Subnetting divides a larger network into smaller, manageable segments, improving security and reducing traffic congestion. Each subnet functions as an individual network with its own range of IP addresses, enhancing performance and simplifying network management. Discover how subnetting can optimize Your network infrastructure by exploring the details in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
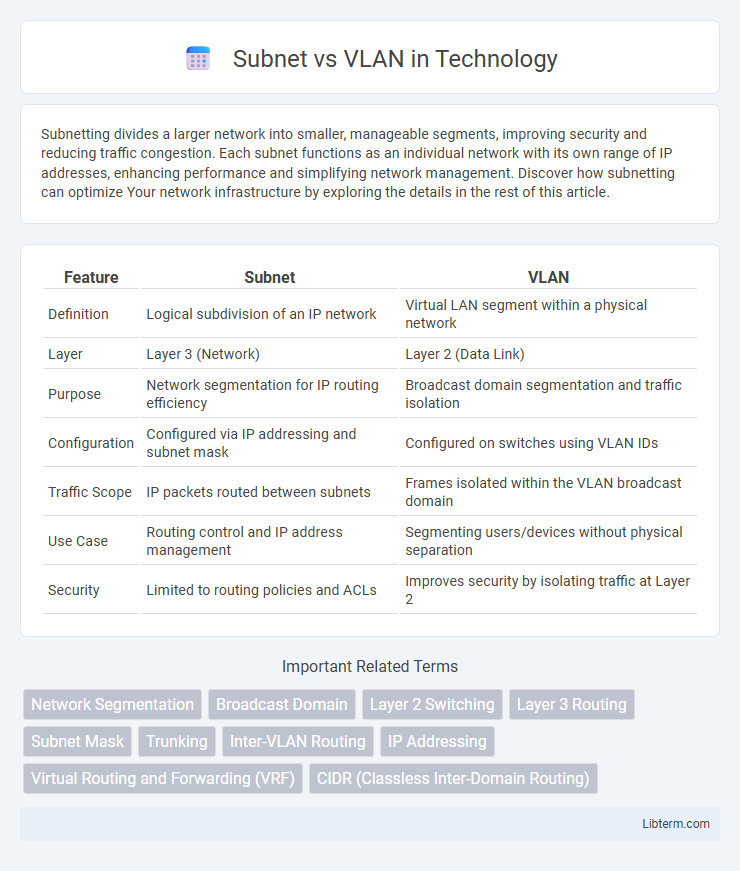
| Feature | Subnet | VLAN |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Logical subdivision of an IP network | Virtual LAN segment within a physical network |
| Layer | Layer 3 (Network) | Layer 2 (Data Link) |
| Purpose | Network segmentation for IP routing efficiency | Broadcast domain segmentation and traffic isolation |
| Configuration | Configured via IP addressing and subnet mask | Configured on switches using VLAN IDs |
| Traffic Scope | IP packets routed between subnets | Frames isolated within the VLAN broadcast domain |
| Use Case | Routing control and IP address management | Segmenting users/devices without physical separation |
| Security | Limited to routing policies and ACLs | Improves security by isolating traffic at Layer 2 |
Introduction to Subnets and VLANs
Subnets divide a single IP network into smaller, manageable segments to improve routing efficiency and enhance security by isolating network traffic. VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) create distinct broadcast domains within a physical network, allowing devices on different switches to communicate as if they were on the same local network while maintaining traffic separation. Both subnets and VLANs optimize network performance and security but operate at different layers, with subnets functioning at the IP layer and VLANs at the data link layer.
Understanding What a Subnet Is
A subnet, or subnetwork, is a segmented piece of a larger IP network that partitions and organizes network traffic by grouping devices within specific IP address ranges. It enhances network performance and security by controlling broadcast traffic and improving routing efficiency within distinct address blocks defined by subnet masks. Unlike VLANs, which operate at the data link layer to segment networks logically regardless of IP addressing, subnets provide Layer 3 segmentation based strictly on IP addressing schemes.
Understanding What a VLAN Is
A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) segments a physical network into multiple logical networks, enhancing security and traffic management by isolating devices within the same switch or across multiple switches. Unlike subnets, which are IP address-based divisions used to manage network traffic at the Layer 3 level, VLANs operate at Layer 2 to control broadcast domains independently from IP addressing schemes. VLANs improve network efficiency by reducing broadcast traffic and allowing flexible network design without changing the physical infrastructure.
Key Differences Between Subnet and VLAN
A subnet segments a network at the IP layer, organizing devices by IP address range to improve routing efficiency and manage traffic within a Layer 3 framework. A VLAN, however, partitions a network at the data link layer (Layer 2), grouping devices based on logical topology rather than physical location to enhance security and reduce broadcast domains. Key differences include subnets working on IP addresses with routers managing traffic, while VLANs use switches and tagging protocols like IEEE 802.1Q to isolate broadcast traffic within the same physical network.
How Subnets Work in Network Segmentation
Subnets work in network segmentation by dividing a larger IP network into smaller, manageable segments called subnetworks, which improve routing efficiency and reduce broadcast traffic. Each subnet acts as a distinct network with its own IP address range and subnet mask, enabling better control over traffic flow and security within an organization. This segmentation allows devices on the same subnet to communicate directly, while communication between different subnets requires routing through a router or Layer 3 device.
How VLANs Work in Network Segmentation
VLANs work by logically segmenting a physical network into multiple broadcast domains, allowing devices on the same switch to be grouped regardless of their physical location. Each VLAN is assigned a unique identifier called a VLAN ID, which tags Ethernet frames to segregate traffic and improve security and performance. This segmentation reduces broadcast traffic and isolates network issues, enabling efficient management compared to traditional subnet division based solely on IP addresses.
Use Cases: When to Use Subnets vs VLANs
Subnets are ideal for segmenting large networks to improve routing efficiency and manage IP address allocation in different geographic locations or departments. VLANs are best used to group devices within the same physical network, enhancing security and traffic management by isolating broadcast domains across switches. Use subnets when addressing hierarchical IP design, and choose VLANs for logical segmentation without changing physical topology.
Security Considerations: Subnet vs VLAN
Subnets provide layer 3 isolation by segmenting network traffic through IP addressing, reducing broadcast domains and limiting exposure to network attacks such as IP spoofing and sniffing. VLANs operate at layer 2, isolating traffic within the same physical network infrastructure by tagging Ethernet frames, which enhances security by enforcing group separation and reducing the risk of unauthorized access across different VLANs. Combining subnets with VLANs strengthens network security by leveraging both IP routing controls and switch-level traffic separation, mitigating threats like VLAN hopping and unauthorized lateral movement.
Performance Impact: Subnet vs VLAN
Subnet segmentation enhances network performance by reducing broadcast domains and isolating traffic at the IP layer, minimizing congestion and latency. VLANs improve efficiency by logically grouping devices within the same physical network, allowing for better traffic management and security without relying on IP subnet boundaries. Combining subnets with VLANs optimizes performance by controlling broadcast traffic and improving resource allocation across Layer 2 and Layer 3 boundaries.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Network
Choosing between a subnet and a VLAN depends on your network's scalability and segmentation needs; subnets organize IP address ranges to improve routing efficiency, while VLANs create logical broadcast domains for enhanced security and traffic management within the same physical network. Subnets are essential for dividing network traffic at the IP layer, making them ideal for large-scale network segmentation and routing optimization. VLANs offer flexibility by isolating network segments without requiring separate physical hardware, which suits environments requiring granular control over broadcast domains and improved network performance.
Subnet Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com