Business Intelligence transforms raw data into actionable insights that drive informed decision-making and optimize business performance. By leveraging advanced analytics, data visualization, and reporting tools, organizations can uncover trends, identify opportunities, and improve operational efficiency. Explore this article to discover how your business can harness the power of Business Intelligence for competitive advantage.
Table of Comparison
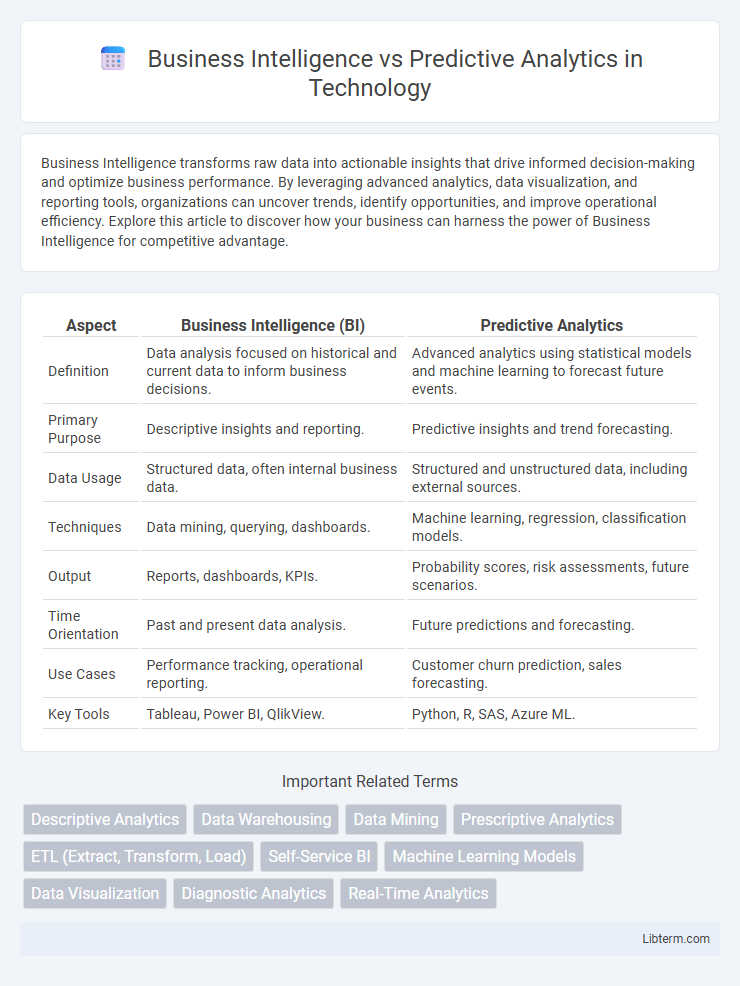
| Aspect | Business Intelligence (BI) | Predictive Analytics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Data analysis focused on historical and current data to inform business decisions. | Advanced analytics using statistical models and machine learning to forecast future events. |
| Primary Purpose | Descriptive insights and reporting. | Predictive insights and trend forecasting. |
| Data Usage | Structured data, often internal business data. | Structured and unstructured data, including external sources. |
| Techniques | Data mining, querying, dashboards. | Machine learning, regression, classification models. |
| Output | Reports, dashboards, KPIs. | Probability scores, risk assessments, future scenarios. |
| Time Orientation | Past and present data analysis. | Future predictions and forecasting. |
| Use Cases | Performance tracking, operational reporting. | Customer churn prediction, sales forecasting. |
| Key Tools | Tableau, Power BI, QlikView. | Python, R, SAS, Azure ML. |
Introduction to Business Intelligence and Predictive Analytics
Business Intelligence (BI) involves the collection, integration, analysis, and presentation of historical business data to support informed decision-making and improve operational efficiency. Predictive Analytics uses statistical algorithms and machine learning techniques to analyze current and historical data, forecasting future trends and behaviors. Both BI and Predictive Analytics leverage data insights, but BI emphasizes descriptive analysis while Predictive Analytics focuses on forecasting and proactive strategies.
Key Definitions: What is Business Intelligence?
Business Intelligence (BI) refers to the technologies, applications, and practices used to collect, integrate, analyze, and present historical and current business data for informed decision-making. BI systems enable organizations to generate descriptive reports, dashboards, and visualizations that reveal trends, patterns, and performance metrics. Unlike Predictive Analytics, which forecasts future outcomes using statistical models and machine learning, BI focuses primarily on understanding past and present business operations.
Key Definitions: What is Predictive Analytics?
Predictive analytics is a data-driven approach that uses statistical algorithms, machine learning techniques, and historical data to forecast future outcomes and trends. It identifies patterns and relationships within data to predict customer behavior, market shifts, or operational risks. Unlike traditional business intelligence, which focuses on analyzing past and current data for reporting, predictive analytics proactively anticipates what might happen next to enable informed decision-making.
Core Objectives of Business Intelligence
Business Intelligence primarily focuses on transforming raw data into actionable insights through data visualization, reporting, and dashboard tools to enhance decision-making across organizations. Its core objectives include improving operational efficiency, identifying market trends, and optimizing business processes by analyzing historical and real-time data. BI enables stakeholders to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) and make data-driven decisions that drive competitive advantage and growth.
Core Objectives of Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics primarily aims to forecast future events by analyzing historical data patterns and statistical algorithms, enabling businesses to anticipate customer behavior, market trends, and potential risks. Unlike traditional Business Intelligence, which focuses on descriptive insights and reporting past performance, predictive analytics drives proactive decision-making through data-driven predictions and risk assessment. Key objectives include improving accuracy in demand forecasting, optimizing resource allocation, and enhancing customer segmentation for targeted marketing strategies.
Technologies and Tools Used in BI vs Predictive Analytics
Business Intelligence (BI) technologies primarily utilize data warehousing, Online Analytical Processing (OLAP), and dashboard tools such as Microsoft Power BI, Tableau, and QlikView for data visualization and historical data analysis. Predictive Analytics relies heavily on machine learning frameworks like TensorFlow, Scikit-learn, and SAS Advanced Analytics, along with statistical programming languages such as R and Python for forecasting future trends based on historical data patterns. While BI focuses on descriptive analytics with ETL tools like Informatica and Apache Nifi, Predictive Analytics integrates advanced algorithms and Big Data platforms like Apache Spark to create predictive models and simulations.
Data Sources and Data Processing Comparison
Business Intelligence primarily relies on historical and structured data from enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, and transactional databases, utilizing extract, transform, load (ETL) processes to generate reports and dashboards for descriptive analysis. Predictive Analytics integrates diverse data sources, including unstructured data from social media, IoT sensors, and external market data, employing advanced machine learning algorithms and real-time data processing to forecast future trends and behaviors. The data processing in Business Intelligence emphasizes aggregation and summarization, while Predictive Analytics focuses on feature engineering, model training, and continuous updating to enhance predictive accuracy.
Use Cases: BI vs Predictive Analytics in Real-World Scenarios
Business Intelligence (BI) primarily supports decision-making through historical data analysis, enabling companies to monitor key performance indicators, track sales trends, and generate operational reports. Predictive Analytics leverages statistical models and machine learning algorithms to forecast future outcomes, such as customer churn, demand forecasting, and risk assessment. In real-world scenarios, BI helps retail businesses optimize inventory management, while Predictive Analytics drives personalized marketing campaigns and proactive fraud detection in finance.
Benefits and Limitations of BI and Predictive Analytics
Business Intelligence (BI) enhances decision-making by providing historical data insights through dashboards, reports, and visualization tools, but it is limited by its reactive nature and reliance on past data trends. Predictive Analytics offers forward-looking forecasts by employing machine learning models and statistical algorithms, enabling proactive strategies, yet it can be constrained by data quality issues and model interpretability challenges. Combining BI's descriptive insights with Predictive Analytics' forecasting capabilities maximizes organizational agility while addressing limitations such as BI's static reporting and predictive models' complexity.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Organization
Business Intelligence (BI) focuses on analyzing historical data to provide actionable insights through dashboards and reports, helping organizations make data-driven decisions based on past performance. Predictive Analytics uses statistical models and machine learning techniques to forecast future trends and behaviors, enabling proactive strategy formulation and risk mitigation. Choosing the right approach depends on your organization's specific needs: BI suits companies requiring comprehensive data visualization and operational insights, while Predictive Analytics benefits those aiming to anticipate market changes and optimize future outcomes.
Business Intelligence Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com