensure recovery in case of data loss, corruption, or disasters. Read Replica is a copy of the primary database that asynchronously replicates data to offload read queries, improve scalability, and enhance application performance. Backups serve primarily for data restoration, while Read Replicas optimize read-heavy workloads and support high availability scenarios.
Core Differences Between Backups and Read Replicas
Backups provide point-in-time copies of data, enabling full recovery in case of data loss or corruption. Read replicas offer real-time, asynchronous copies of a primary database for read scalability and load balancing, without serving as recovery points. Backup processes are typically periodic and stored separately, while read replicas maintain continuous synchronization with the primary database to support high availability and disaster recovery.
Use Cases: When to Choose Backup vs Read Replica
Backups are essential for disaster recovery, allowing point-in-time restoration of data after accidental deletion, corruption, or ransomware attacks. Read replicas improve application performance and scalability by offloading read-heavy database queries, ideal for reporting, analytics, or geographically distributed applications. Choose backups for data protection and recovery needs, while read replicas suit scenarios requiring real-time read scaling and high availability.
Data Recovery Strategies: Backup vs Read Replica
Backup provides a point-in-time copy of data to restore systems after data loss or corruption, ensuring data integrity through scheduled snapshots or continuous backups stored offline. Read replicas replicate live database instances asynchronously to distribute read traffic and can be promoted to a primary node during failover, offering near-real-time data recovery with minimal downtime. Combining backups with read replicas enhances data recovery strategies by balancing data restoration speed and completeness in disaster recovery scenarios.
Performance Impact: Backup vs Read Replica
Backup processes often consume significant I/O and CPU resources, potentially causing performance degradation on the primary database during peak hours. In contrast, Read Replicas offload read-heavy workloads to secondary nodes, minimizing the performance impact on the primary database by distributing query loads. Using Read Replicas improves overall system responsiveness by isolating resource-intensive backup operations from user queries.
Cost Considerations: Backups Compared to Read Replicas
Backups incur typically lower ongoing costs as they store data snapshots less frequently, reducing storage and compute expenses compared to read replicas that maintain real-time data synchronization. Read replicas, while more expensive due to continuous replication and additional instance charges, provide faster failover options and improved read scalability for high-demand applications. Selecting between backups and read replicas depends on budget constraints and performance requirements, balancing cost with the need for data availability and system responsiveness.
Data Consistency and Integrity: Backup vs Read Replica
Backups provide point-in-time copies of data ensuring consistency and integrity by capturing the exact state of a database, allowing full recovery from failures or corruption. Read replicas offer near real-time data synchronization for scalability and load balancing but may present eventual consistency, risking slight data lag or inconsistency during replication. For applications requiring strict consistency and data integrity, backups are essential, while read replicas favor high availability and read performance with some replication delay.
Scalability: Leveraging Backups and Read Replicas
Read replicas enhance scalability by distributing read traffic across multiple database instances, reducing load on the primary database and improving query performance during high-demand scenarios. Backups primarily serve as data recovery solutions and do not contribute to real-time scalability but ensure data durability and availability after failures. Leveraging read replicas alongside scheduled backups provides both immediate load balancing for reads and reliable disaster recovery options for comprehensive data management.
Security and Compliance in Backups and Read Replicas
Backup solutions ensure data integrity and regulatory compliance by providing encrypted, point-in-time snapshots that can be securely stored and audited for disaster recovery purposes. Read replicas enhance security by isolating read traffic from the primary database, reducing exposure to potential attacks, but they typically lack the comprehensive compliance features and audit trails present in backup systems. Implementing encrypted backups with strict access controls supports compliance with standards like GDPR and HIPAA, whereas read replicas mainly support high availability and performance with limited compliance assurances.
Best Practices for Implementing Backups and Read Replicas
Implementing backups requires scheduling regular full and incremental backups to ensure data integrity and minimize recovery time objectives (RTOs), with offsite storage to protect against disasters. Read replicas should be configured with asynchronous replication to offload read traffic, enhance application performance, and provide redundancy without affecting primary database writes. Combining automated backup strategies with read replicas supports both data durability and high availability in production environments.
Backup Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com