Lean methodology streamlines processes by eliminating waste and focusing on value creation, enhancing overall efficiency in business operations. Implementing Lean principles can significantly boost productivity and reduce costs, enabling companies to respond swiftly to customer needs. Discover how Lean practices can transform your workflow by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
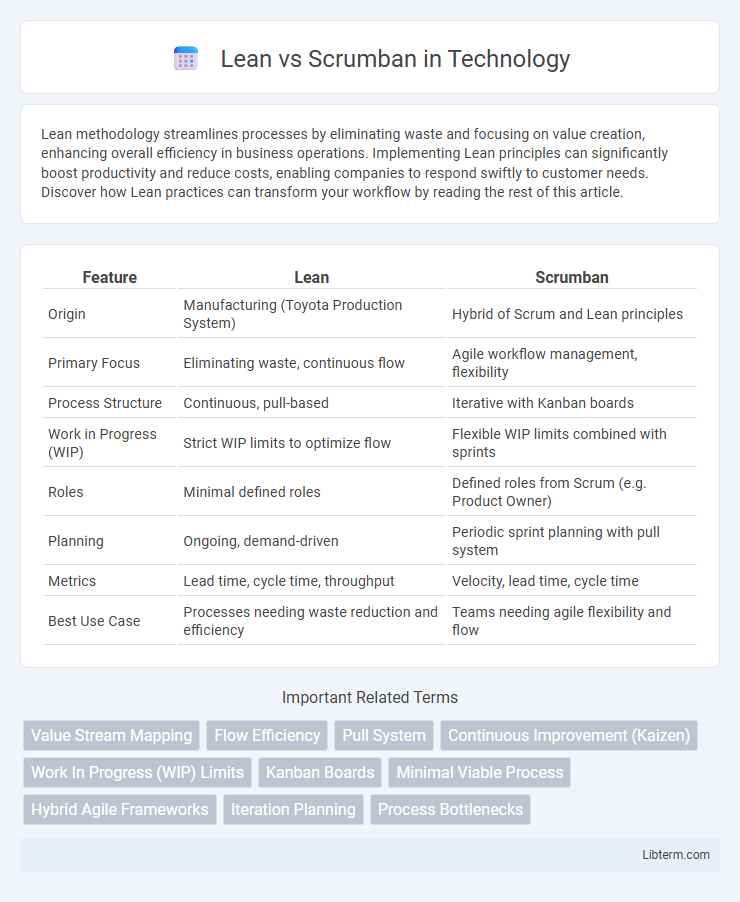
| Feature | Lean | Scrumban |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Manufacturing (Toyota Production System) | Hybrid of Scrum and Lean principles |
| Primary Focus | Eliminating waste, continuous flow | Agile workflow management, flexibility |
| Process Structure | Continuous, pull-based | Iterative with Kanban boards |
| Work in Progress (WIP) | Strict WIP limits to optimize flow | Flexible WIP limits combined with sprints |
| Roles | Minimal defined roles | Defined roles from Scrum (e.g. Product Owner) |
| Planning | Ongoing, demand-driven | Periodic sprint planning with pull system |
| Metrics | Lead time, cycle time, throughput | Velocity, lead time, cycle time |
| Best Use Case | Processes needing waste reduction and efficiency | Teams needing agile flexibility and flow |
Introduction to Lean and Scrumban
Lean is a methodology that emphasizes waste reduction, continuous improvement, and delivering value efficiently by streamlining processes and eliminating non-value-added activities. Scrumban combines the structured framework of Scrum with the flexibility of Kanban, integrating Lean principles to optimize workflows and improve team adaptability. Both methodologies prioritize enhancing productivity and responsiveness by focusing on iterative development and efficient resource management.
Core Principles of Lean Methodology
Lean methodology centers on eliminating waste, optimizing processes, and delivering maximum value to customers through continuous improvement and respect for people. Core principles include defining value from the customer's perspective, mapping the value stream to identify and remove non-value-adding activities, creating flow by ensuring smooth, uninterrupted workflow, establishing pull systems to produce only what is needed, and pursuing perfection through iterative refinement. Lean emphasizes efficiency, quality, and responsiveness, which contrasts with Scrumban's hybrid approach that incorporates Scrum's iterative planning with Lean's flow-based principles to balance flexibility and process control.
Key Concepts of Scrumban
Scrumban integrates Lean principles of waste reduction and continuous improvement with Scrum's structured iterations and prioritization, emphasizing flexibility and flow. Key concepts include the use of Kanban boards for visual workflow management, limiting work in progress (WIP) to prevent overload, and continuous planning with pull-based task selection. This hybrid approach enhances team adaptability, optimizes cycle time, and supports incremental delivery in dynamic project environments.
Workflow Visualization: Lean vs Scrumban
Lean workflow visualization emphasizes continuous flow by mapping value streams and identifying waste through tools like value stream mapping and Kanban boards. Scrumban integrates Scrum's iterative approach with Lean's flow principles, utilizing task boards that combine kanban columns with sprint backlogs to balance flexibility and time-boxed delivery. Both methodologies prioritize real-time transparency but differ in structure, with Lean focusing on pull systems and cycle efficiency, while Scrumban blends pull with sprint cadence for adaptive project management.
Process Optimization and Waste Reduction
Lean focuses on process optimization by systematically identifying and eliminating waste through techniques such as value stream mapping and continuous improvement cycles, resulting in streamlined workflows and increased efficiency. Scrumban combines Lean's waste reduction principles with Scrum's iterative approach, enabling teams to adapt processes dynamically while maintaining a focus on minimizing non-value-added activities. Both methodologies prioritize reducing delays, excess inventory, and redundant tasks, which enhances productivity and accelerates delivery in software development and manufacturing environments.
Flexibility and Adaptation in Project Management
Lean emphasizes continuous improvement and waste reduction, offering project teams the flexibility to streamline processes and adapt workflows based on real-time feedback. Scrumban integrates Scrum's structured sprint cycles with Lean's flow-based principles, enabling teams to adjust priorities dynamically while maintaining clear delivery goals. This hybrid approach provides superior adaptability in project management by balancing planned iterations with responsive task management.
Roles and Responsibilities in Lean vs Scrumban
Lean emphasizes cross-functional teams where roles are fluid and focus on eliminating waste, continuous improvement, and delivering value, with team members often sharing responsibilities. Scrumban combines Scrum's defined roles--Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team--with Lean principles, promoting flexibility in task management and continuous flow while maintaining role clarity. Responsibilities in Scrumban include backlog prioritization by the Product Owner, workflow facilitation by the Scrum Master, and collaborative execution by the team, blending Scrum's structure with Lean's efficiency focus.
Performance Metrics and Continuous Improvement
Lean emphasizes cycle time reduction and throughput as key performance metrics, driving waste elimination and process efficiency to enhance continuous improvement. Scrumban integrates Lean's flow-based metrics with Scrum's velocity measurement, enabling teams to adapt work-in-progress limits and prioritize tasks dynamically for sustained performance gains. Continuous improvement in Scrumban relies on iterative feedback loops and flexible workflows, combining Lean's systematic waste reduction with Scrum's empirical process control to optimize productivity.
Real-World Applications and Industry Use Cases
Lean methodology excels in manufacturing and healthcare by minimizing waste and enhancing efficiency through continuous improvement, widely adopted in automotive and medical device industries. Scrumban, blending Scrum's agility with Lean's flow principles, suits software development and IT operations where flexibility and iterative changes are critical, commonly used in tech startups and digital marketing firms. Both frameworks drive productivity but cater to different operational dynamics: Lean emphasizes stability in production, while Scrumban supports adaptive project environments with evolving requirements.
Choosing the Right Approach: Lean or Scrumban
Choosing between Lean and Scrumban depends on project complexity and team workflow preferences. Lean emphasizes eliminating waste and maximizing efficiency through continuous improvement, making it ideal for stable, repeatable processes. Scrumban combines Scrum's structure with Lean's flexibility, suited for teams needing adaptive planning and iterative progress in dynamic environments.
Lean Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com