Autonomy empowers individuals to make independent decisions and take control of their actions, enhancing personal growth and satisfaction. Embracing autonomy in your professional and personal life fosters confidence and creativity, driving success in various endeavors. Explore the full article to discover how cultivating autonomy can transform your life.
Table of Comparison
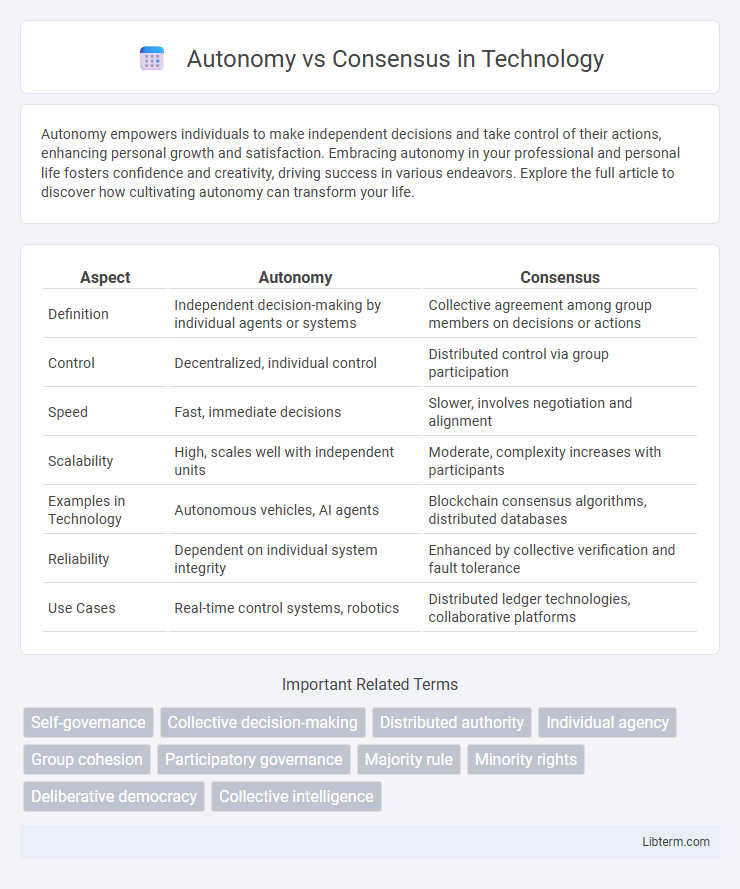
| Aspect | Autonomy | Consensus |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Independent decision-making by individual agents or systems | Collective agreement among group members on decisions or actions |
| Control | Decentralized, individual control | Distributed control via group participation |
| Speed | Fast, immediate decisions | Slower, involves negotiation and alignment |
| Scalability | High, scales well with independent units | Moderate, complexity increases with participants |
| Examples in Technology | Autonomous vehicles, AI agents | Blockchain consensus algorithms, distributed databases |
| Reliability | Dependent on individual system integrity | Enhanced by collective verification and fault tolerance |
| Use Cases | Real-time control systems, robotics | Distributed ledger technologies, collaborative platforms |
Understanding Autonomy and Consensus
Understanding autonomy involves recognizing the individual's capacity for self-governance, independent decision-making, and personal responsibility within various contexts such as ethics, psychology, and organizational behavior. Consensus refers to collective agreement reached through collaborative dialogue and negotiation, prioritizing shared goals and mutual understanding among group members. Balancing autonomy and consensus is critical in fostering environments where individual freedom coexists with harmonious group dynamics, enhancing both innovation and cohesion.
Historical Perspectives on Decision-Making
Historical perspectives on decision-making contrast autonomy, emphasizing individual authority and swift judgment, with consensus, which prioritizes collective agreement and collaboration. Early governance systems often favored autonomy for decisive leadership, while democratic models evolved to emphasize consensus as a means to incorporate diverse viewpoints and ensure legitimacy. This tension between autonomous decision-making and consensus-driven processes continues to shape organizational behavior and political theory.
Key Differences Between Autonomy and Consensus
Autonomy emphasizes individual decision-making power and self-governance, allowing entities or individuals to act independently without external control. Consensus involves collaborative agreement and collective input, prioritizing group harmony and mutual understanding to reach decisions. The key difference lies in autonomy's focus on independent authority versus consensus's emphasis on shared agreement and cooperative decision-making.
Advantages of Autonomous Decision-Making
Autonomous decision-making enhances organizational agility by enabling faster responses to changing market conditions and customer needs. It empowers employees, boosting motivation and innovation through increased ownership of tasks and responsibilities. This approach reduces bottlenecks in hierarchical approval processes, resulting in improved efficiency and adaptability.
Benefits of Consensus-Based Approaches
Consensus-based approaches foster collaborative decision-making by integrating diverse perspectives, which enhances group cohesion and commitment to shared outcomes. These methods reduce conflicts and increase transparency, ensuring that decisions reflect collective interests and promote sustainable implementation. Empirical studies show consensus processes lead to higher satisfaction levels and stronger alignment within teams, driving long-term organizational success.
Challenges and Limitations of Autonomy
Autonomy in decision-making often faces challenges such as the risk of isolation from broader organizational goals and lack of alignment with team consensus, leading to potential conflicts and inefficiencies. Limited access to diverse perspectives can reduce the quality and acceptance of autonomous decisions, while excessive autonomy may hinder collaboration and integrated problem-solving within groups. These limitations necessitate balancing individual independence with collective input to optimize outcomes in complex environments.
Drawbacks and Pitfalls of Consensus
Consensus decision-making often leads to groupthink, undermining creativity and critical evaluation by prioritizing harmony over diverse perspectives. Prolonged discussions and compromises can delay urgent decisions, reducing organizational agility and responsiveness. The risk of minority voices being suppressed or ignored further weakens inclusivity and can result in suboptimal outcomes.
Balancing Autonomy and Consensus in Organizations
Balancing autonomy and consensus in organizations requires fostering independent decision-making while ensuring alignment with collective goals to enhance productivity and innovation. Effective strategies include creating clear frameworks that empower individual team members with responsibility while facilitating collaborative processes for key decisions. Prioritizing transparent communication and trust-building mechanisms supports a dynamic culture where autonomy coexists with consensus-driven outcomes.
Real-World Examples: Autonomy vs Consensus
In corporate settings, Tesla showcases autonomy through its flat organizational structure that empowers engineers to innovate rapidly without lengthy approval processes. In contrast, companies like Toyota emphasize consensus-driven decision-making, utilizing the "ringi" system where collective input ensures high-quality outcomes and employee buy-in. These real-world examples highlight how autonomy facilitates agility and innovation, whereas consensus promotes stability and broad agreement.
Strategies for Integrating Autonomy and Consensus
Effective strategies for integrating autonomy and consensus include establishing clear communication channels that respect individual decision-making while aligning with collective goals. Implementing collaborative frameworks such as decentralized decision-making combined with periodic consensus meetings fosters flexibility and shared responsibility. Leveraging technology platforms that support transparent feedback and real-time input enhances trust and balances personal initiative with group cohesion.
Autonomy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com