Geolocation routing directs internet traffic based on the physical location of the user's device, enhancing connection speed and security by routing data through the closest servers. This method improves user experience by reducing latency and optimizing network performance, especially for content delivery and compliance with regional regulations. Discover how geolocation routing can transform your network efficiency and safeguard your data by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
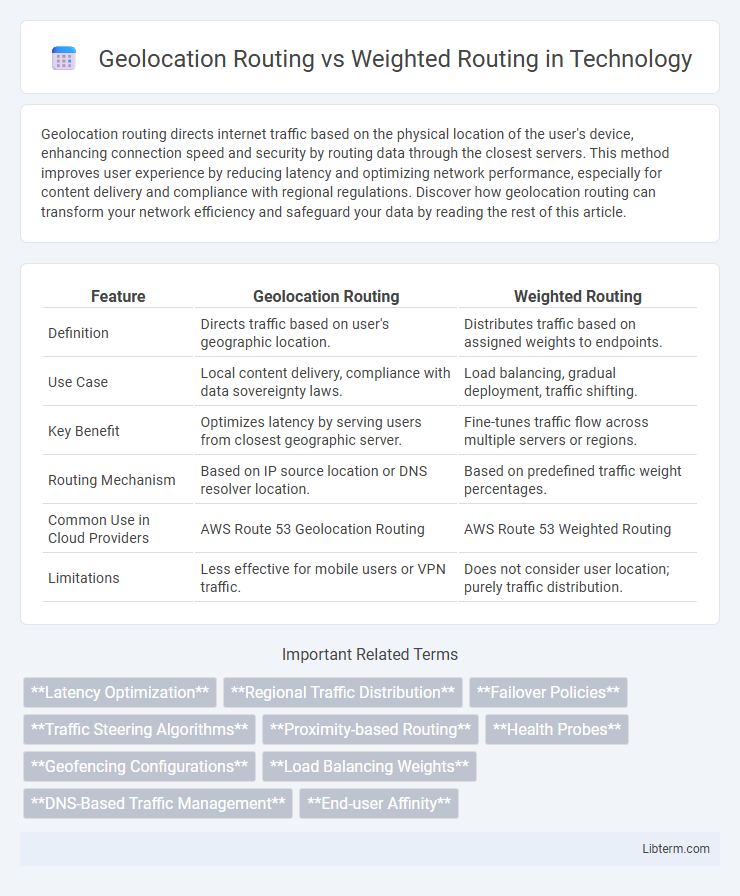
| Feature | Geolocation Routing | Weighted Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Directs traffic based on user's geographic location. | Distributes traffic based on assigned weights to endpoints. |
| Use Case | Local content delivery, compliance with data sovereignty laws. | Load balancing, gradual deployment, traffic shifting. |
| Key Benefit | Optimizes latency by serving users from closest geographic server. | Fine-tunes traffic flow across multiple servers or regions. |
| Routing Mechanism | Based on IP source location or DNS resolver location. | Based on predefined traffic weight percentages. |
| Common Use in Cloud Providers | AWS Route 53 Geolocation Routing | AWS Route 53 Weighted Routing |
| Limitations | Less effective for mobile users or VPN traffic. | Does not consider user location; purely traffic distribution. |
Introduction to Geolocation Routing and Weighted Routing
Geolocation routing directs internet traffic based on the physical location of the user, enhancing performance by connecting them to the nearest data center or server. Weighted routing distributes traffic across multiple endpoints according to predefined weights, optimizing resource utilization and balancing loads effectively. Both routing methods improve network efficiency but cater to different needs: geolocation routing prioritizes proximity, while weighted routing emphasizes traffic management.
How Geolocation Routing Works
Geolocation routing directs user requests to servers based on the geographic location of the IP address, ensuring faster load times and localized content delivery. It uses DNS queries to detect a user's location and routes traffic to the nearest or region-specific data center to minimize latency and comply with regulatory requirements. Unlike weighted routing, which distributes traffic based on preset proportions, geolocation routing dynamically optimizes user experience by matching requests to geographically relevant resources.
Understanding Weighted Routing Mechanisms
Weighted routing mechanisms distribute traffic across multiple endpoints based on predefined weight values, allowing precise control over load balancing and resource allocation. Each endpoint receives a proportion of traffic corresponding to its assigned weight, optimizing performance and cost-efficiency by directing more requests to higher-capacity or lower-cost servers. Unlike geolocation routing, which routes users based on their geographic location, weighted routing dynamically balances traffic regardless of user location, making it ideal for managing traffic across global multi-region deployments.
Key Differences Between Geolocation and Weighted Routing
Geolocation routing directs user requests based on the physical location of the requester, enhancing performance and compliance with regional laws, while weighted routing distributes traffic across multiple endpoints according to assigned weights for load balancing and resource optimization. Geolocation routing ensures users connect to the nearest or most appropriate server region, reducing latency and improving user experience, whereas weighted routing adjusts traffic dynamically to manage server capacity and availability. The key difference lies in geolocation's focus on user location for traffic control versus weighted routing's emphasis on balancing traffic volume across endpoints regardless of their geographic position.
Benefits of Geolocation Routing
Geolocation routing enhances user experience by directing traffic to the nearest or most regionally appropriate server, reducing latency and improving load times. It supports compliance with local data regulations by ensuring data is routed and stored within specific geographic boundaries. This routing method also enables businesses to deliver personalized content based on the user's location, increasing relevance and engagement.
Advantages of Weighted Routing
Weighted routing enables precise traffic distribution across multiple resources based on assigned weights, ensuring optimal load balancing and improved service reliability. It allows dynamic adjustment of traffic flow to accommodate changes in resource capacity or performance, maximizing resource utilization. This routing method supports granular control over routing policies, enhancing flexibility for complex deployment scenarios compared to geolocation routing, which mainly directs traffic based on user location.
When to Use Geolocation Routing
Geolocation routing is ideal for directing user traffic based on geographic location, ensuring low latency and compliance with regional regulations by serving content from the nearest server or datacenter. This routing strategy enhances user experience by reducing load times and optimizing data sovereignty, making it essential for global applications requiring localized content delivery. Use geolocation routing when user location matters for performance, legal, or content customization reasons, rather than distribution based solely on server capacity or weight.
Scenarios Ideal for Weighted Routing
Weighted Routing is ideal for scenarios requiring traffic distribution across multiple endpoints based on predefined weights, such as load balancing between servers or regions with varying capacities. It suits applications where evenly distributing user requests or managing capacity differences is crucial for performance optimization. This routing policy optimizes resource utilization and ensures seamless user experience in multi-region deployments.
Performance and Scalability Considerations
Geolocation routing improves performance by directing user requests to the nearest data center, reducing latency and enhancing response times in global applications. Weighted routing distributes traffic based on assigned weights to endpoints, optimizing resource utilization and enabling fine-grained control over server loads. Scalability in geolocation routing depends on the accuracy of location data and DNS resolution speed, while weighted routing scales effectively with dynamic traffic adjustments but requires continuous monitoring to maintain optimal load distribution.
Choosing the Right Routing Strategy for Your Needs
Geolocation routing directs traffic based on the user's physical location, ideal for delivering region-specific content and complying with local regulations. Weighted routing distributes traffic according to assigned weights, enabling load balancing and gradual deployment of new services. Selecting the right strategy depends on your goals: prioritize geolocation routing for localized performance and legal compliance, or weighted routing for flexible traffic management and testing environments.
Geolocation Routing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com