Rollback is a database operation that reverses changes made during a transaction, restoring the system to its previous stable state before the transaction began. This mechanism ensures data integrity by preventing incomplete or erroneous data from being permanently applied. Discover how understanding rollback can protect your data and enhance your system's reliability by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
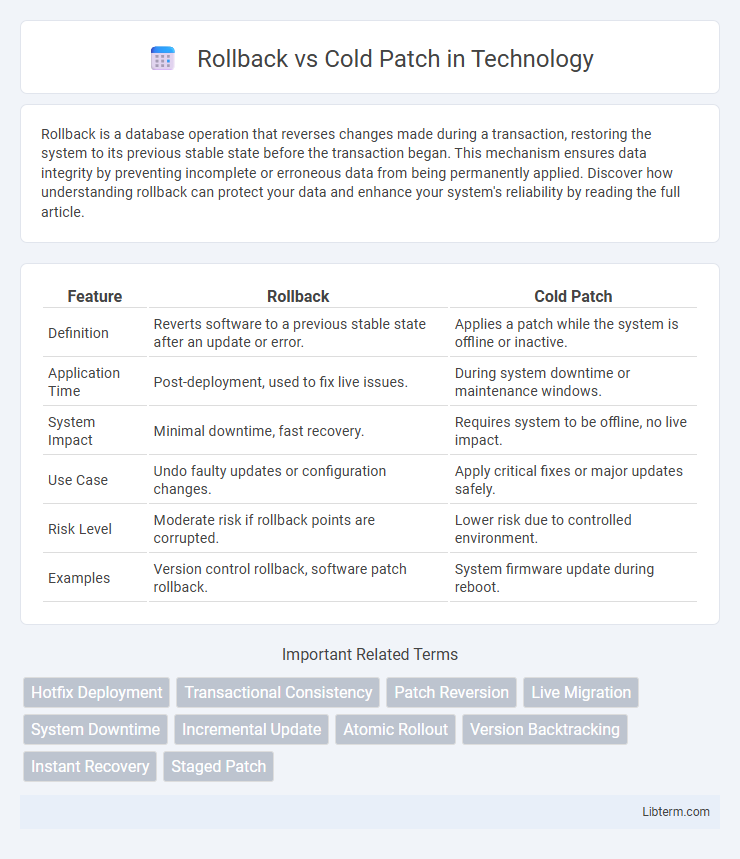
| Feature | Rollback | Cold Patch |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reverts software to a previous stable state after an update or error. | Applies a patch while the system is offline or inactive. |
| Application Time | Post-deployment, used to fix live issues. | During system downtime or maintenance windows. |
| System Impact | Minimal downtime, fast recovery. | Requires system to be offline, no live impact. |
| Use Case | Undo faulty updates or configuration changes. | Apply critical fixes or major updates safely. |
| Risk Level | Moderate risk if rollback points are corrupted. | Lower risk due to controlled environment. |
| Examples | Version control rollback, software patch rollback. | System firmware update during reboot. |
Understanding Rollback and Cold Patch
Rollback enables restoration of a system or software to a previous stable state, effectively undoing recent changes or updates that caused issues. Cold patch involves applying fixes or updates while the system is offline or inactive, ensuring integration without disrupting ongoing operations. Understanding these methods is crucial for effective system maintenance and minimizing downtime during updates or error recovery.
Key Differences Between Rollback and Cold Patch
Rollback involves reverting a system or software to a previous stable state to undo recent changes, ensuring system stability and integrity. Cold patch, on the other hand, applies updates or fixes while the system is offline or during downtime, minimizing disruption but requiring system restart to take effect. The key difference lies in rollback's ability to reverse changes after deployment, whereas cold patch focuses on applying maintenance during inactive periods without immediate reversals.
When to Use Rollback in Software Deployment
Rollback in software deployment is essential when a newly released version causes critical failures, performance degradation, or security vulnerabilities that impact end-users or system stability. It is most effective when immediate restoration to the previous stable state is needed to minimize downtime and prevent data loss. Rollback should be used in environments requiring high availability and fast recovery, such as financial services, healthcare systems, or large-scale web applications.
Scenarios Best Suited for Cold Patch
Cold patch asphalt repair is best suited for emergency pothole fixes and small surface cracks in moderate to low traffic areas where quick curing is essential. It performs optimally in temperatures above freezing and requires no heating equipment, making it ideal for rapid, on-site repairs during colder months or unpredictable weather. Cold patch materials provide a durable, temporary solution until more permanent hot mix repairs or rollbacks can be scheduled.
Advantages of Rollback Strategies
Rollback strategies provide immediate restoration to a previous stable state, minimizing downtime and service disruption. They enable precise problem identification by isolating recent changes, facilitating faster troubleshooting and recovery. Rollbacks reduce risk during deployment by allowing quick reversal of faulty updates, ensuring system reliability and continuity.
Benefits of Implementing Cold Patch
Cold patch offers significant benefits such as reducing downtime by allowing repairs without waiting for asphalt to heat up, enabling quick and efficient pothole fixes in various weather conditions. It improves safety by providing an immediate, durable solution that prevents further road deterioration and accidents. Cold patch materials are cost-effective, easy to store, and require minimal equipment, making them ideal for emergency repairs and routine maintenance.
Limitations and Risks of Rollback
Rollback procedures can lead to data loss and inconsistency if backups are outdated or incomplete, posing significant risks to system integrity. Downtime during rollback may disrupt business operations, impacting productivity and revenue. Compatibility issues may arise when reverting to previous versions, causing potential conflicts with newer applications or security vulnerabilities.
Challenges Associated with Cold Patch
Cold patch applications often face significant challenges such as poor adhesion to existing pavement, leading to premature failure and pothole reappearance. Temperature sensitivity during installation can cause inconsistent curing times, affecting durability and overall performance. Limited flexibility and lower load-bearing capacity compared to rollbacks make cold patches less reliable for heavy traffic areas, increasing maintenance costs.
Best Practices for Choosing Between Rollback and Cold Patch
Rollback is ideal for quickly reverting software or system changes to a previous stable state when updates cause critical issues. Cold patch is best suited for applying fixes without restarting the system, especially in environments requiring high availability and minimal downtime. Choosing between rollback and cold patch depends on system stability, urgency of the fix, and operational impact, with rollback providing a safety net and cold patch enabling seamless updates.
Real-World Examples: Rollback vs Cold Patch Outcomes
Rollback implementation in database systems often prevents extensive downtime by reverting to a previous stable state, as demonstrated by Amazon's use of rollback during transactional failures, ensuring data integrity and continuous service. Cold patch methods, common in software maintenance at companies like Microsoft, involve applying updates during system shutdown, minimizing runtime errors but causing planned downtime. Real-world outcomes show rollback provides faster recovery from unexpected errors, while cold patch guarantees thorough updates with reduced online disruption, ideal for critical system maintenance windows.
Rollback Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com