Mirror backup creates an exact copy of your data, ensuring all files remain identical to the original at the time of backup. This method allows for quick restoration and easy access to the latest versions without complex retrieval processes. Explore the full article to learn how mirror backup can safeguard your important files efficiently.
Table of Comparison
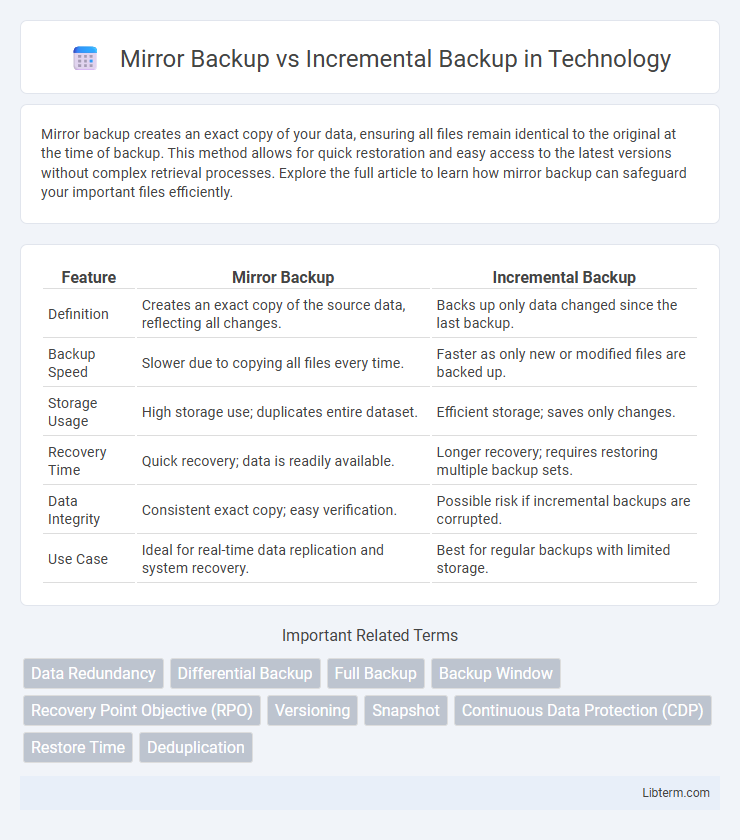
| Feature | Mirror Backup | Incremental Backup |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Creates an exact copy of the source data, reflecting all changes. | Backs up only data changed since the last backup. |
| Backup Speed | Slower due to copying all files every time. | Faster as only new or modified files are backed up. |
| Storage Usage | High storage use; duplicates entire dataset. | Efficient storage; saves only changes. |
| Recovery Time | Quick recovery; data is readily available. | Longer recovery; requires restoring multiple backup sets. |
| Data Integrity | Consistent exact copy; easy verification. | Possible risk if incremental backups are corrupted. |
| Use Case | Ideal for real-time data replication and system recovery. | Best for regular backups with limited storage. |
Introduction to Backup Strategies
Mirror backup creates an exact replica of the source data, ensuring immediate availability for recovery by maintaining an up-to-date copy. Incremental backup saves only the changes made since the last backup, optimizing storage space and reducing backup time. Both strategies are essential for comprehensive data protection, balancing between recovery speed and storage efficiency.
What is Mirror Backup?
Mirror backup creates an exact, real-time replica of the source data, ensuring every file and folder is duplicated precisely as it exists at the moment of backup. It allows immediate restoration by maintaining a synchronized copy that reflects all changes, deletions, and updates made to the original files. Mirror backup is ideal for users needing quick access to an up-to-date duplicate without the complexities of versioning or incremental changes.
What is Incremental Backup?
Incremental backup is a data protection method that saves only the changes made since the last backup, reducing storage space and backup time compared to full or mirror backups. It creates a sequence of backups where each captures only the modified files, requiring all previous increments for a full restoration. This approach contrasts with mirror backup, which duplicates an exact copy of the entire data set at each backup point without storing historical versions.
Key Differences Between Mirror and Incremental Backups
Mirror backup creates an exact replica of the source data, storing all files in their current state, which enables quick full restoration but requires more storage space. Incremental backup saves only the changes made since the last backup, optimizing storage efficiency and reducing backup time but requiring multiple backup sets for a complete restore. Key differences include storage usage, backup speed, and recovery process complexity, with mirror backup favoring simplicity and incremental backup emphasizing efficiency.
Advantages of Mirror Backup
Mirror Backup offers real-time data replication, ensuring an exact copy of files is maintained for immediate restoration. This method simplifies recovery by eliminating the need for multiple backup sets, reducing complexity and saving time during data retrieval. It provides continuous protection, making it ideal for critical systems requiring up-to-date data availability.
Benefits of Incremental Backup
Incremental backup significantly reduces storage space by only saving changes made since the last backup, making it highly efficient for ongoing data protection. It speeds up backup processes, minimizing system downtime and allowing for more frequent backups without straining resources. The ability to restore data from multiple incremental backups ensures that users can recover specific versions of files, enhancing data recovery flexibility and accuracy.
Potential Drawbacks of Both Methods
Mirror backup can lead to accidental data deletion since it exactly replicates the source drive and removes files no longer present, risking the loss of important data. Incremental backup creates numerous small backup files over time, which can complicate data restoration and increase the time required to recover complete datasets. Both methods demand careful management to avoid data loss or extended recovery periods, especially in environments with frequent file changes.
Ideal Use Cases for Mirror Backup
Mirror backup is ideal for environments requiring real-time data replication and exact file copies, such as active project folders or dynamic databases. It enables immediate access to the most current version without restoring from multiple backup points, making it suitable for fast recovery scenarios in business-critical operations. Large enterprises with continuous data change benefit from mirror backup to minimize downtime and ensure seamless workflow continuity.
Best Scenarios for Incremental Backup
Incremental backup is best suited for environments requiring frequent data protection with minimal storage consumption, such as enterprise servers and virtual machines. It efficiently captures only the changes made since the last backup, significantly reducing backup time and resource usage compared to mirror backups. This approach excels in scenarios demanding fast recovery points and optimized bandwidth, making it ideal for businesses with rapidly changing data and limited backup windows.
Choosing the Right Backup Method for Your Needs
Mirror backup creates an exact copy of your entire data set, ensuring immediate access to all files but requiring significant storage space. Incremental backup saves only the changes made since the last backup, optimizing storage efficiency and speeding up backup processes. Selecting the right backup method depends on your storage capacity, recovery time objectives, and the frequency of data changes within your environment.
Mirror Backup Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com